- 有料閲覧
- 文献概要
- 1ページ目
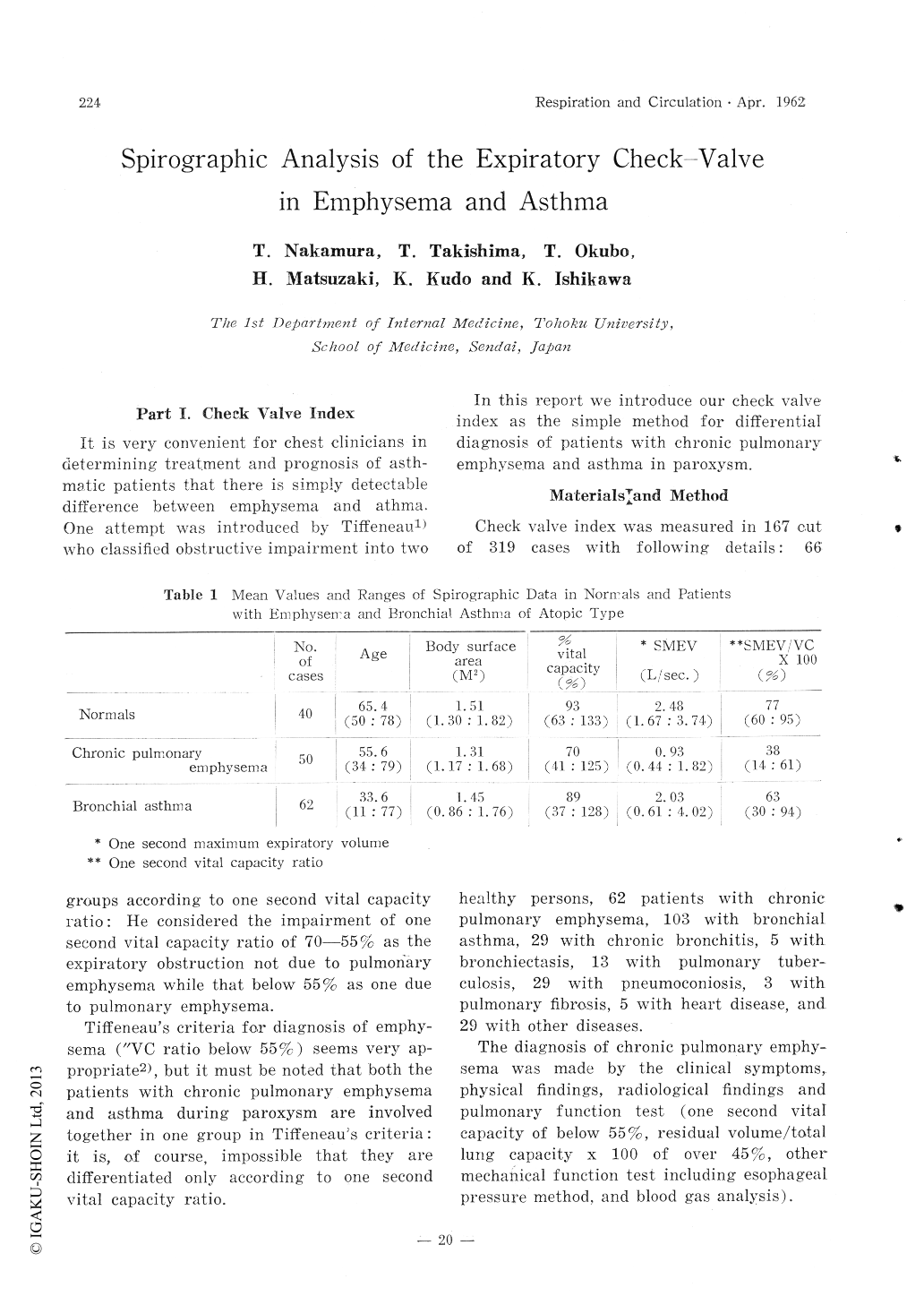
In 59 patients with both chronic pulmonary emphysema and bronchial asthma, expiratory volume (Δ V) and the expiratory time (Δ t) were calculated in a relatively straight portion from the beginning of expiration to check valve point on maximum expiratory flow curve (Tiffeneau's test), and these values were analyzed in relating with the viscoelastic abnormality of the lungs.
Δ t was shown to be fairly constant value (0.06-0.07 sec.) in both diseases. In contrast with this, Δ V was 0.26 L in emphysema patients, while 0.46 L in athmatic patients, indicating considerable difference between 2 groups in flow rate until the check valve point.
The theoretical relationship between Δ V and lung tension, and airway resistance was confirmed actually by the fact that Δ V was a function of both maximum inspiratory esophageal pressure and pulmonary viscous resistance. Especially it was confirmed that Δ V seemed to have a clinical significance as a good indicator to presume pulmonary re-sistance.
Copyright © 1962, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


