Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
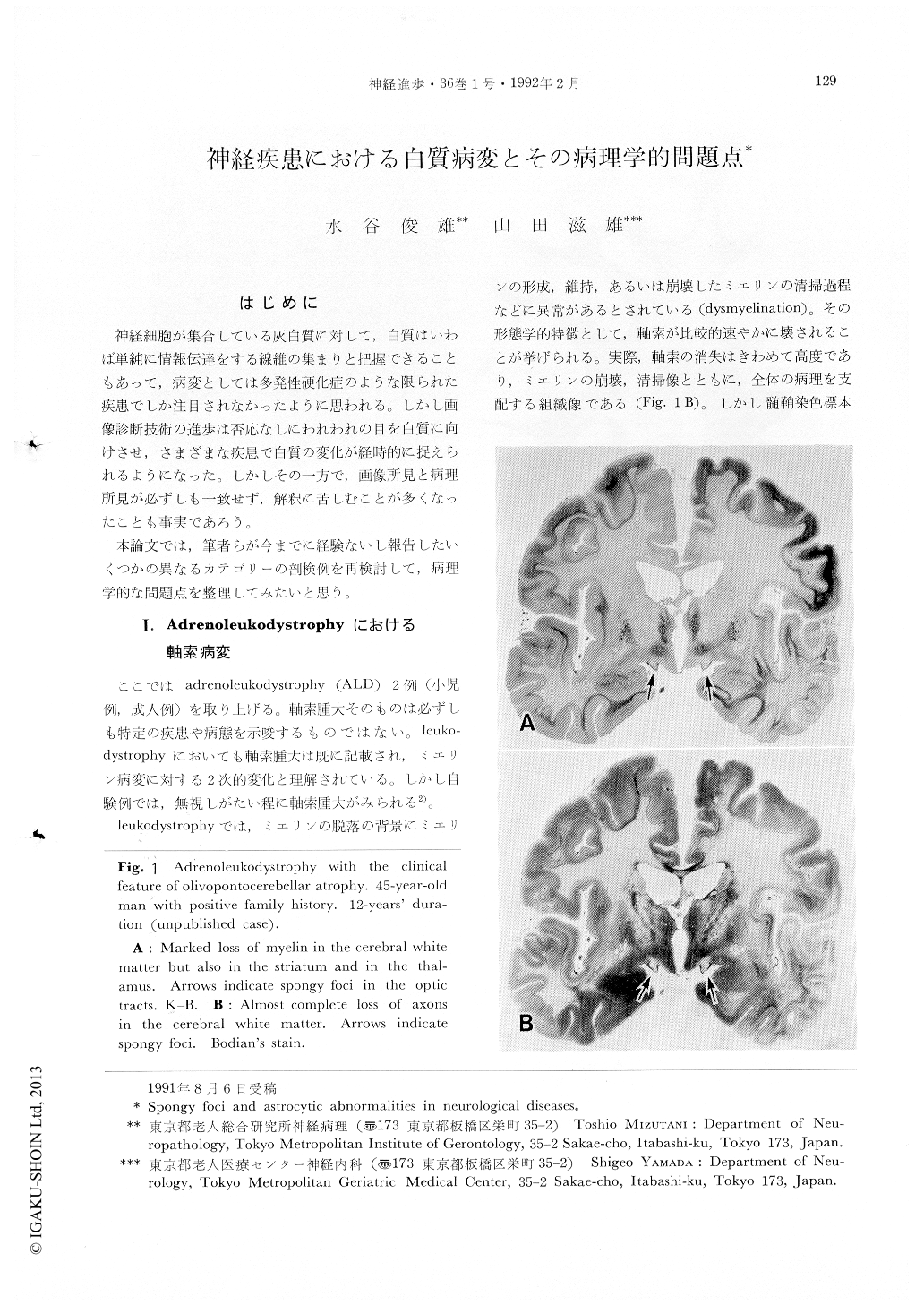
神経細胞が集合している灰白質に対して,白質はいわば単純に情報伝達をする線維の集まりと把握できることもあって,病変としては多発性硬化症のような限られた疾患でしか注日されなかったように思われる。しかし画像診断技術の進歩は否応なしにわれわれの目を白質に向けさせ,さまざまな疾患で白質の変化が経時的に捉えられるようになった。しかしその一方で,画像所見と病理所見が必ずしも一致せず,解釈に苦しむことが多くなったことも事実であろう。
本論文では,筆者らが今までに経験ないし報告したいくつかの異なるカテゴリーの剖検例を再検討して,病理学的な問題点を整理してみたいと思う。
Spongy foci and astrocytic abnormalities in the white matter of the different neurological diseases were reported. While “demyelination” could be shown morphologically, it is difficult to demonstrate morphological substrate for “dysmyelination” in leukodystrophy. The former term actually means morphological change of relative preservation of axons to loss of myelin, but the latter is based more on the biochemical aspect than the former. Leukodystrophies generally show most severe loss of axons as well as myelin sheath in the white matter (Fig. 1). From this point of view, axonal swellings in the fresh lesion in adrenoleukodystrophy should be more remarked. They were found exclusively in the front of the progressively extending lesion (Fig. 2), and many of them had still thin myelin sheath. Although they could not be a primary change, it is likely that axonal change and myelin sheath breakdown occurred in close relationship to each other or occurred simultaneously. Furthermore, axonal swellings in the front of the diffuse lesion could contribute greatly to disappearance of axons.
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


