Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
緒言
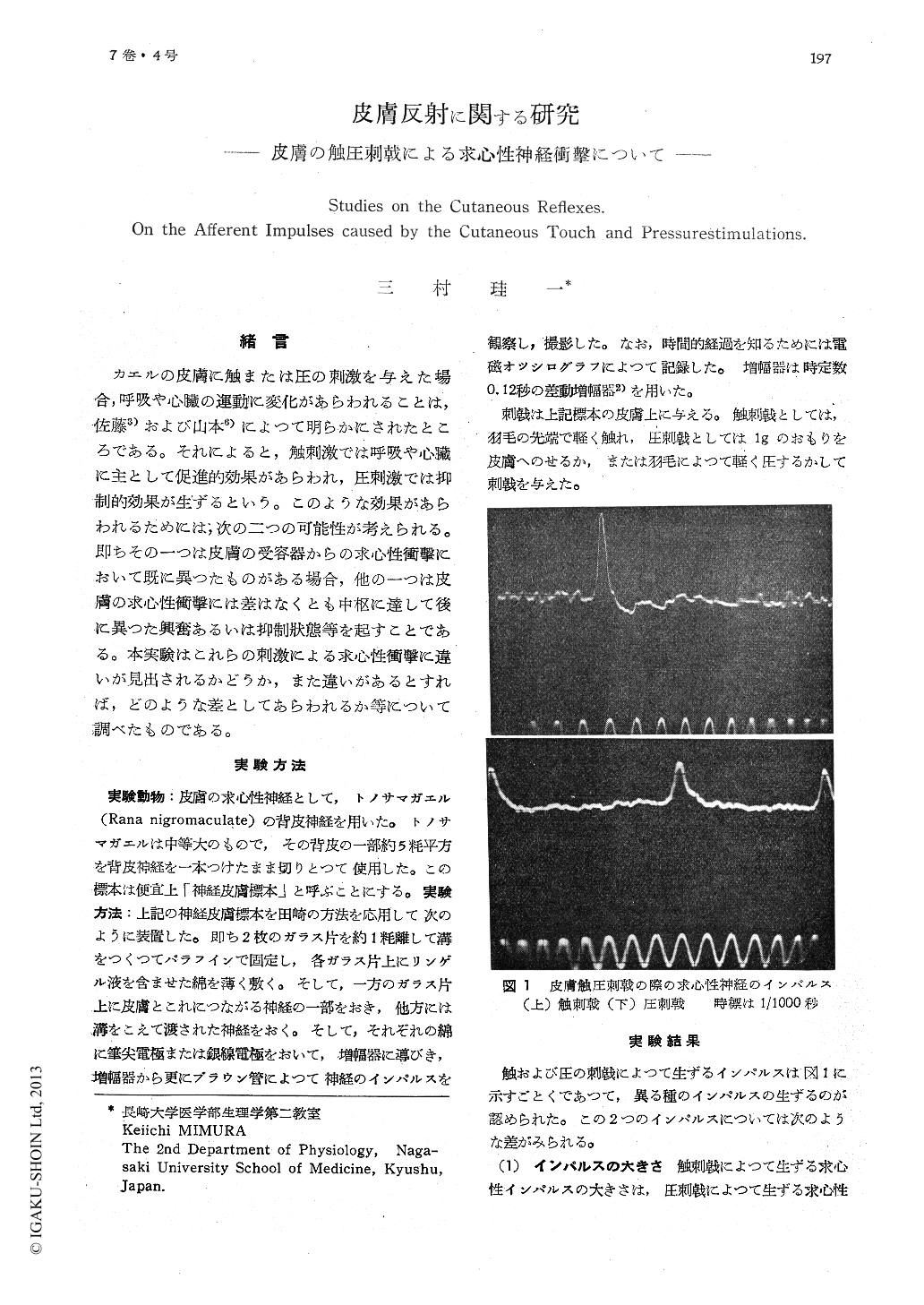
カエルの皮膚に触または圧の刺激を与えた場合,呼吸や心臓の運動に変化があらわれることは,佐藤3)および山本6)によつて明らかにされたところである。それによると,触刺激では呼吸や心臟に主として促進的効果があらわれ,圧刺激では抑制的効果が生ずるという。このような効果があらわれるためには,次の二つの可能性が考えられる。即ちその一つは皮膚の受容器からの求心性衝撃において既に異つたものがある場合,他の一つは皮膚の求心性衝撃には差はなくとも中枢に達して後に異つた興奮あるいは抑制状態等を起すことである。本実験はこれらの刺激による求心性衝撃に違いが見出されるかどうか,また違いがあるとすれば,どのような差としてあらわれるか等について調べたものである。
It has been comfirmed by Sato and Yamamoto that the cutaneous touch and pressure cause the augmentation and inhibition of the res-piratory and cardiac movement. So the afferent impulses elicited by the cutaneous touch and pressure was observed, in order to know whe-ther the above difference occurs or not on the peripheral activity. The skin-nerve pre-paration severed from frog (Rana nigromacu-lata) were used.
1) The impulses elicited by the cutaneous touch and pressre show the different height, i.e. the former shows 1.5-2 times higher than the latter.
2) The former shows longer duration and occurs temporally (phasic fibre). The latter shows shorter duration and occurs continuously (tonic fibre).
3) From these results it is recognizable that the impulses caused by the cutaneous touch-stimulation are different from those by the pressure-stimulation. It assumes that by the cutaneous touch and pressure stimulation the different receptors following different afferent signals are transmitted into the central nervous system. Thus the one of the reason for the above two effects comfirmed by Sato and Yamamoto is obtained.
Copyright © 1955, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


