Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
肺静脈系(肺静脈と左心房)は,左心系の容量血管として肺静脈還流量を調節し心機能を制御していることが知られているが,外科においては,生理的状態を逸脱した状態で体外循環や人工心臓を駆動する際にも,その容量血管としての機能が問題になることがある。例えば,肺静脈系の容量(capacitance)の低下という病的状態において,体外循環や人工心臓制御下における左心系の静脈還流量と拍出量に少しでも不均衡が生じれば,肺静脈系が虚脱するか肺静脈圧が急上昇して肺水腫が発生する危険がある。この意味で,容量血管としての機能を規定する基本的な壁の弾性特性を表す指標としてコンプライアンス(ΔV/ΔP)を測定することは,心拍出量(CO)や左心房圧調節の研究の他に体外循環や人工心臓の至適制御を行うための1つの指標になりうると考えられる。
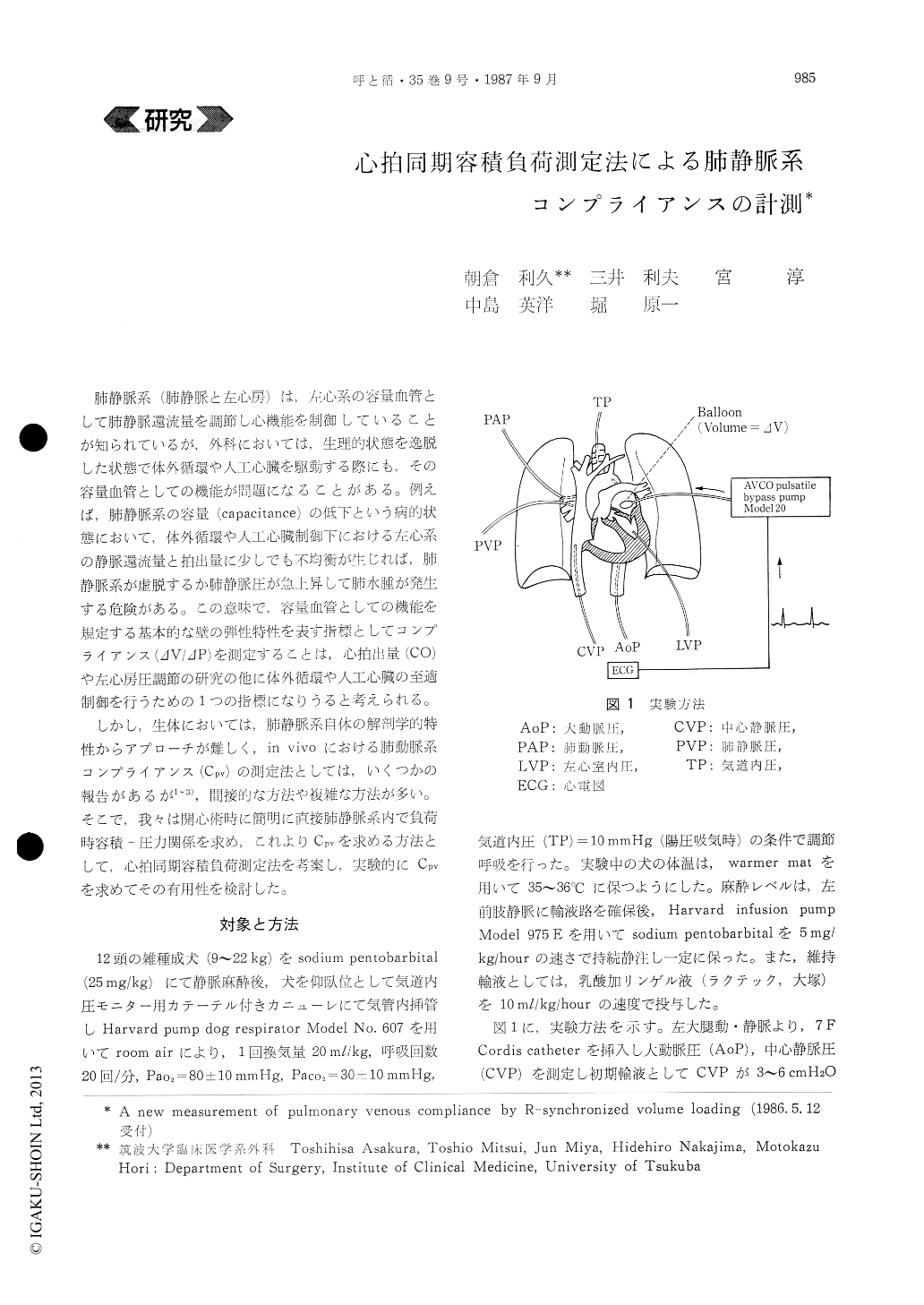
しかし,生体においては,肺静脈系自体の解剖学的特性からアプローチが難しく,in vivoにおける肺動脈系コンプライアンス(Cpv)の測定法としては,いくつかの報告があるが1〜3),間接的な方法や複雑な方法が多い。そこで,我々は開心術時に簡明に直接肺静脈系内で負荷時容積一圧力関係を求め,これよりCpvを求める方法として,心拍同期容積負荷測定法を考案し,実験的にCpvを求めてその有用性を検討した。
It is known that pulmonary venous system, which consists of the pulmonary veins and left atrium plays an important role for the upstream vascular capacity of left heart system and pulmonary venous compliance (Cpv) indicates a function of vascular capacity. In spite of the importance of Cpv, there are few appropriate methods to measure Cpv due to a difficulty in approaching the pulmonary venous sys-tem. Therefore, we designed a direct and simple measurement of Cpv by R-synchronized volume load-ing during the open-heart operation and evaluated its utility experimentally.
In 12 anesthetized open-chest dogs, a balloon (volume=ΔV) was inserted in the left atrium through the left auricle. Pulmonary venous pressure (PVP) wave measured with a low pressure transducer in-dicated v wave during mitral valve closure. Elevated pressure (ΔP) from control v wave was measured when the balloon (ΔV=3~10ml) was inflated during mitral valve closure at the rate of one time per two beats using Model 20-AVCO in a synchro-nized fashion.
PVP along with volume loading (JV) standardized by body weight was plotted on a regression line with a statistical significance (r =0.98±0.02). Cpv obtained from this slope was concluded to be 0. 146 ±0.056ml・mmHg-1・ kg-1 when PVP was 8.8±2.1 mmHg and Cpv developed a tendency to decrease as PVP increased.
We designed a new method of pulmonary venous compliance measurement by R-synchronized volume loading, and the utility of our method is charac-terized by the prevention of leakage of loading volume to the ventricle and by the variableness of loading volume. Cpv was concluded to be in a state of static compliance, because it indicated the almost constant value to loading volume change. Cpv obtained with our method was 0.146±0. 056 mi.mmHg-1・kg-1, which was almost the same as proposed in previous reports.
Copyright © 1987, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


