Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
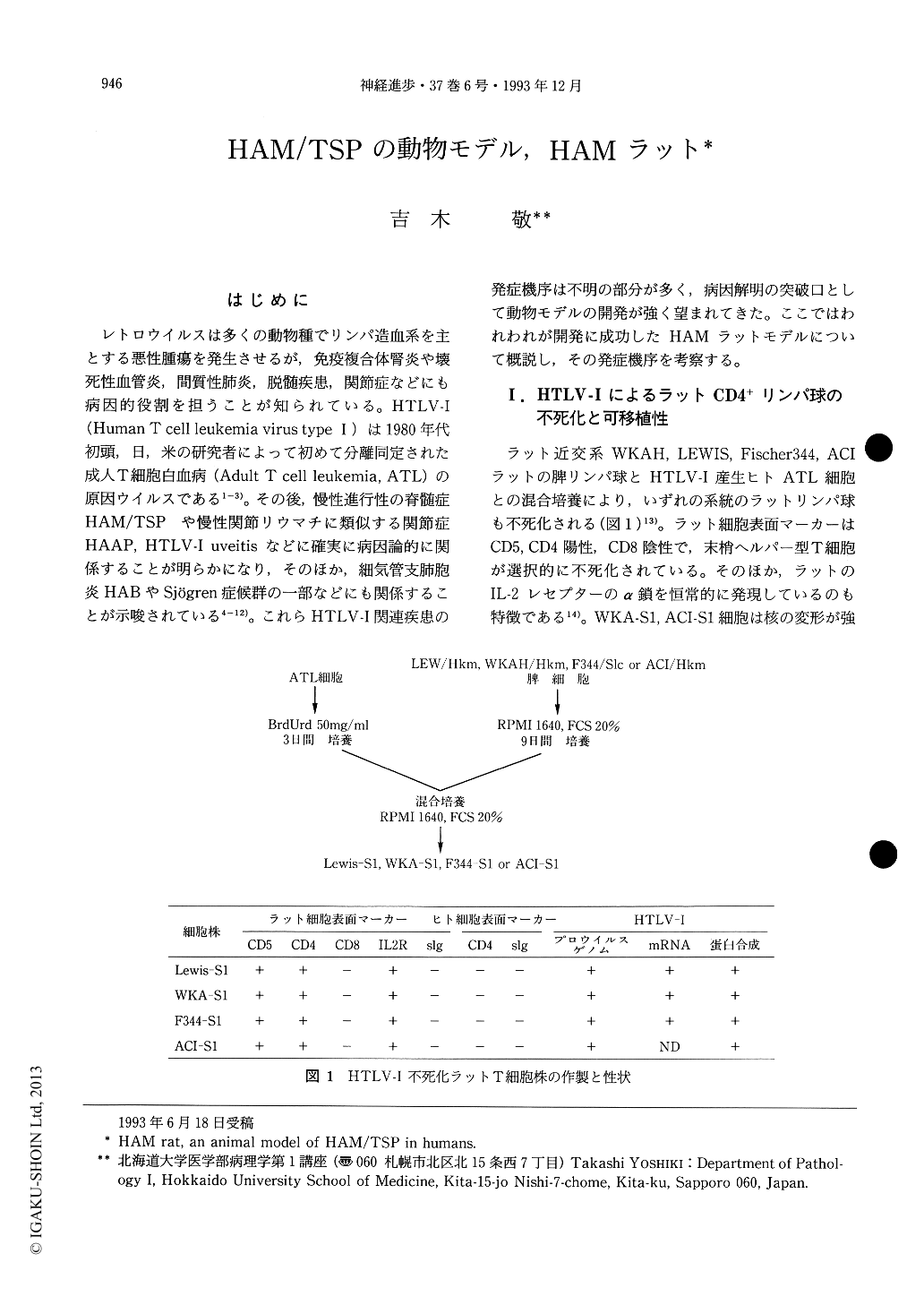
レトロウイルスは多くの動物種でリンパ造血系を主とする悪性腫瘍を発生させるが,免疫複合体腎炎や壊死性血管炎,間質性肺炎,脱髄疾患,関節症などにも病因的役割を担うことが知られている。HTLV-I(Human T cell leukemia virus type I)は1980年代初頭,日,米の研究者によって初めて分離同定された成人T細胞白血病(Adult T cell leukemia,ATL)の原因ウイルスである1-3)。その後,慢性進行性の脊髄症HAM/TSPや慢性関節リウマチに類似する関節症HAAP,HTLV-I uveitisなどに確実に病因論的に関係することが明らかになり,そのほか,細気管支肺胞炎HABやSjögren症候群の一部などにも関係することが示唆されている4-12)。これらHTLV-I関連疾患の発症機序は不明の部分が多く,病因解明の突破口として動物モデルの開発が強く望まれてきた。ここではわれわれが開発に成功したHAMラットモデルについて概説し,その発症機序を考察する。
Both seronegative and seropositive HTLV-I carrier rats of WKAH strain develop chronic progressive spastic paraparesis of the hind legs, after long incubation periods of 16 months. The clinical symptoms and neuropathology of seropositive adult carriers are basically identical to, but are apparently milder than those of seronegative newborn carriers. Humoral antibodies to HTLV-I in the host, therefore, do not play an active role in the pathogenesis of rat HAM. Rather, production of humoral antibodies to HTLV-I may be self-protective against disease progression. Seronegative and seropositive carriers of other strains, LEW, F344, ACI, BUF, SDJ, and LEJ do not develop rat HAM clinically and pathologically at comparable ages. It is concluded that development of rat HAM is under strict genetic restriction of the host strain, although HTLV-I can be transmitted equally into several strains of the rat. Neuropathological examinations show that the lesions are confined primarily to the anterior and lateral funiculi of the spinal cord. Marked demyelination with less dominant axonal damage is observed in a symmetrical fashion, and infiltration with massive foamy macrophages laden with fragmented myelins is evident. Diffuse vacuolar changes with reactive gliosis are also noted. Lymphocytic infiltration is minimal or virtually absent in the affected spinal cord. The most severe lesions are at levels of the thoracic cord and continue from the cervical to the lumbar area. The inner portion of the funiculi and central gray matter appear intact. Loss of myelin or axonal degeneration is not seen in the cerebrum, the cerebellum, or the brain stem above the level of the medulla oblongata. These histopathological features as well as clinical symptoms largely parallel findings in humans with HAM/TSP. The provirus genome is detected in the affected spinal cord by PCR but pX mRNA has not been demonstrated by in situ hybridization so far tested. Lack of lymphocytic infiltration in the affected spinal cords and no positive correlation between humoral antibodies to HTLV-I and the development of rat HAM lead us to propose that rat HAM appears to be the non-immunological demyelinating disease mediated by HTLV-I infection.
Copyright © 1993, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


