Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
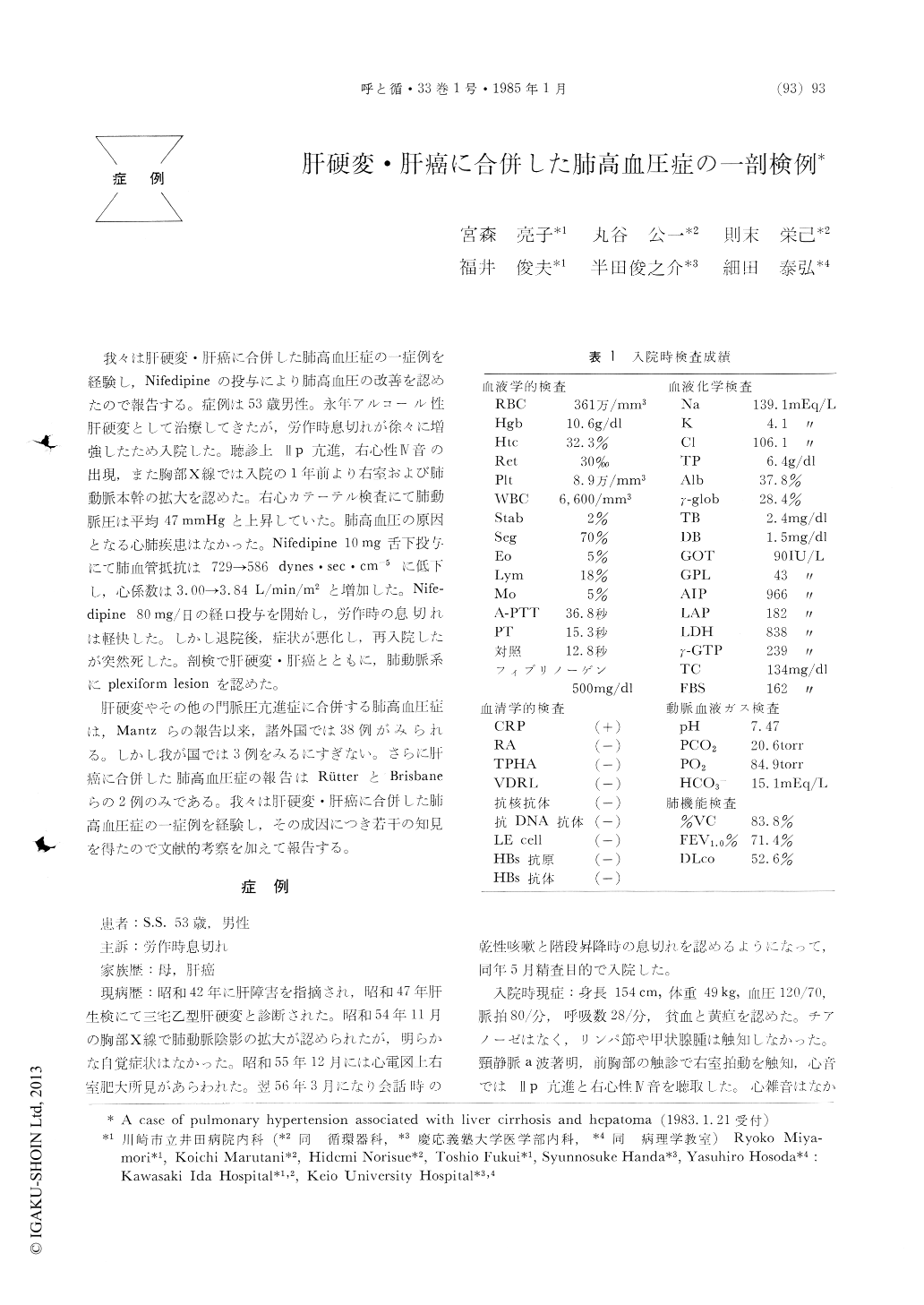
我々は肝硬変・肝癌に合併した肺高血圧症の一症例を経験し,Nifedipineの投与により肺高血圧の改善を認めたので報告する。症例は53歳男性。永年アルコール性肝硬変として治療してきたが,労作時息切れが徐々に増強したため入院した。聴診上IIp亢進,右心性IV音の出現,また胸部X線では入院の1年前より右室および肺動脈本幹の拡大を認めた。右心カテーテル検査にて肺動脈圧は平均47mmHgと上昇していた。肺高血圧の原因となる心肺疾患はなかった。Nifedipine 10mg舌下投与にて肺血管抵抗は729→586 dynes・sec・cm−5に低下し,心係数は3.00→3.84L/min/m2と増加した。Nife—dipine 80mg/日の経口投与を開始し,労作時の息切れは軽快した。しかし退院後,症状が悪化し,再入院したが突然死した。剖検で肝硬変・肝癌とともに,肺動脈系にplexiform lesionを認めた。
肝硬変やその他の門脈圧亢進症に合併する肺高血圧症は,Mantzらの報告以来,諸外国では38例がみられる。しかし我が国では3例をみるにすぎない。さらに肝癌に合併した肺高血圧症の報告はRutterとBrisbaneらの2例のみである。我々は肝硬変・肝癌に合併した肺高血圧症の一症例を経験し,その成因につき若干の知見を得たので文献的考察を加えて報告する。
A case of pulmonary hypertension associated with liver cirrhosis and hepatoma was reported. Since the first report of Mantz, 41 cases of pulmonary hypertension associated with portal hypertension, and only 2 cases of pulmonary hypertension with hepatoma, were reported.
The patient was a 52 years old man with liver cirrhosis at least for 10 years. He was admitted to our hospital because of DOE. The positive physical findings were, moderate anemia, jaundice and hepa-tomegaly. There was prominent a wave in iugularpulse. Accentuated 2nd pulmonic sound and right-sided 4th sound were audible. ECG showed RVH. A chest X-ray revealed cardiomegaly with marked central pulmonary arteries. Right heart catheteriza-tion showed PH with PAP of 75/27, 47 and mean PCWP of 4. C.I. was 3. 13 L/min/m2. Sublingual nifedipine diminished PAP down to 80/29, 38 with C.I. of 3.84. Chronic administration of the medi-cine improved his complaint. A celiac angiography showed hepatoma with portal venous thrombosis of tumor. He died suddenly 3 months later. Autopsyrevealed hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease of grade VI, with a lot of plexiform lesions. There was no pulmonary thrombus. The liver cirrhosis with hepatoma was comfirmed.
One of the hypothesis for the rare combination of pulmonary and portal hypertension was the devel-opment of pulmonary thromboemboli from portal circulation. The evidence of PH without pulmonary thrombus in this case, however, suggested other mechanism, such as humoral factor for the progres-sion of pulmonary hypertension.
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


