Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
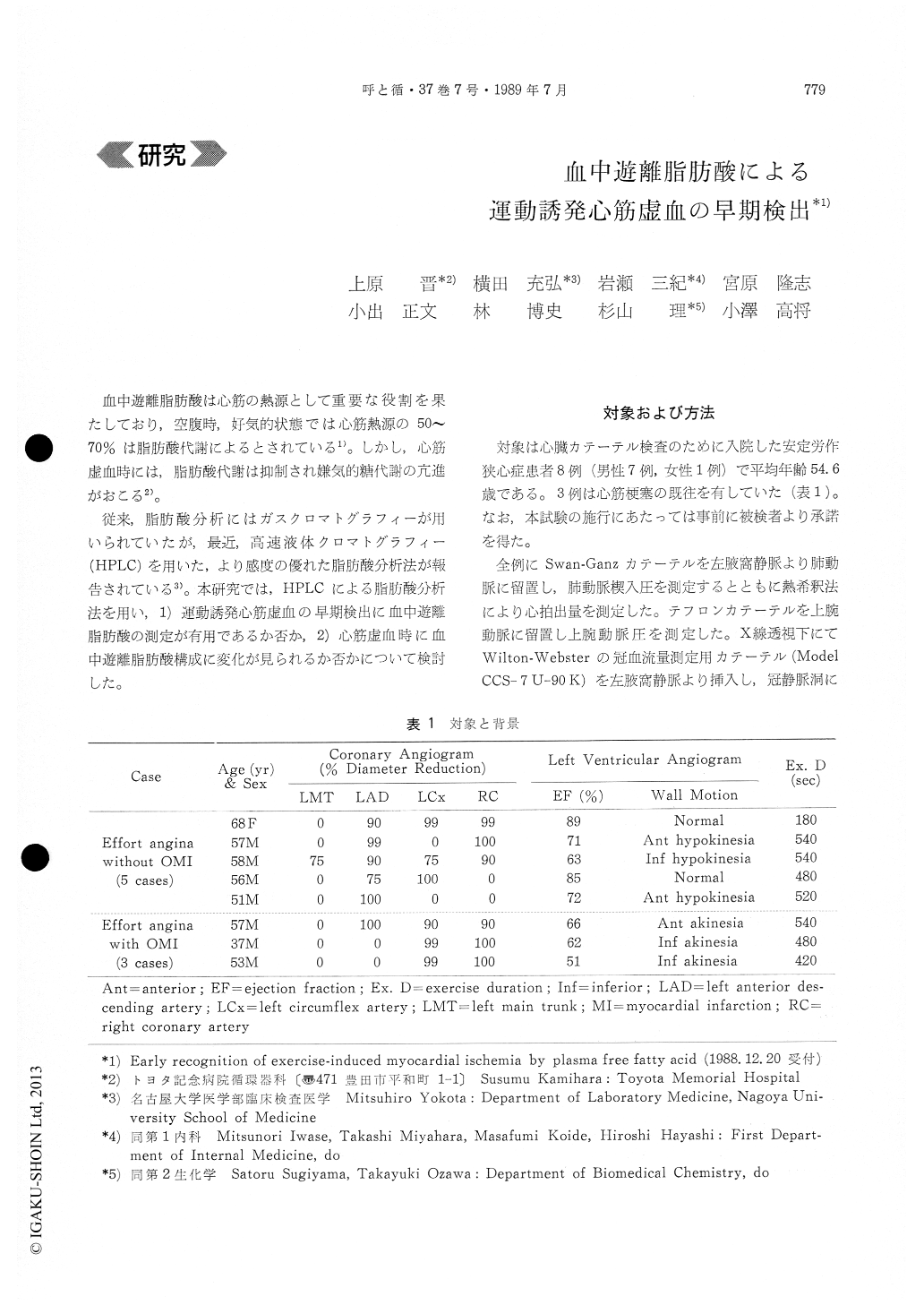
血中遊離脂肪酸は心筋の熱源として重要な役割を果たしており,空腹時,好気的状態では心筋熱源の50〜70%は脂肪酸代謝によるとされている1)。しかし,心筋虚血時には,脂肪酸代謝は抑制され嫌気的糖代謝の亢進がおこる2)。
従来,脂肪酸分析にはガスクロマトグラフィーが用いられていたが,最近,高速液体クロマトグラフィー(HPLC)を用いた,より感度の優れた脂肪酸分析法が報告されている3)。本研究では,HPLCによる脂肪酸分析法を用い,1)運動誘発心筋虚血の早期検出に血中遊離脂肪酸の測定が有用であるか否か,2)心筋虚血時に血中遊離脂肪酸構成に変化が見られるか否かについて検討した。
To investigate whether or not myocardial free fatty acid (FFA) uptake is useful for early recog-nition of exercise-induced myocardial ischemia com-pared with myocardial lactate uptake, we studied in 8 patients with stable effort angina pectoris bymeasuring hemodynamic and metabolic parameters during supine multistage bicycle ergometer exercise (BEx). Analysis of FFA composition was performed by high performance liquid chromatography. The exercise endpoint in the control study was moderate chest pain in all cases. In all cases, BEx testing us-ing the same method, duration and workload was repeated 1. 5 hours after the oral administration of 6 mg of nilvadipine (a new calcium antagonist). Exercise time of the subjects studied was 463=40 sec (mean±SE, 180-540 sec). After administration of nilvadipine, chest pain was not induced in 6 patients and was lessened in severity in 2 patients. Mean ST segment depression was 0. 21±0. 05 mV in the cont-rol period and it was significantly reduced to 0. 08± 0. 03 mV after nilvadipine administration (p< 0. 05). Myocardial FFA uptake decreased from 21. 1±4. 4% at rest to 8. 1±2. 1% at peak exercise in the control study (p < 0. 05). Myocardial lactate uptake was unchanged at rest and peak exercise in the control study (21.6±2. 7 vs 22. 2± 3. 3%). After administra-tion of nilvadipine, myocardial FFA uptake did not change during BEx (25. 3±2. 7 at rest and 21.3± 3. 6% at peak exercise). At peak exercise, myocar-dial FFA uptake increased significantly after admini-stration of nilvadipine (21. 3± 3. 6 vs 8. 1=2. 1%, p<0. 05). In FFA composition, the percentage of each of 12 FFA did not change during myocardial passage at rest and peak exercise.
Therefore, it is suggested that myocardial FFA up-take would be useful for early recognition of exer-cise-induced myocardial ischemia compared with myocardial lactate uptake.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


