Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
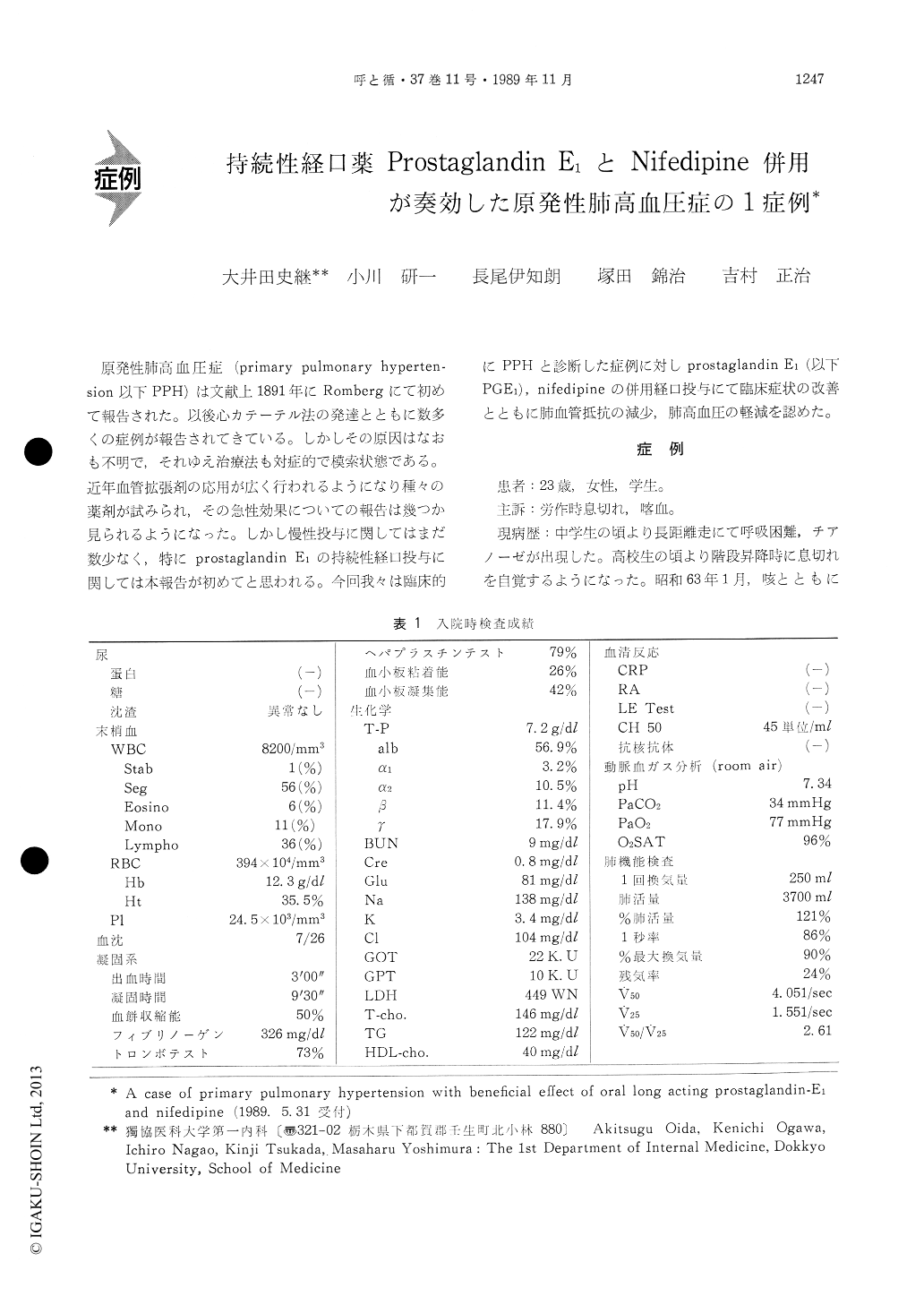
原発性肺高血圧症(primary pulmonary hyperten—sion以下PPH)は文献上1891年にRombergにて初めて報告された。以後心カテーテル法の発達とともに数多くの症例が報告されてきている。しかしその原因はなおも不明で,それゆえ治療法も対症的で模索状態である。近年血管拡張剤の応用が広く行われるようになり種々の薬剤が試みられ,その急性効果についての報告は幾つか見られるようになった。しかし慢性投与に関してはまだ数少なく,特にprostaglandin E1の持続性経口投与に関しては本報告が初めてと思われる。今回我々は臨床的にPPHと診断した症例に対しprostaglandin E1(以下PGE1),nifedipineの併用経口投与にて臨床症状の改善とともに肺血管抵抗の減少,肺高血圧の軽減を認めた。
A 23-year-old female with moderate primary pul-monary hypertension (PPH) was treated by chronic oral administration of long-acting prostaglandin-El (PGE1) and nifedipine. Cardiac catheterization re-vealed evidence that both drugs had beneficial effects on this case. Total pulmonary resistance (TSR) de-creased from 1089 to 955 dyne・sec・cm-5 by intrave-nous administration of PGE1at a rate of 0. 04 μg/kg /min and from 1089 to 710 dyne・sec・cm-5 by sub-lingual administration of nifedipine 10 mg respec-tively. After ten months of treatment with these two drugs, her pulmonary arterial pressure decreased from 85/40 (mean ; 58) mmHg to 55/36 (mean ; 45) mmHg, TSR decreased from 1089 to 829 dyne・sec・ cm-5 and Pa02 in room air increased from 74.5 to 94.9 mmHg. Chest X-P and ECG revealed the de-crease in the loading of the right ventricle. Thus, combined administration of PGE1 and nifedipine is expected to benefit PPH.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


