Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
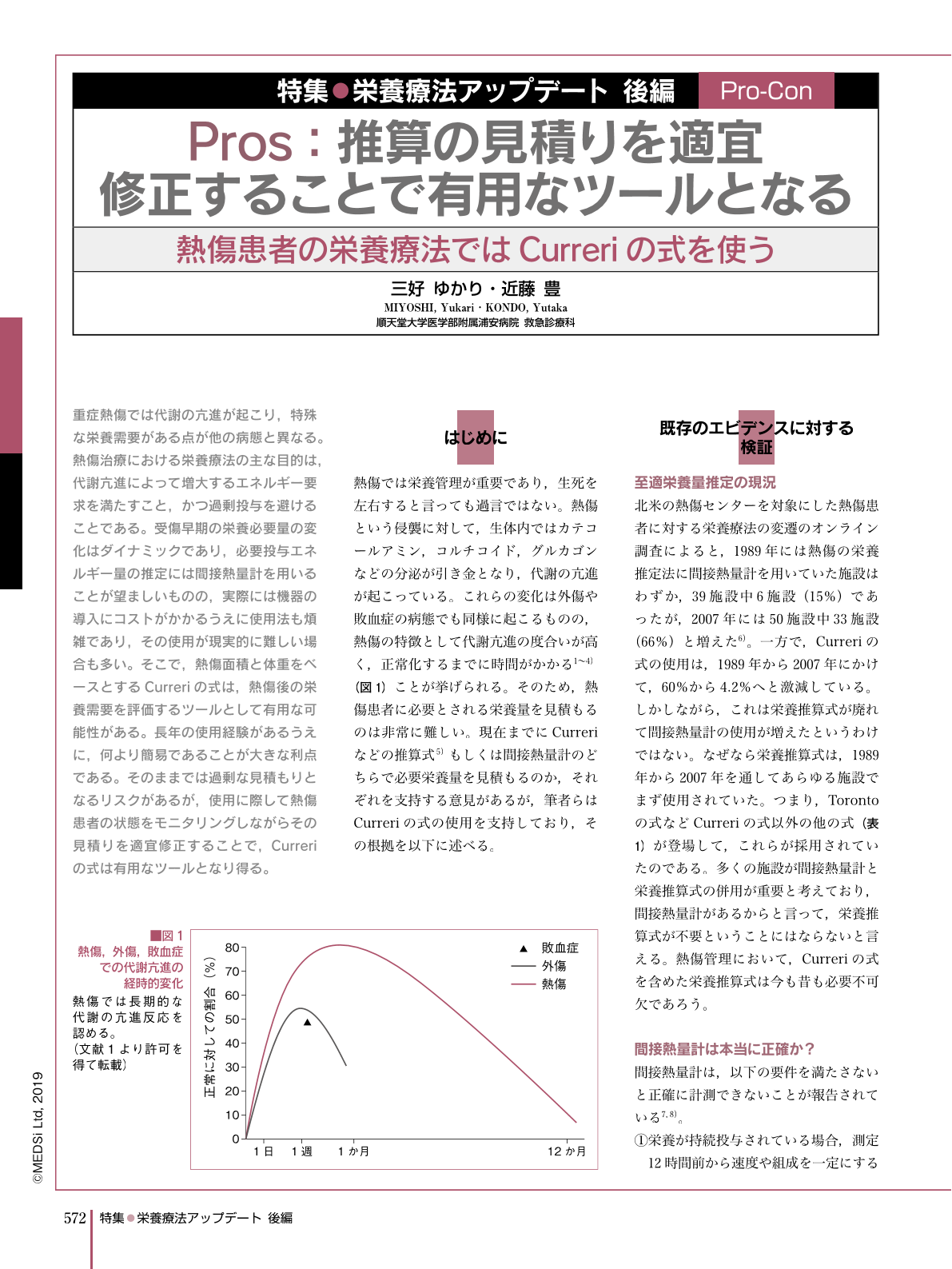
重症熱傷では代謝の亢進が起こり,特殊な栄養需要がある点が他の病態と異なる。熱傷治療における栄養療法の主な目的は,代謝亢進によって増大するエネルギー要求を満たすこと,かつ過剰投与を避けることである。受傷早期の栄養必要量の変化はダイナミックであり,必要投与エネルギー量の推定には間接熱量計を用いることが望ましいものの,実際には機器の導入にコストがかかるうえに使用法も煩雑であり,その使用が現実的に難しい場合も多い。そこで,熱傷面積と体重をベースとするCurreriの式は,熱傷後の栄養需要を評価するツールとして有用な可能性がある。長年の使用経験があるうえに,何より簡易であることが大きな利点である。そのままでは過剰な見積もりとなるリスクがあるが,使用に際して熱傷患者の状態をモニタリングしながらその見積りを適宜修正することで,Curreriの式は有用なツールとなり得る。
Severe burn injuries cause prolonged and persistent hypermetabolic responses. The primary goal of nutritional support in patients with burns is to meet the increased caloric requirements caused by the hypermetabolic state while avoiding overfeeding. Energy expenditures fluctuate after burn injuries and indirect calorimetry is needed to accurately determine the energy expenditure, which is not practical on a routine basis. There are a variety of formulas used to estimate the energy requirements of patients with burns. Older formulas such as the Curreri formula are reported to overestimate requirements. This is thought to be due to advances in the medical management of patients with burns which have reduced the hypermetabolism associated with a burn injury. The Curreri formula is still considered useful to estimate nutritional needs because it accounts for important parameters including the percent of body surface area burned and weight. Above all, it is very simple and convenient to use. The estimated energy expenditure determined by using the Curreri formula can be modified, considering the condition of the burn and general status.
Copyright © 2019, MEDICAL SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, LTD. All rights reserved.


