Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
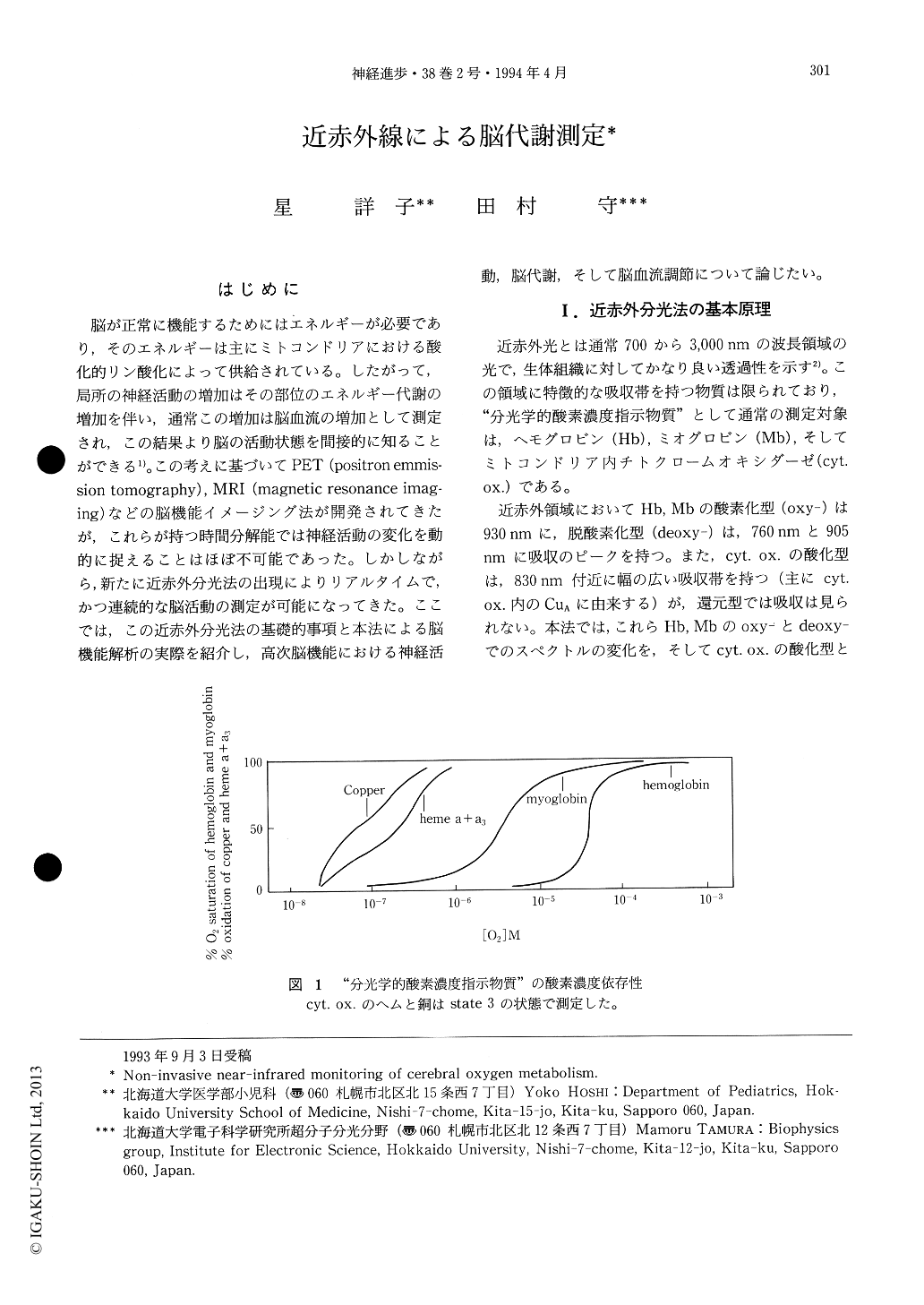
はじめに
脳が正常に機能するためにはエネルギーが必要であり,そのエネルギーは主にミトコンドリアにおける酸化的リン酸化によって供給されている。したがって,局所の神経活動の増加はその部位のエネルギー代謝の増加を伴い,通常この増加は脳血流の増加として測定され,この結果より脳の活動状態を間接的に知ることができる1)。この考えに基づいてPET(positron emmission tomography),MRI(magnetic resonance imaging)などの脳機能イメージング法が開発されてきたが,これらが持つ時間分解能では神経活動の変化を動的に捉えることはほぼ不可能であった。しかしながら,新たに近赤外分光法の出現によりリアルタイムで,かつ連続的な脳活動の測定が可能になってきた。ここでは,この近赤外分光法の基礎的事項と本法による脳機能解析の実際を紹介し,高次脳機能における神経活動,脳代謝,そして脳血流調節について論じたい。
Local increases in neuronal activity induce augmentations in local metabolism, which are compensated for by increases in blood supply. Thus, increases in cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) have been used as criteria for increases in neuronal activity. However, it has been impossible to detect these events in the timedimension as closely as is practical. Currently, near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) , which achieves a high temporal resolution (1 second) , enables continuous real-time measurements.
Copyright © 1994, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


