Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
糖尿病患者における涙腺の自律神経支配の障害の有無を検討するため,糖尿病患者27名,54眼にシルマーテストⅠ法の変法を施行し,涙液の基礎分泌を測定し,同時に検査した自律神経障害のひとつの指標を示すと考えられる心電図CVR-R%と比較検討し,さらにHbA1C,眼底所見,および神経障害の有無を検討した。
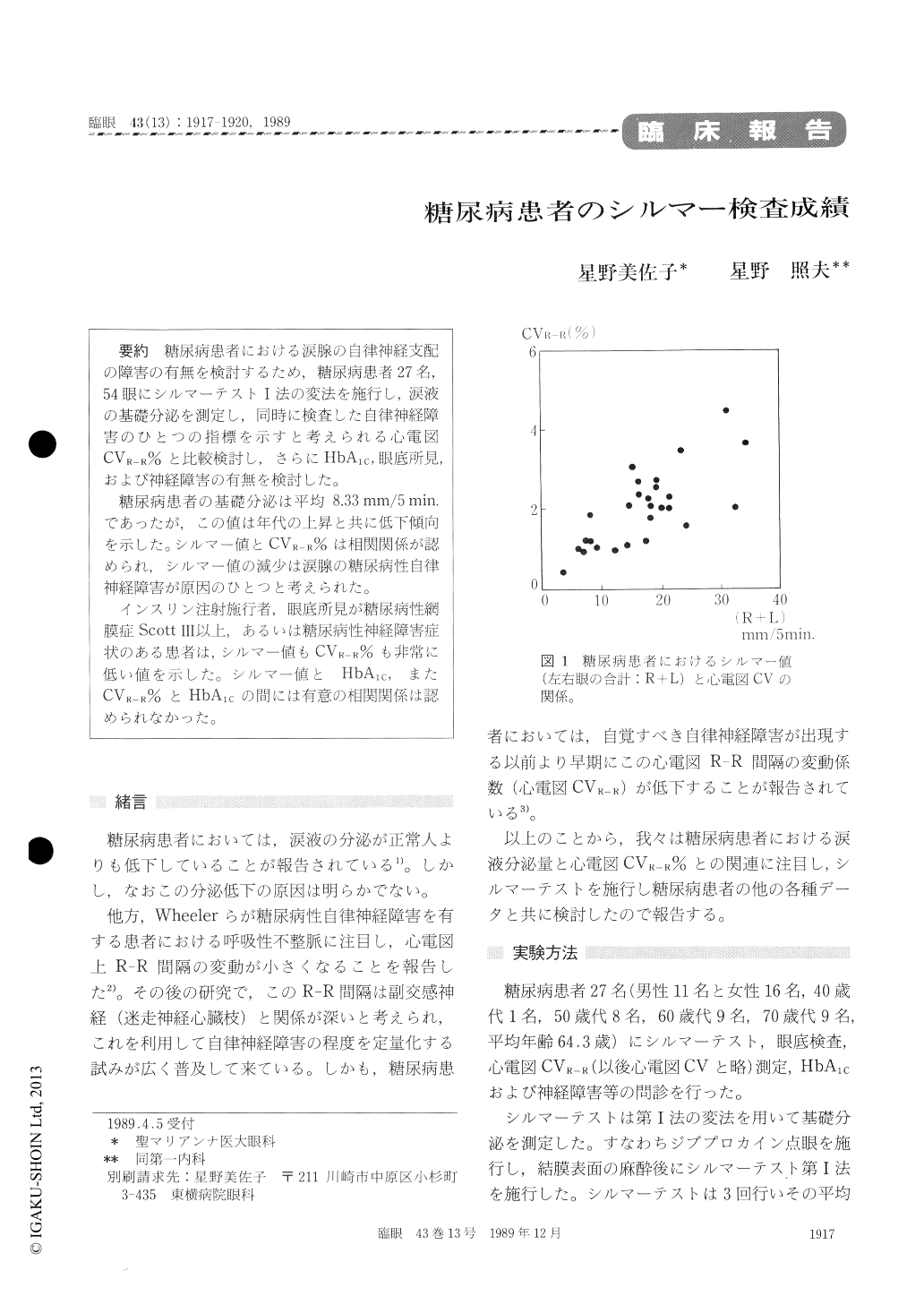
糖尿病患者の基礎分泌は平均8.33mm/5min.であったが,この値は年代の上昇と共に低下傾向を示した。シルマー値とCVR-R%は相関関係が認められ,シルマー値の減少は涙腺の糖尿病性自律神経障害が原因のひとつと考えられた。
インスリン注射施行者,眼底所見が糖尿病性網膜症Scott Ⅲ以上,あるいは糖尿病性神経障害症状のある患者は,シルマー値もCVR-R%も非常に低い値を示した。シルマー値とHbA1C,またCVR-R%とHbA1Cの間には有意の相関関係は認められなかった。
With a view to assess the autonomic innervation to the lacrimal gland, we measured the basal tear secretion in 27 diabetic patients by a modified Schirmer test Ⅰ . The values were compared with other parameters including" R-R interval (CV) in electrocardiogram, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), fun-dus findings and systemic manifestations of neur-opathy.
The Schirmer values for added both eyes were positively correlated with CV (P<0.005). Diabetic autonomic neuropathy seemed to underly the de-creased basal tear secretion. Both the basal tear secretion and CV were very low in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes, advanced fundus lesions of stage 3 or more by Scott, and/or neuro-pathic symptoms. Neither the Schirmer values nor CV ones were correlated HbA1c values.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


