Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
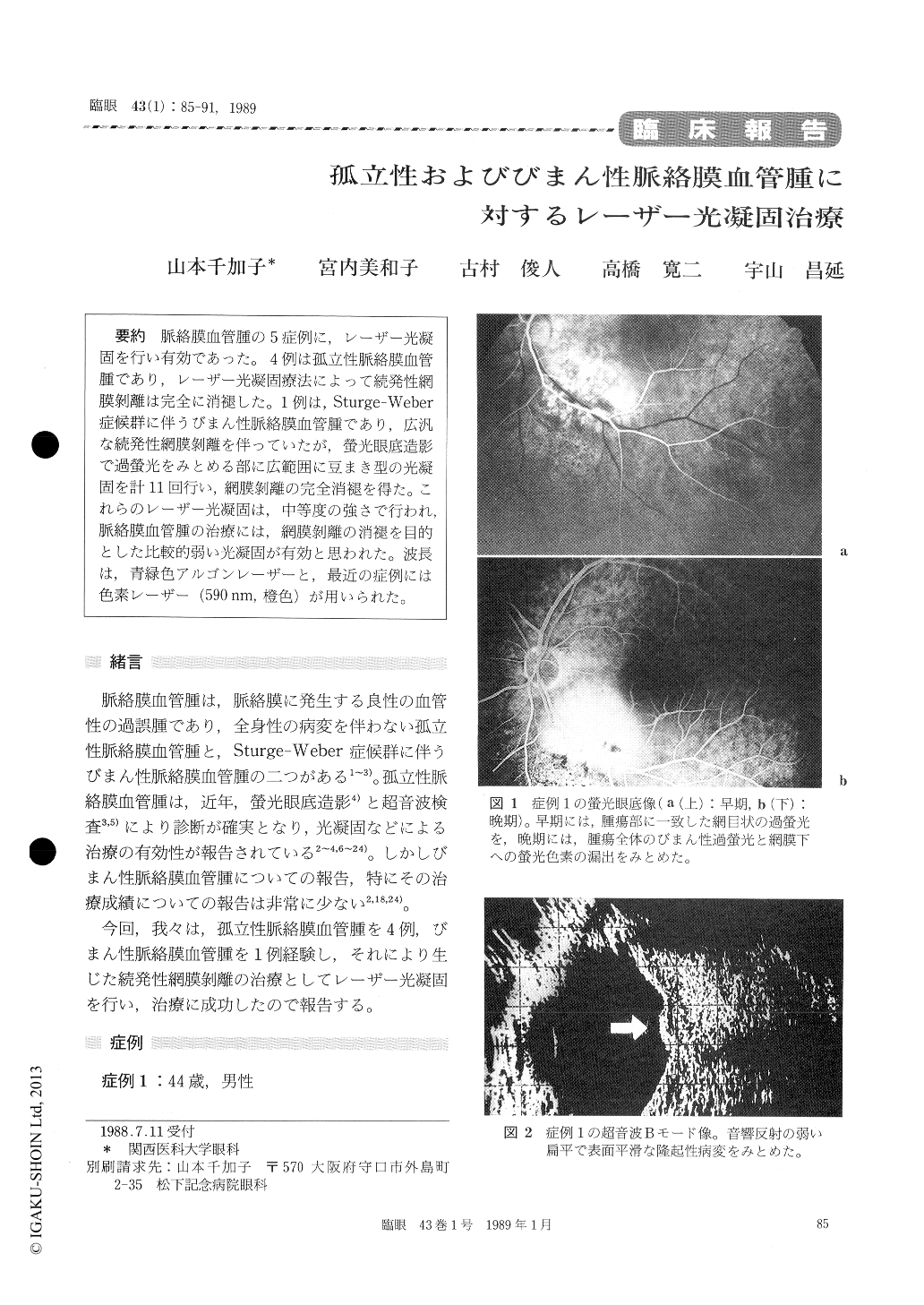
脈絡膜血管腫の5症例に,レーザー光凝固を行い有効であった。4例は孤立性脈絡膜血管腫であり,レーザー光凝固療法によって続発性網膜剥離は完全に消褪した。1例は,Sturge-Weber症候群に伴うびまん性脈絡膜血管腫であり,広汎な続発性網膜剥離を伴っていたが,螢光眼底造影で過螢光をみとめる部に広範囲に豆まき型の光凝固を計11回行い,網膜剥離の完全消褪を得た。これらのレーザー光凝固は,中等度の強さで行われ,脈絡膜血管腫の治療には,網膜剥離の消褪を目的とした比較的弱い光凝固が有効と思われた。波長は,青緑色アルゴンレーザーと,最近の症例には色素レーザー(590nm,橙色)が用いられた。
We treated 5 eyes with choroidal hemangioma by applying photocoagulation with blue-green argon laser or dye laser tuned to 590nm wavelength. Four eyes manifested retinal detachment secondary to solitary choroidal hemangioma and were treated with photocoagulation at modest power output. Retinal detachment disappeared in all the treated cases. A fifth case, a 11-year-old boy, manifested extensive retinal detachment with diffuse choroidal hemangioma in the left eye as typical manifestation of Sturge-Weber syndrome. We treated the affected eye by applying scattered photocoagula-tion to the hyper fluorescent areas as shown by fluorescein angiography, a total of 1,150 burns with blue-green argon. Retinal detachment started to subside 3 months after the first session of photocoagulation and disappeared after 1 year.
The findings indicate that laser photocoagulation at moderate intensity is effective for retinal detach-ment secondary to choroidal hemangioma.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


