Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
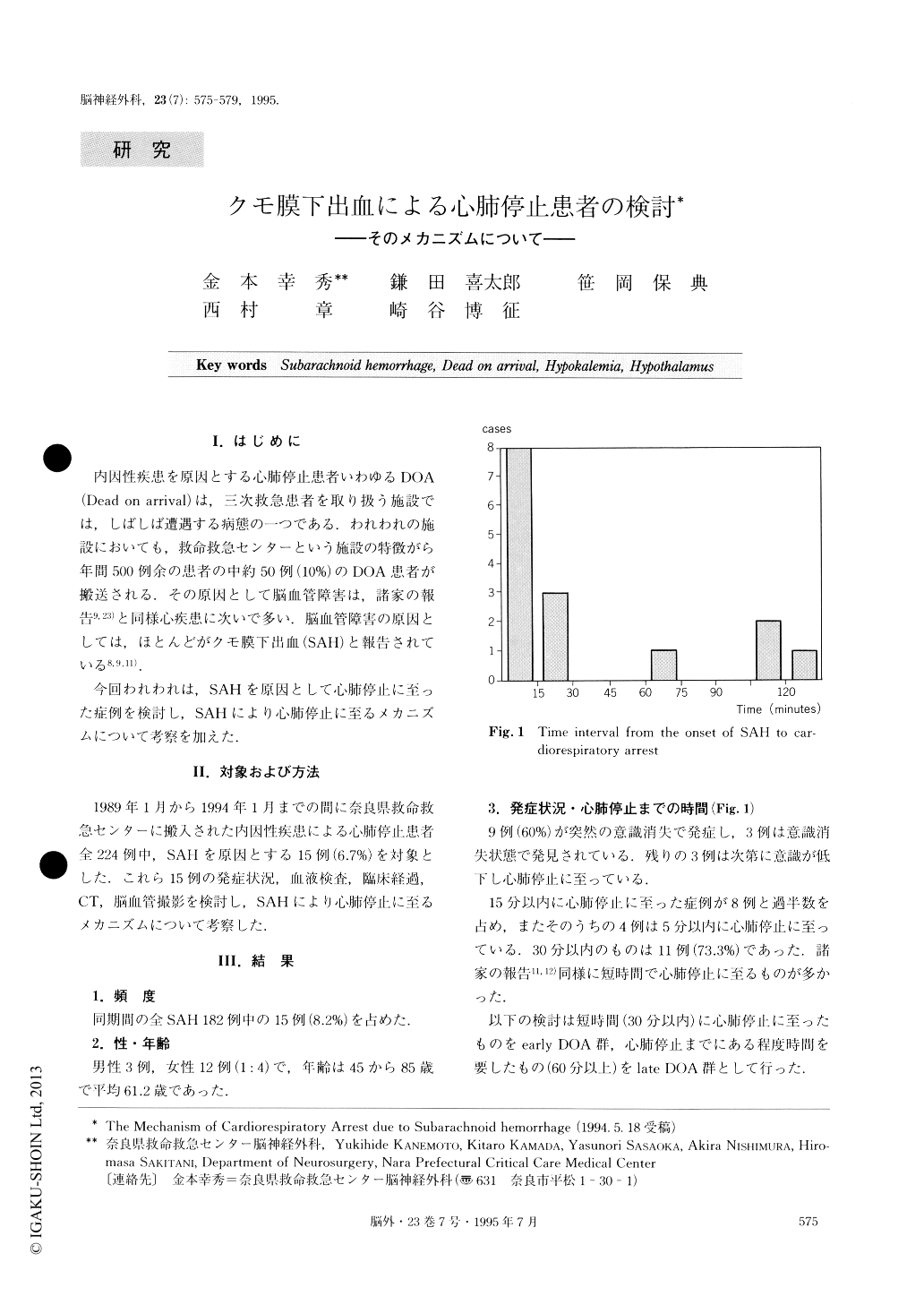
I.はじめに
内因性疾患を原因とする心肺停止患者いわゆるDOA(Dead on arrival)は,三次救急患者を取り扱う施設では,しばしば遭遇する病態の一つである.われわれの施設においても,救命救急センターという施設の特徴がら年間500例余の患者の中約500例(10%)のDOA患者が搬送される.その原因として脳血管障害は,諸家の報告9,23)と同様心疾患に次いで多い.脳血管障害の原因としては,ほとんどがクモ膜下出血(SAH)と報告されている8,9,11).
今回われわれは,SAHを原因として心肺停止に至った症例を検討し,SAHにより心肺停止に至るメカニズムについて考察を加えた.
This report describes the clinical course of patients with sudden cardiorespiratory arrest (CRA) due to sub-arachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). We have seen fifteen patients of SAH that presented initially as CRA. All of them were diagnosed as SAH by CT scan. The patients were divided into two groups; one group (early DOA group) included 11 patients, who had been recognized as CRA within 60 minutes from the onset of SAH, the other group (late DOA group) consisted of 4 patients, who developed CRA more than 60 minutes after the in-itial onset. The major mechanism leading to delayed CRA in the late DOA group appeared to have been from brain stem herniation, but another mechanism appeared to be involved in sudden CRA in the early DOA group. Sixty percent of our patients with CRA due to SAH had a low serum potassium concentration, though hypokalemia was observed in only 4 out of 100 patients with CRA due to diseases other than SAH. These facts suggest that sympathetic hyperstimulation might result not only from stress but also from a dis-order of the central autonomic nervous system. We speculate that the mechanism leading to early CRA af-ter SAH appears to result from a disorder of the cen-tral autonomic nerve system.
Copyright © 1995, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


