Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.脱髄巣とその周辺の白質
脱髄巣およびその周辺の一般的な化学的組成の変化としては,水成分の増加,全脂質の減少,とくにコレステロール,セレブロシド,サルファチド,エタノラミン,ブラスマローゲン,フォスファチヂールセリンなどの減少が明らかである。またコレステロールエステルの増加がみられる1,2)。脱髄巣の乾燥重量当りのガングリオシドは増加しているが,ミエリン特異なガングリオシドであるGM4は完全に消失していると報告されている3)。脂肪酸の変化については,脱髄巣にて飽和脂肪酸の増加と一価不飽和脂肪酸の減少が,一致した見解であるが,それらの変化は細胞成分の増加などを反映した二次性のものであろうとする考えが一般的である4)。
蛋白の化学的組成の変化に関しては,基本的には脱髄を反映した各ミエリン特異蛋白の減少,二次的な神経軸索変性を反映したニューロフィラメントの減少5),およびグリオーシスを反映したglial fibrillary acidic protein(GFAP)などのグリア蛋白の増加である(図1)6,7)。
The general changes of chemical composition in multiple sclerosis (MS) plaque and around plaque are an increase of water, a decrease of total lipid, especially cholesterol, cerebroside, sulfatides, ethanolamine plasmalogens and phosphatidylserine are most affected. Although plaque has a increase of total gangliosides on a dry weight basis, a complete loss of myelin specific ganglioside GM4 is found.
The myelin proteins, myelin-basic protein, proteolipid protein and 2′, 3′-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphohydrolase and myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) are reduced, especially MAG is reduced most significantly in the plaques and the margin of plaques. The glial fibrillary acidic protein, a marker protein of astrocyte, are increased because of gliosis.
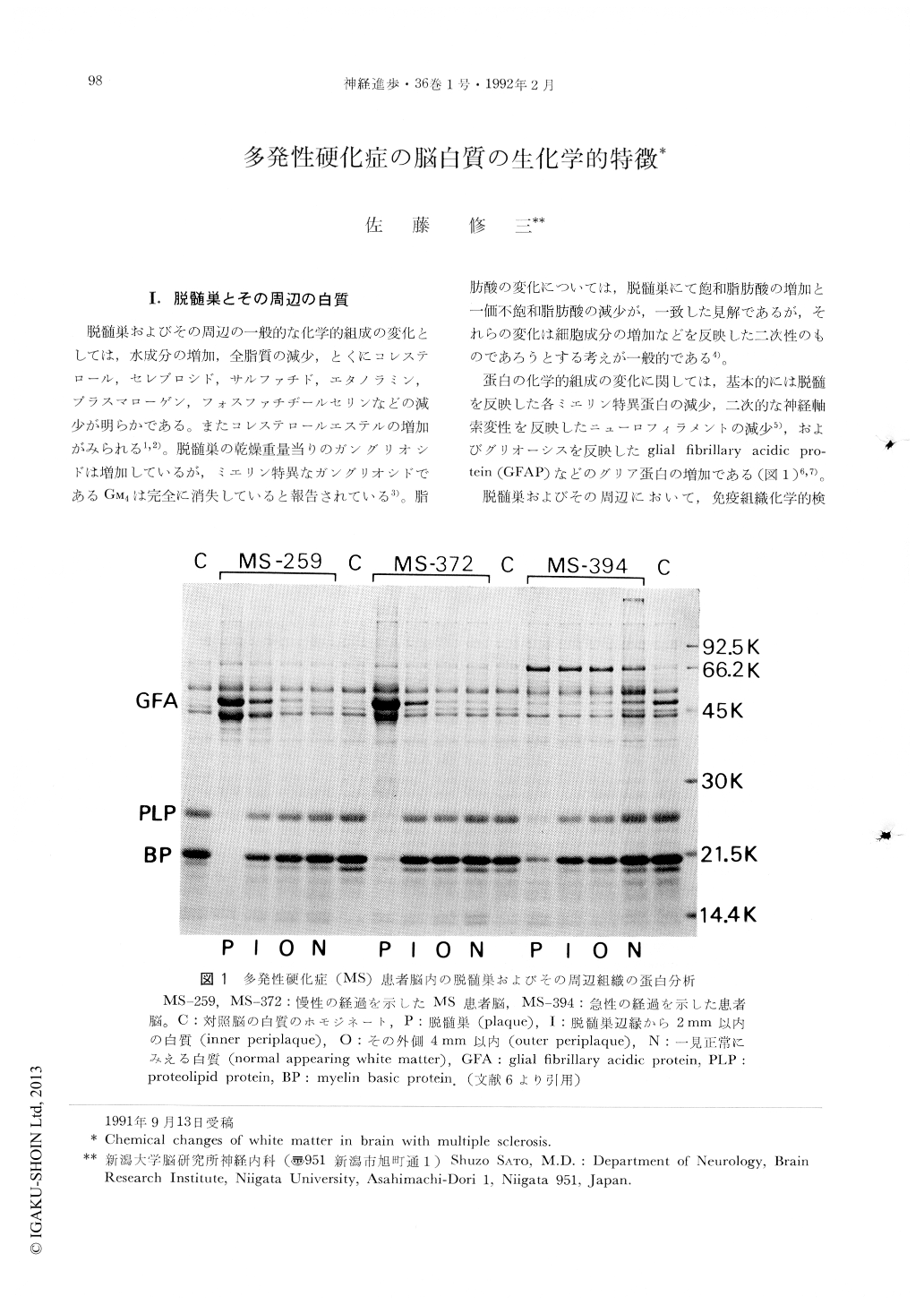
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


