Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
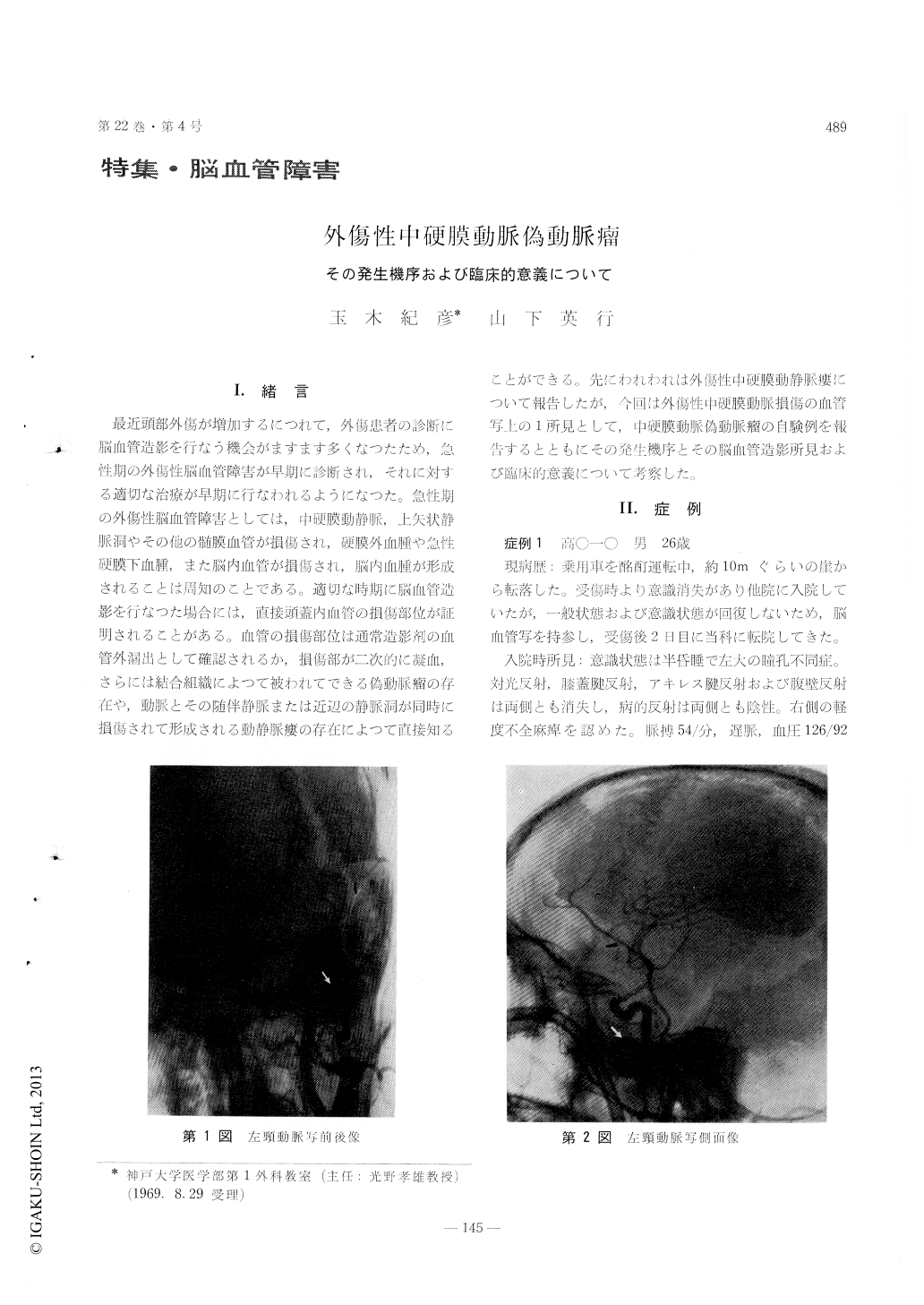
外傷性中硬膜動脈偽脈瘤の自験例3例を中心に,その発生機序およびその臨床的意義にっいて検討を加えた。3例とも硬膜外血腫を伴つて発生し,2例に頭蓋骨骨折を認めた。
手術を要しない頭部外傷後または頭蓋内血腫除去術後に全身状態および神経症状の回復が遷延したり,また急激に悪化したりする場合には,中硬膜動脈損傷によつて生じた偽動脈瘤の破裂の可能性があるため,早期に総頸動脈撮影を行なうよう努めなければならない。
診断は典型的な血管造影所見によつて行なわれるが,見逃がせば致命的な再出血をきたすため注意を要する。
Three cases of traumatic false aneurysm of the middle meningeal artery were described. All pa-tients had suffered from head injury, resulting in extradural hematoma, two of the three patients having a fracture in the overlying vault. The pos-sible mode of aneurysm formation and its clinical significance were discussed.
The associated literatures on the middle menin-geal artery aneurysm were also reviewed.
When recovery of the general physical condition and improvement of neurological clinical findings are retarded, or when the general conditions are abruptly exacerbated after removal of the intracra-nial hematoma or after the head injury in which operation was not performed, the common carotid angiography should be performed as soon as possible to identify the possible rupture of the false aneu-rysm. The diagnosis of the traumatic false aneu-rysm of the middle meningeal artery could be made by typical angiographical findings, but care should be drawn on making a diagnosis of the false aneu-rysm of the middle meningeal artery to avoid the fatal recurrent haemorrhage after head injury.
Copyright © 1970, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


