Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
心臓性ショックの原因に.急性心臓タンポナーデがある。その病態は心臓全体の拡張不全に起因することが多く,他の原因,例えば心筋の部分的収縮・拡張不全を起こす急性心筋梗塞とは異なり,ショックの臨床像も同様に特異であることは経験的に知られている。
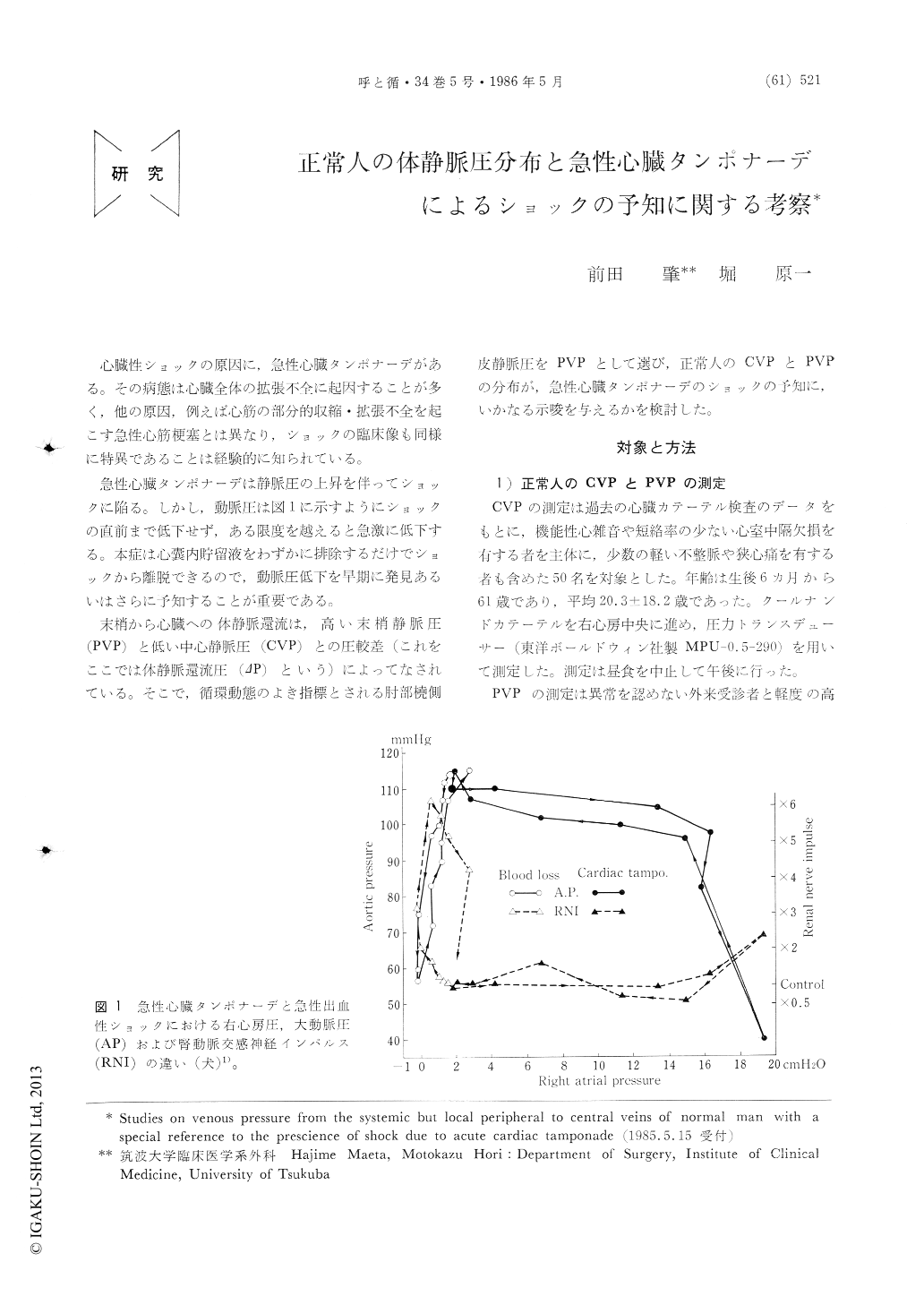
急性心臓タンポナーデは静脈圧の上昇を伴ってショックに陥る。しかし,動脈圧は図1に示すようにショックの直前まで低下せず,ある限度を越えると急激に低下する。本症は心嚢内貯留液をわずかに排除するだけでショックから離脱できるので,動脈圧低下を早期に発見あるいはさらに予知することが重要である。
The acute cardiac tamponade falls in shock with elevation of the venous pressure and the arterial pressure abruptly decreases when the venous pressure becomes over the range. Therefore, it is very important to fore-know the arterial pressure drop. This study was per-formed in order to clarify the venous return in normal condition and to foreknow the shock in the acute cardiac tamponade (SACT) from the point of view of venous return.
The mean and range of the central venous pressure (CVP) and antecubital cephalic venous pressure (PVP) were presented with the phlebostatic axis as a reference point.
It was recognized to be normal in distribution of CVP and PVP. The normal CVP was 4.1+ 2. 0 mmHg (mean±SD) and its range was 0.1 to 9 mmHg. The normal PVP was 5.3±1.8 mmHg and its range was 2.2 to 9.6 mmHg. The upper range of normal CVP was 8.1 mmHg (11 cmH2O) and that of PVP was 8.9 mmHg (12.1 cmH2O), with 2.5% of risk.
Relationship between driving pressure of venous return from the peripheral to central veins (ΔP) and CVP resulted in the equation of ΔP=1.61-0.098×CVP. The normal ΔP calculated from this equation was 1.2 mmHg and the calculated ΔP at the supremum of normal CVP was 0.8 mmHg.
At SACT with normal circulatory volume in clinical cases, CVP was 11~12 mmHg and ΔP was only 0.4 mmHg. At the same CVP, calculated ΔP was 0.39 mmHg. A best correspondence was recognized in these two ΔPs.
No difference in CVP was observed between man and dog.
The prescience of SACT was made possible from the venous pressures. When the CVP elevates to higher than 8 mmHg (11 cmH2O) and AP drops to lower than 0.8 mmHg (1 cmH2O), a strict precaution is needed to prevent the SACT, as the cardiac return is disturved and, therefore, cardiac output is decreased. The SACT tends to occur at the 11-12 mmHg of CVP and/or below 0.4 mmHg of ΔP.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


