Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
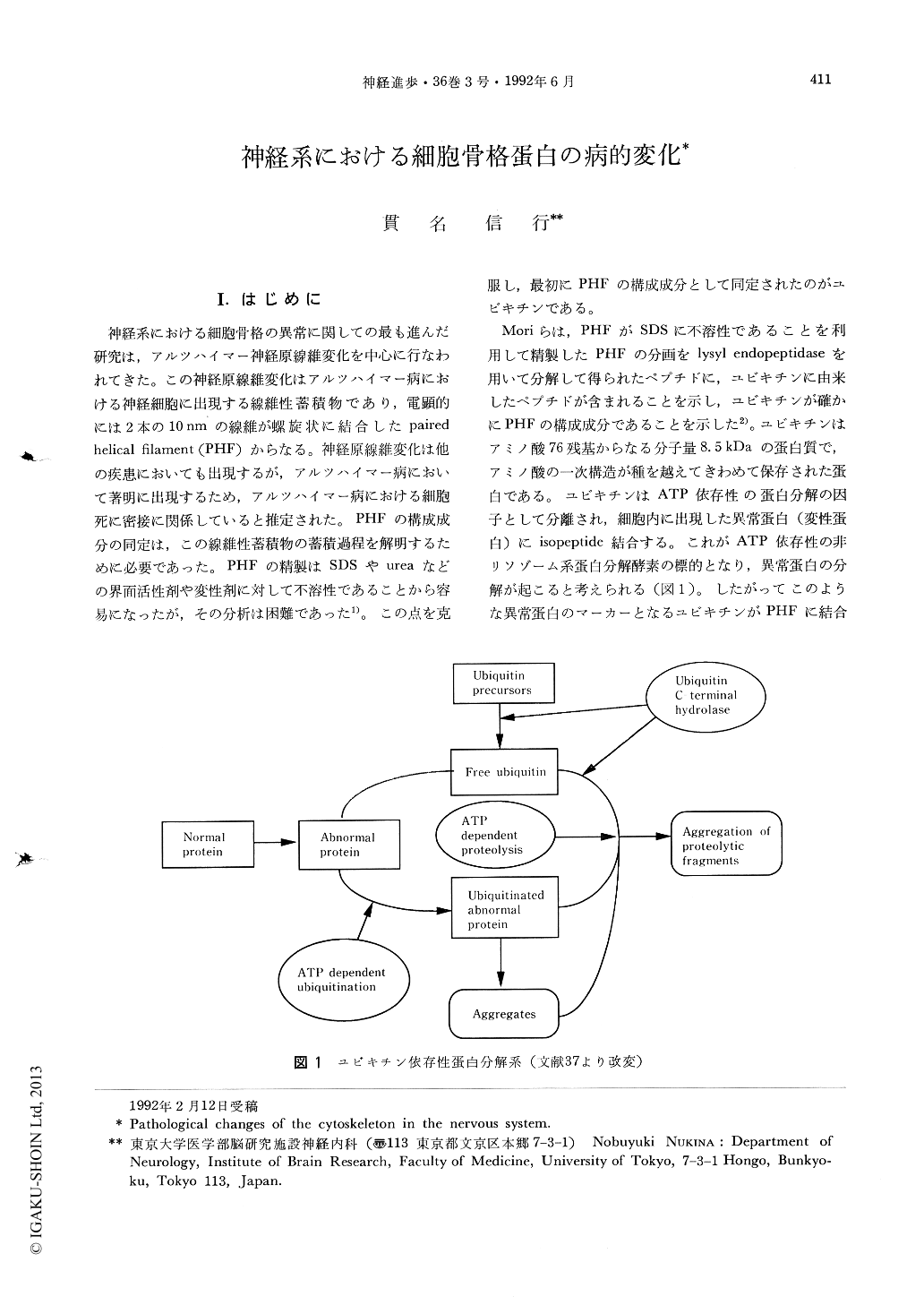
神経系における細胞骨格の異常に関しての最も進んだ研究は,アルツハイマー神経原線維変化を中心に行なわれてきた。この神経原線維変化はアルツハイマー病における神経細胞に出現する線維性蓄積物であり,電顕的には2本の10nmの線維が螺旋状に結合したpairedhelical filament(PHF)からなる。神経原線維変化は他の疾患においても出現するが,アルツハイマー病において著明に出現するため,アルツハイマー病における細胞死に密接に関係していると推定された。PHFの構成成分の同定は,この線維性蓄積物の蓄積過程を解明するために必要であった。PHFの精製はSDSやureaなどの界面活性剤や変性剤に対して不溶性であることから容易になったが,その分析は困難であった1)。この点を克服し,最初にPHFの構成成分として同定されたのがユビキチンである。
Moriらは,PHFがSDSに不溶性であることを利用して精製したPHFの分画をlysyl endopeptidaseを用いて分解して得られたペプチドに,ユビキチンに由来したペプチドが含まれることを示し,ユビキチンが確かにPHFの構成成分であることを示した2)。ユビキチンはアミノ酸76残基からなる分子量8.5kDaの蛋白質で,アミノ酸の一次構造が種を越えてきわめて保存された蛋白である。
Several cytoskeletal changes are observed in the neurological diseases. Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles, one of the major pathological features of Alzheimer's disease, are composed of paired helical filaments (PHF). PHF has been revealed to he composed of phosphorylated tau, one of the microtubule-associated proteins, and ubiquitin. Ubiquitin binds with the abnormal protein, which becomes a target of ATP-dependent proteolytic system. Since ubiquitin was reported to be a component of PHF, other ubiquitinated proteins in the nervous systems have been reported. Pick body, Lewy body, Glial cytoplasmic inclusion, Rosenthal fiber and abnormal inclusions in the motor neurons of patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are ubiquitinated. Pick body is also composed of tau protein. Lewy bodies contain epitopes of neurofilament and gelsolin which is recently reported to be a component of amyloid-Finnish type. Glial cytoplasmic inclusions are immunostained with anti-α, β tubulin and MAPS. GCI is a specific pathological marker for multiple system atrophy. Thus it is important to isolate GCI and determine the component of GCI by the protein chemical analysis. The component of Rosenthal fiber (RF) is α B-crystallin and the crystallin in RF is ubiquitinated. The skein-like inclusion in motor neuron is also ubiquitinated. However its component has not been determined yet.
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


