Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- サイト内被引用 Cited by
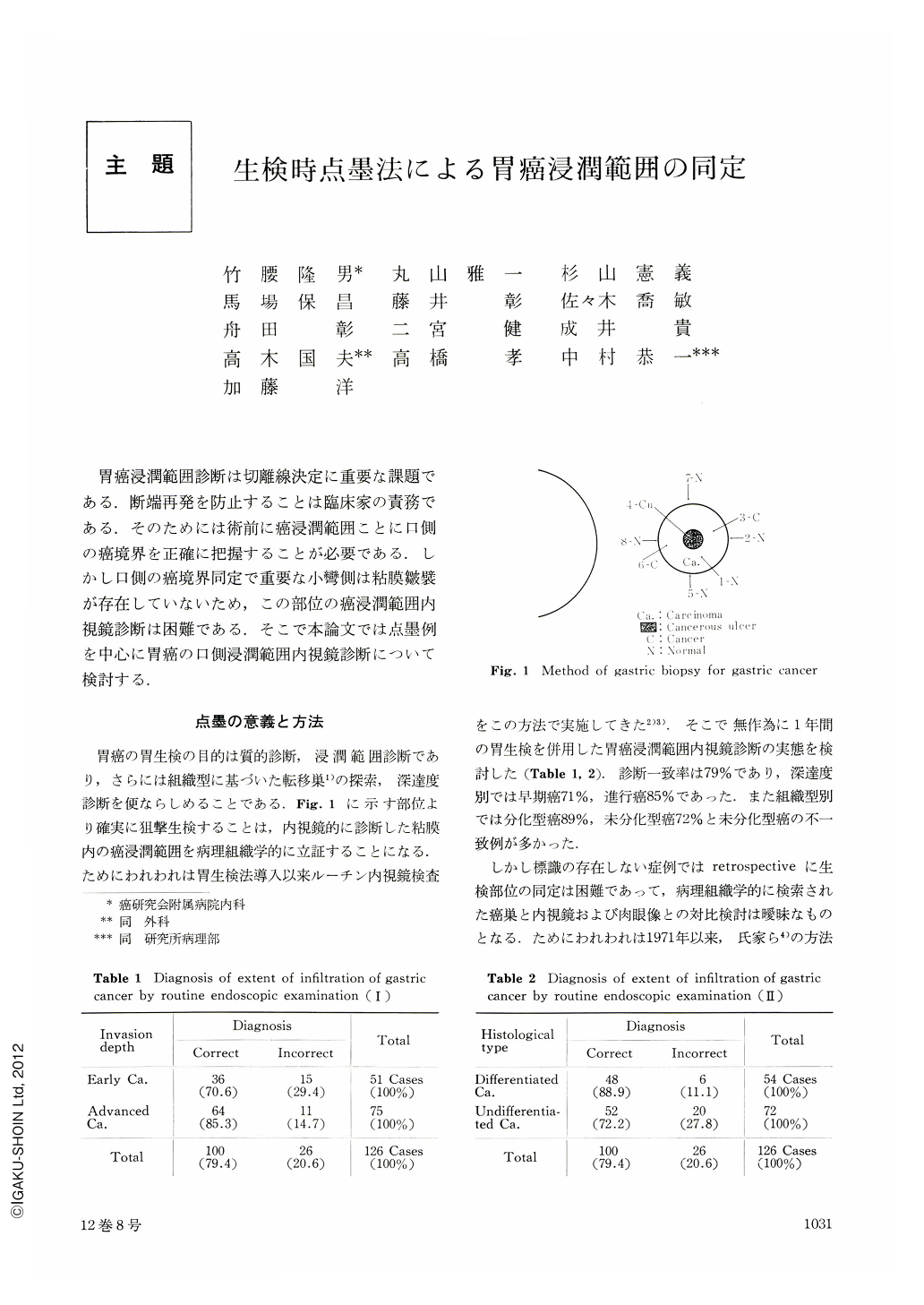
胃癌浸潤範囲診断は切離線決定に重要な課題である.断端再発を防止することは臨床家の責務である.そのためには術前に癌浸潤範囲ことに口側の癌境界を正確に把握することが必要である.しかし口側の癌境界同定で重要な小彎側は粘膜皺襞が存在していないため,この部位の癌浸潤範囲内視鏡診断は困難である.そこで本論文では点墨例を中心に胃癌の口側浸潤範囲内視鏡診断について検討する.
The significance of carbon ink injection method in gastric biopsy was described and the neighbouring area of carcinoma, including its boundary which was histologically proved, was defined instead of referring to marginal zone of carcinoma. In the routine endoscopic examination, the extent of cancerous infiltration was correctly diagnosed in 79% of the whole cases in comparison with the boundary of the lesion which was histologically proved. The detailed endoscopic examination with the combined use of the carbon ink injection method increased the diagnostic accuracy to 95% in terms of defining the boundary. But there still remained 5% whose boundary could not be correctly diagnosed even with this method.
For the correct diagnosis of the boundary of the lesion in the detailed fiberscopy, recognition of minute endoscopic findings, including the neighbouring area as well as the lesion was required, based upon the histologic type of carcinoma which was obtained in the first routine biopsy. The most reliable endoscopic signs for the diagnosis of the proximal boundary of carcinoma could be mucosal depression, discoloration and changing pattern of “areae gastricae”, but it was dangerous to expect the mucosal depression to be the reliable sign intuitively on observation, because there were various lesions showing very shallow depression, double contoured surface depression or Ⅱb-like intramucosal spread to the proximal boundary.
The endoscopic findings of the neighbouring area, inclusive of cancerous lesion, was closely associated with the state of intramucosal spread and its histologic type. Namely, redness and irregular granularity were most characteristic of differentiated carcinoma. On the other hand, discolored mucosa without granularity was most frequent in undifferentiated carcinomas. Discolored mucosa with unchanged pattern of “areae gastricae” was secondarily frequent and discolored mucosa with small irregular granularity was the third.
An analysis of intramucosal spreading pattern of carcinoma revealed that discoloration of the mucosa was not ascribed to the mode of intramucosal spread but to the histologic type. On the other hand, changing pattern of “areae gastricae” was found to be caused by the difference in the mode of intramucosal spread. Generally, granularity of the mucosa became more rough and irregular in the differentiated carcinomas as the intramucosal spread reached more deeply into the thickness of the mucosa. In the undifferentiated carcinomas variuos endoscopic findings were observed if the surface of the lesion was covered with the foveolar epithelium and those which were exposed without the covering feveolar epithelium revealed flat mucosal surface as the intramuccsal spread reached more deeply into the thickness of the mucosa.
Copyright © 1977, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


