Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- サイト内被引用 Cited by
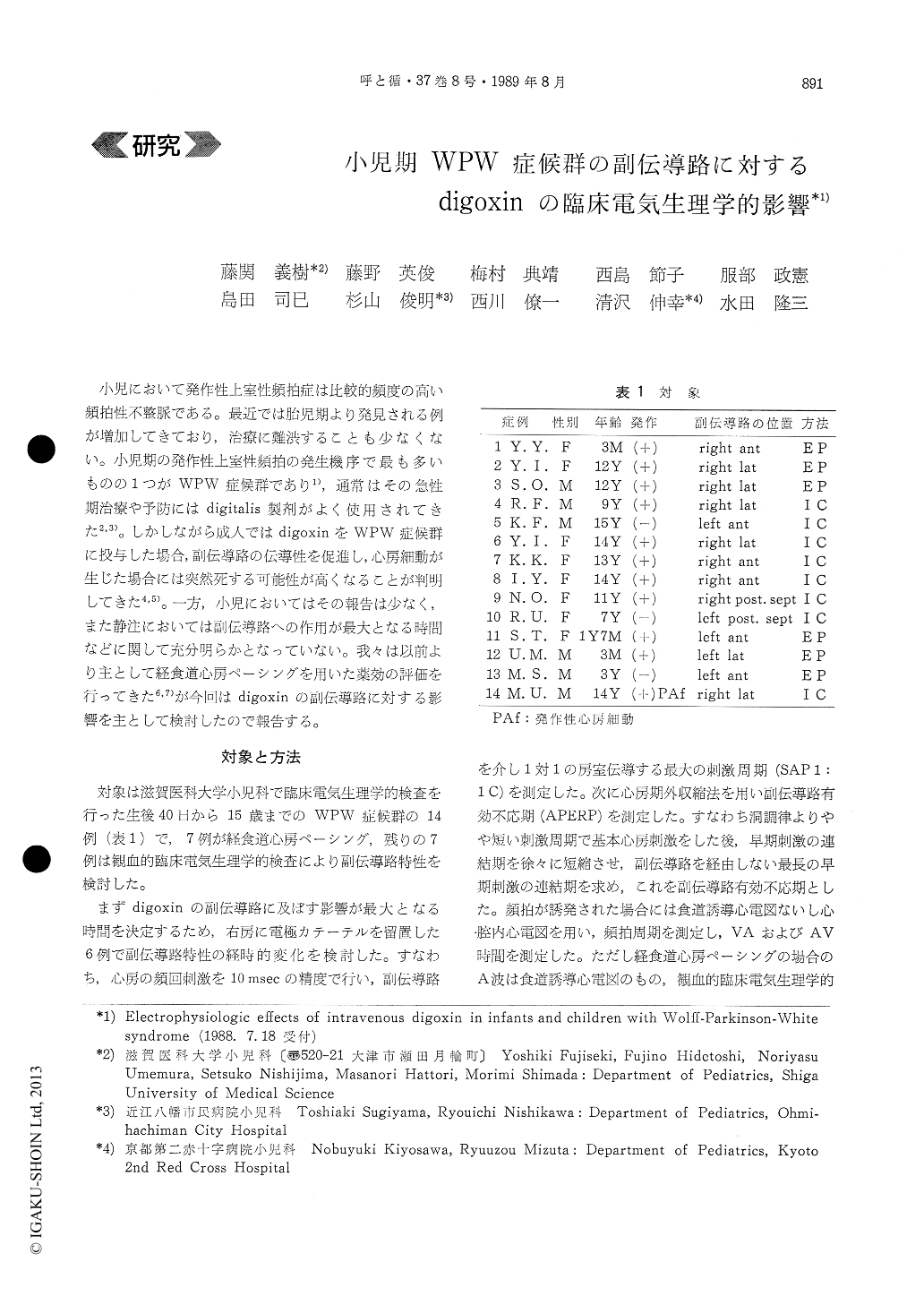
小児において発作性上室性頻拍症は比較的頻度の高い頻拍性不整脈である。最近では胎児期より発見される例が増加してきており,治療に難渋することも少なくない。小児期の発作性上室性頻拍の発生機序で最も多いものの1つがWPW症候群であり1),通常はその急性期治療や予防にはdigitalis製剤がよく使用されてきた2,3)。しかしながら成人ではdigoxinをWPW症候群に投与した場合,副伝導路の伝導性を促進し,心房細動が生じた場合には突然死する可能性が高くなることが判明してきた4,5)。一方,小児においてはその報告は少なく,また静注においては副伝導路への作用が最大となる時間などに関して充分明らかとなっていない。我々は以前より主として経食道心房ペーシングを用いた薬効の評価を行ってきた6,7)が今回はdigoxinの副伝導路に対する影響を主として検討したので報告する。
Electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pa-thway were investigated before and after the intra-venous administration of digoxin (0.01~0.02mg/kg) during electrophysiologic studies in 14 infants and children with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Determination of electrophysiologic properties of the accessory pathway was made using transesopha-geal atrial pacing and/or intracardiac right atrial pacing.
Maximal effect on the accessory pathway after in-travenous digoxin was observed during one to six hours. Effective refractory period of the accessory pathway increased in 6 of the 14 patients, de-creased in 4 and unchanged in 4. Shortest AP 1 : 1 conduction increased in 5 of the 12 patients, decrea-sed in 3 and unchanged in 4.
Tachycardia was not induced after digoxin in only one patient. Tachycardia cycle length, ventriculo-atrial conduction time and atrioventricular conduc-tion time were unchanged after digoxin in almost all cases.
Thus, digoxin is not the first choice drug for ter-mination and prevention of the preexcitation syndro-me.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


