Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
食道静脈瘤のX線診断にはいろいろな方法が用いられているが,そのなかでもっとも有効な検査法の1つは左胃動脈造影である1)2).門脈高圧症の患者で食道静脈瘤が疑われる場合に腹腔動脈と上腸間膜動脈のarterial portographyを行なっても門脈血流の方向によって食道静脈瘤が造影されない例が多く,経脾門脈造影でも門脈血流が脾に向かっているときには食道静脈瘤を十分に造影することは困難である.
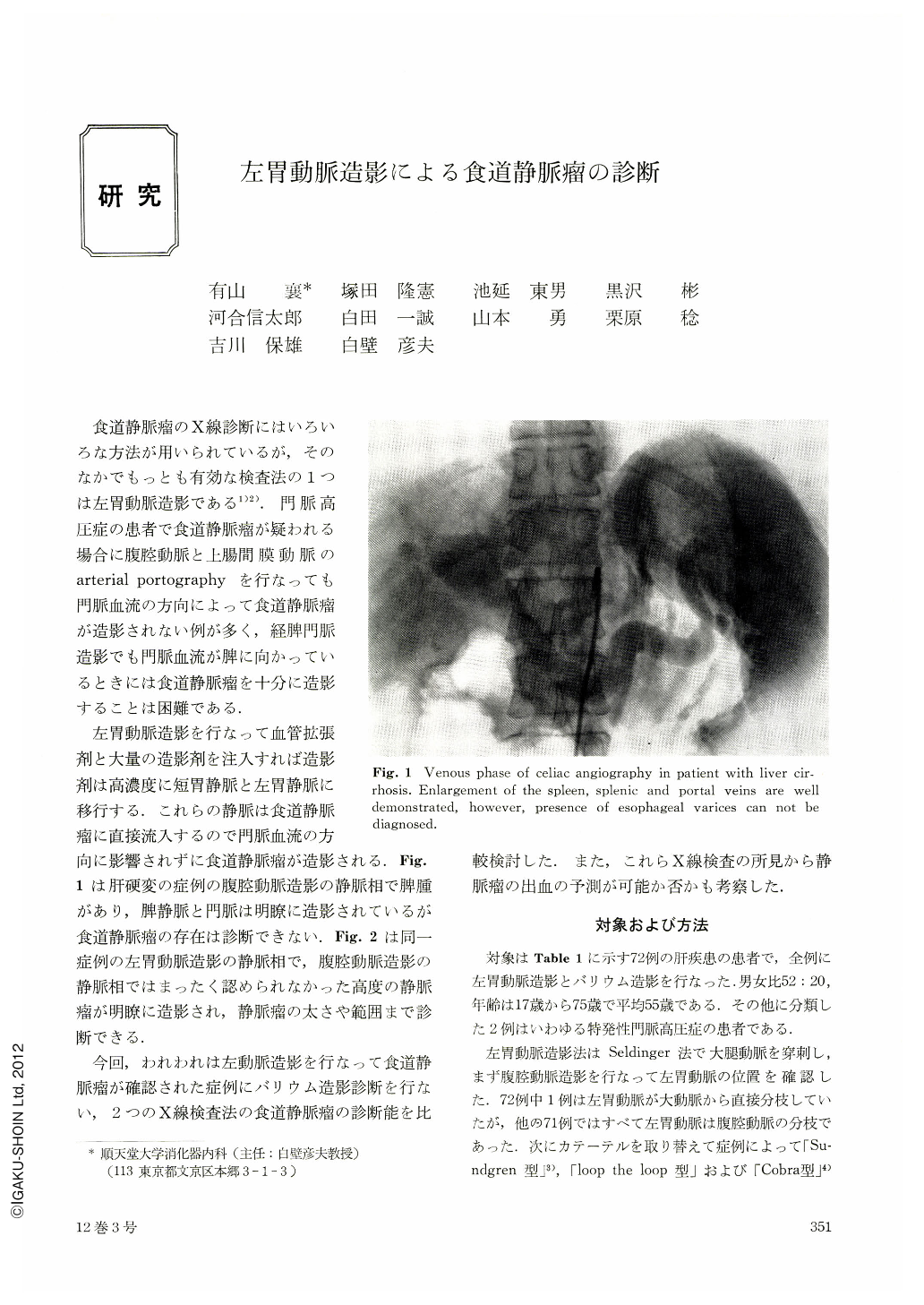
左胃動脈造影を行なって血管拡張剤と大量の造影剤を注入すれば造影剤は高濃度に短胃静脈と左胃静脈に移行する.これらの静脈は食道静脈瘤に直接流入するので門脈血流の方向に影響されずに食道静脈瘤が造影される.Fig.1は肝硬変の症例の腹腔動脈造影の静脈相で脾腫があり,脾静脈と門脈は明瞭に造影されているが食道静脈瘤の存在は診断できない.Fig.2は同一症例の左胃動脈造影の静脈相で,腹腔動脈造影の静脈相ではまったく認められなかった高度の静脈瘤が明瞭に造影され,静脈瘤の太さや範囲まで診断できる.
Experience in Juntendo University, Medical School indicates 20% of patients who bleed for the first time from the esophageal varices die and that mortality raises to 60% for subsequent bleed. Our experience suggests that those patients with the most extensive varices run the highest risk of bleeding and therefore the assessment of presence and severity of the varices has become important in the selection of the patients for prophylactic transection of the esophagus. In this study we have compared reputedly the most accurate method (left gastric angiography) and the most common technique (barium swallow) for demonstration of esophageal varices.
Subjects and Method
Seventy two adult subjects with esophageal varices clue to variety of underlying disorders (Table 1) were studied between 1972 to 1975. Barium swallow technique was using 160 W/V% barium sulfate in a container which permitted air to be swallowed in large amount with the barium sulfate. To inhibit primary peristalsis and impair esophageal transit of the barium, anticholinergic agent (Coliopan 4 mg) were administered. Left gastric angiography was performed by the trans-femoral route using preshaped catheters for selective canulation. Thirty ml of contrast medium were injected over 4 seconds and 40 mg of papaverine having been injected into the left gastric artery before the injection of the the contrast medium.
Radiological Assessment
In all subjects, the varices were well demonstrated by left gastric angiography. In 53 of 72 patients, varices were detected by barium swallow (73%). Comparison of three different modes of barium meal studies revealed double contrast study with small amount of air is the most effective for demonstration of the varices (Table 2). According to the radiological findings, varices were classified into three groups. (Table 3, 4, Fig. 3~8) However, grade of varices diagnosed by both methods does not correlate with each other (Table 5). This indicates the varices limited to the lower esophagus and the stomach are difficult to be detected by barium swallow, and in some cases esophageal varices are not well filled by left gastric angiography may be due to dilution of contrast medium or reverse blood flow. Assessment of cranial extent of the varices is difficult by left gastric angiography.
Incidence of bleeding from the varices is well correlated with angiographic severity (Table 6) and patients with grade Ⅲ varices should be considered for prophylactic transection of the esophagus.
Copyright © 1977, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


