Japanese
English
特集 第30回 脳のシンポジウム
神経疾患の分子遺伝学
Charcot-Marie-Tooth病の分子病態
Molecular basis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy
早坂 清
1
Kiyoshi HAYASAKA
1
1山形大学医学部小児科学教室
1Department of Pediatrics, Yamagata University School of Medicine
pp.1043-1048
発行日 1995年12月10日
Published Date 1995/12/10
DOI https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1431900710
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
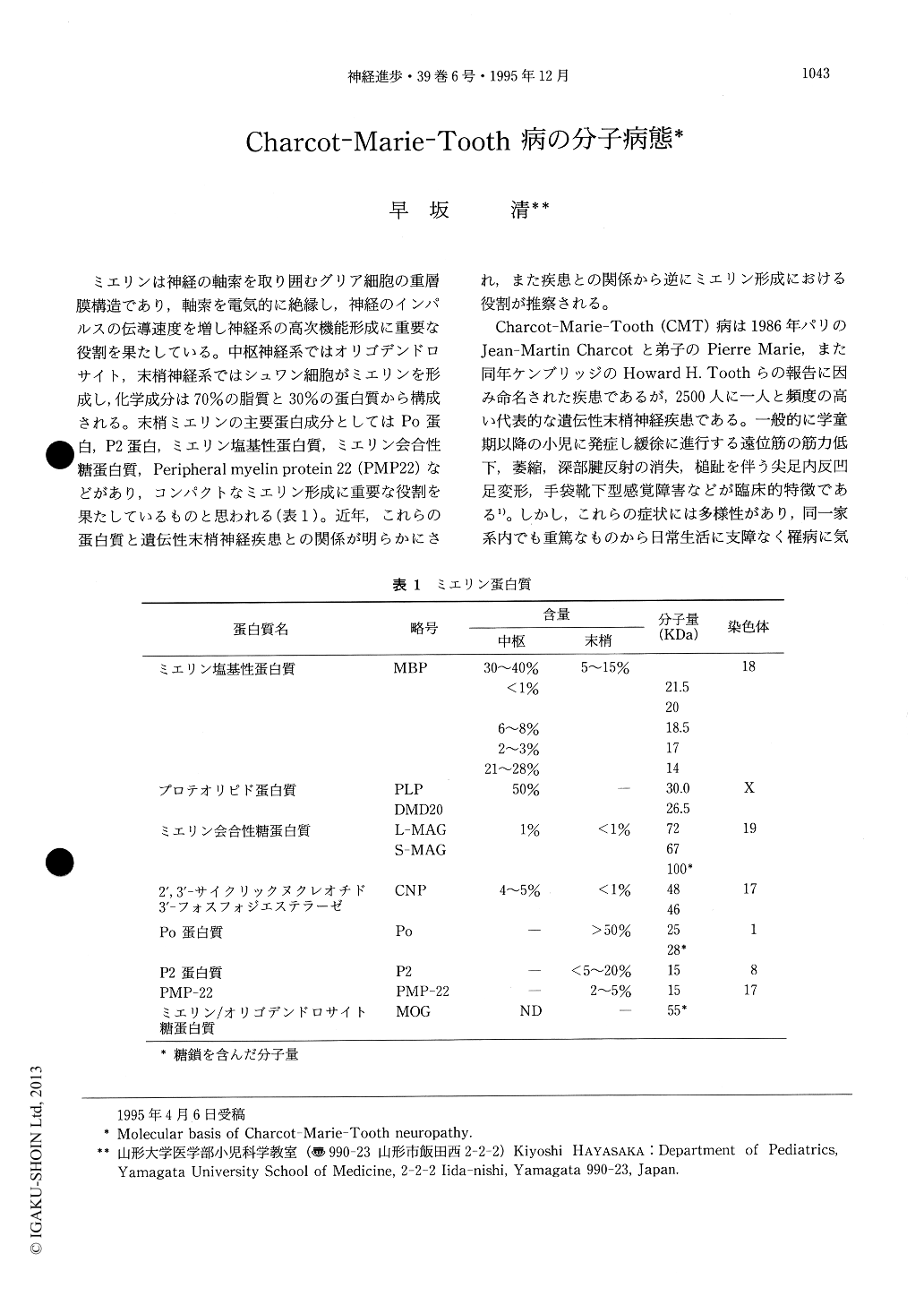
ミエリンは神経の軸索を取り囲むグリア細胞の重層膜構造であり,軸索を電気的に絶縁し,神経のインパルスの伝導速度を増し神経系の高次機能形成に重要な役割を果たしている。中枢神経系ではオリゴデンドロサイト,末梢神経系ではシュワン細胞がミエリンを形成し,化学成分は70%の脂質と30%の蛋白質から構成される。末梢ミエリンの主要蛋白成分としてはPo蛋白,P2蛋白,ミエリン塩基性蛋白質,ミエリン会合性糖蛋白質,Peripheral myelin protein 22(PMP22)などがあり,コンパクトなミエリン形成に重要な役割を果たしているものと思われる(表1)。近年,これらの蛋白質と遺伝性末梢神経疾患との関係が明らかにされ,また疾患との関係から逆にミエリン形成における役割が推察される。
Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy (CMT) is the most common inherited peripheral neuropathy and is characterized clinically by slowly progressive distal muscle weakness, absent deep tendon reflexes, mild sensory impairment, and pes cavus deformity of the foot. Most cases show dominant inheritance.
Copyright © 1995, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


