Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
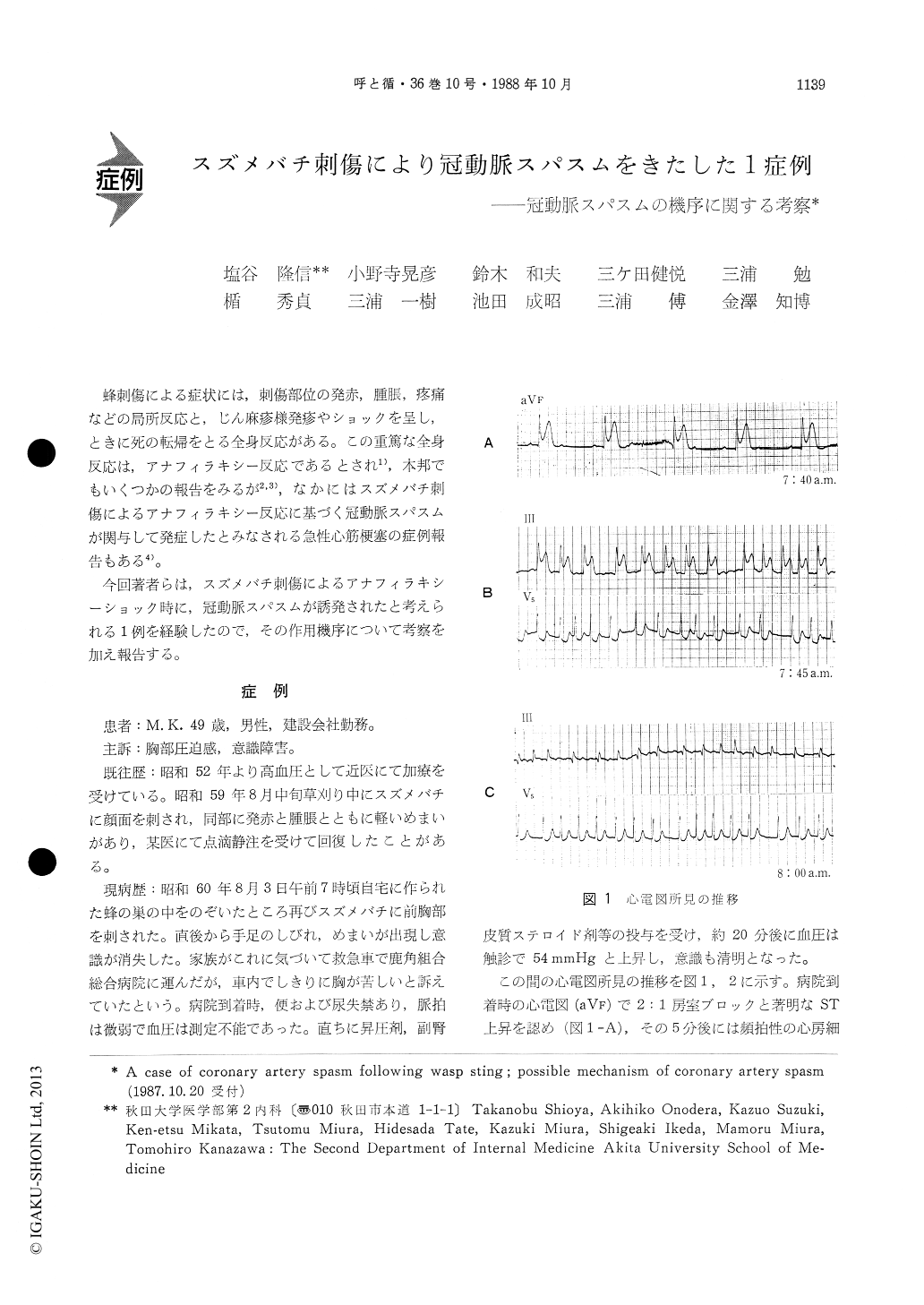
蜂刺傷による症状には,刺傷部位の発赤,腫脹,疼痛などの局所反応と,じん麻疹様発疹やショックを呈し,ときに死の転帰をとる全身反応がある。この重篤な全身反応ははアナフィラキシー反応であるとされ1),本邦でもいくつかの報告をみるが2,3),なかにはスズメバチ刺傷によるアナフィラキシー反応に基づく冠動脈スパスムが関与して発症したとみなされる急性心筋梗塞の症例報告もある4)。
今回著者らは,スズメバチ刺傷によるアナフィラキシーショック時に,冠動脈スパスムが誘発されたと考えられる1例を経験したので,その作用機序について考察を加え報告する。
Coronary artery spasm is now widely accepted as the cause of variant angina pectoris. Current hypo-thesis regarding the pathophysiology of coronary artery spasm includes abnormalities in sympathetic or parasympathetic neural control, excessive respon-siveness to circulatory vasoactive substances (chemi-cal mediators), and local coronary lesion, or some combination of these factors. We report the case of severe coronary artery spasm following wasp sting suggesting the importance of vasoactive substances.
A 49-year-old man became suddenly unconscious being stung by wasp on his chest. On admission his blood pressure was not measurable and the electro-rocardiogram showed 2 : 1 AV block and ST segment elevation in leads II, III, aVF and also ST segmentdepressions in leads V2 to V6. After administration of iv catecholamine and hydrocortisone, the BP rose to 54mmHg in 20min. After 20 min, these ST eleva-tions returned to the baseline. Cardiac enzymes did not indicate evidence of acute myocardial infarction.
The patient was reffered to Akita University Hos-pital for coronary arteriography. Coronary arterio-graphy revealed no obstruction of right and left co-ronary arteries and left ventriculograms were normal. After intravenous infusion of ergonovine malate (0. 4 mg), the right cornary artery showed vasospastic narrowing and reduced its lumial diameter by 60%, whereas the left coronary artery showed slight vaso-spastic narrowing. Intracoronary infusion of nitro-glycerin (0. 2 mg) dilated these coronary spasm imme-diately.
Recent investigations have shown that various vasoactive subsances such as histamine, serotonin, thomboxane Az, platelet activating factor are releas-ed and played significant role in anaphylaxic shock due to wasp sting. These vasoactive substances have been shown to cause coronary artery contraction in vivo and in vitro. Accordingly our findings suggest that these vasoactive substances might be the cause of coronary artery spasms.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


