Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
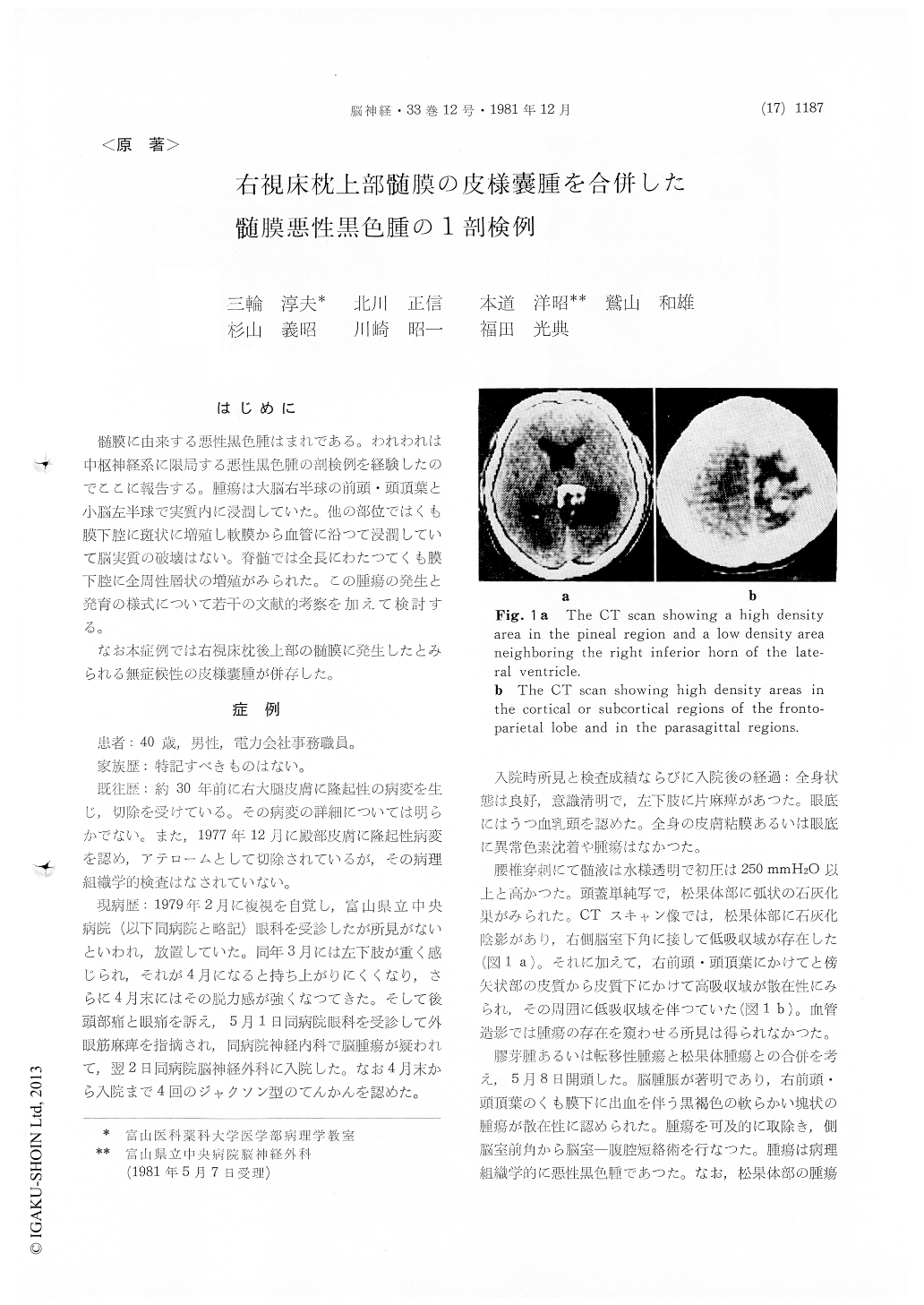
髄膜に由来する悪性黒色腫はまれである。われわれは中枢神経系に限局する悪性黒色腫の剖検例を経験したのでここに報告する。腫瘍は大脳右半球の前頭・頭頂葉と小脳左半球で実質内に浸潤していた。他の部位ではくも膜下腔に斑状に増殖し軟膜から血管に沿つて浸潤していて脳実質の破壊はない。脊髄では全長にわたつてくも膜下腔に全周性層状の増殖がみられた。この腫瘍の発生と発育の様式について若干の文献的考察を加えて検討する。
なお本症例では右視床枕後上部の髄膜に発生したとみられる無症候性の皮様嚢腫が併存した。
An autopsied rare case of meningeal malignant melanoma associated with meningeal dermoid cyst is described. A 40-year-old male visited the Toyama Prefectural Central Hospital complaining of double vision in February 1979. As occipital headache, ocular pain and attacks of Jacksonian seizure developed in the following months, he was admitted to the department of neurosurgery on May 2 under the diagnosis of brain tumor. On admission left-sided hemiparesis was present. No abnormal cutaneous pigmentation was noted. The skull x-ray examination revealed a small bracket-shaped shadow of calcification in the pineal region. In the CT scan high density areas in the cortical or subcortical region of the right fronto-parietal lobe of the cerebrum and the right parasagittal regions were found. Also in the pineal region a higher density area was observed.
On May 5, 1979, craniotomy for removal of a black-colored tumor of the right fronto-parietal lobe, combined with ventriculo-peritoneal drainage, was performed. The pineal lesion was notexplored. The removed tumor was histologically confirmed to be malignant melanoma. The CT scan taken two months later revealed another high density area in the left cerebellar hemisphere in addition to the recurrent tumor in the right fronto-parietal lobe. The patient became comatose in August and expired on October 8. The duration of the illness was 8 months.
At autopsy, the brain was moderately swollen (1200g). The recurrent melanoma in the right fronto-parietal lobe invaded the cerebral substance deeply and an independent melanoma mass was also present in the left cerebellar hemisphere, extending to the middle peduncle. In the other part of the brain surface, there was irregularly distributed patchy network of black pigmentation, implying leptomeningeal involvement of the tumor. Most part of the spinal cord was wrapped with thick spread of the tumor, giving rise to partial softening of the cord at the level of Th. 5-Th. 10.
A clinically silent dermoid cyst measuring 2×3×3cm in size was found on the back of the right pulvinar with protrusion into the inferior horn of the ipsilateral lateral ventricle, which was identified to have arisen from the regional leptomeninx. Calcification was present in the wall of the cyst as well as inside of it, namely in the keratohyalin material. The pineal body was intact. The co-existence of the dermoid cyst with malignant melanoma of the leptomeninx suggests that the latter may have arisen from the heterotopic melanin producing cells in loco.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


