Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
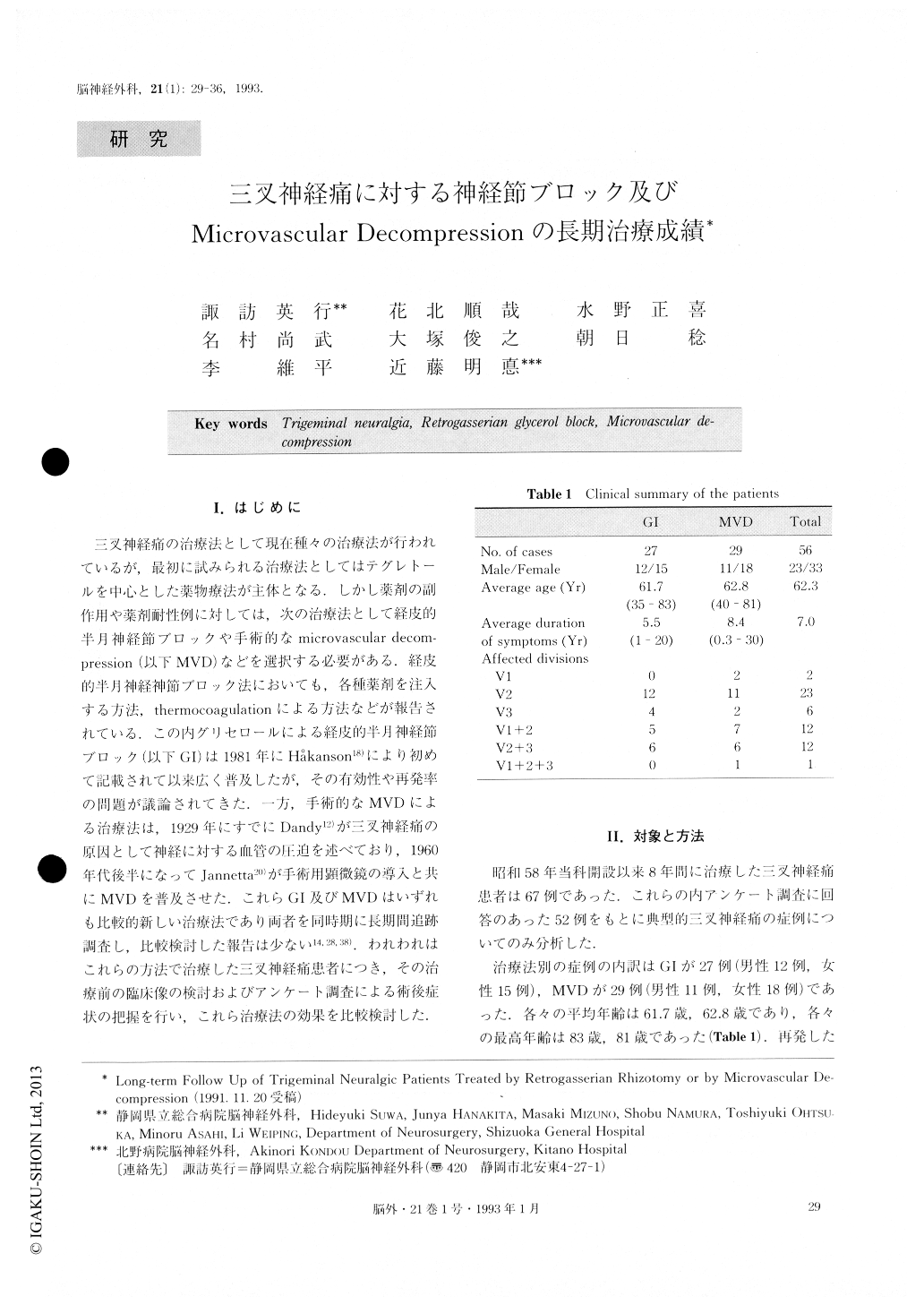
三叉神経痛の治療法として現在種々の治療法が行われているが,最初に試みられる治療法としてはテグレトールを中心とした薬物療法が主体となる.しかし薬剤の副作用や薬剤耐性例に対しては,次の治療法として経皮的半月神経節ブロックや手術的なmicrovascular decom—pression(以下MVD)などを選択する必要がある.経皮的半月神経神節ブロック法においても,各種薬剤を注入する方法,thermocoagulationによる方法などが報告されている.この内グリセロールによる経皮的半月神経節ブロック(以下GI)は1981年にHakanson18)により初めて記載されて以来広く普及したが,その有効性や再発率の問題が議論されてきた.一方,手術的なMVDによる治療法は,1929年にすでにDandy12)が三叉神経痛の原因として神経に対する血管の圧迫を述べており,1960年代後半になってJannetta20)が手術用顕微鏡の導入と共にMVDを普及させた.これらGI及びMVDはいずれも比較的新しい治療法であり両者を同時期に長期間追跡調査し,比較検討した報告は少ない14,28,38).われわれはこれらの方法で治療した.三叉神経痛患者につき,その治療前の臨床像の検討およびアンケート調査による術後症状の把握を行い,これら治療法の効果を比較検討した.
The authors studied the long-term follow up of trigeminal neuralgic patients treated by retrogasserian rhizotomy with anhydrous glycerol injection (GI) or by microvascular decompression (MVD) and compared the satisfaction rates between them. Since 1983, 67 patients had been treated either by 01 or MVD. The authors analyzed the results of the treatment by the method of questionnaire. Fifty-two patients of these 67 answered the questions, on which the present analysis was based. 01 group consisted of 27 patients and MVD group 29 patients. The average follow-up period was 30.9 months in 01 group (maximum follow-up: 84 months) and 50.9 months in MVD group (maximum follow-up: 95 months), respectively. The technique of 01 used was Hiirtel's method with cisternography of Meckel's cave. The operations of MVD were performed by J.H. A.K.. One patient out of 29 failed to be treated by MVD and two recurred within one year. On the otherhand, 2 patients out of 27 failed to be treated by GI and 11 recurred. The recurrence was seen earlier in pa-tients who had undergone GI, while one patient recur-red the neuralgia at 76 months later. The recurrence rate in patients treated by MVD is 7.0% at 95 months, while that by GI is 49.0% at 84 months based on Ka-plan-Meier survival analysis. The pathogenesis of trigeminal neuralgia is speculated to be an ephatic con-duction caused by segmental demyelination and artifi-cial synapse formation at the junction of central and peripheral myelin. The factors of this demyelination may be multiple sclerosis, basilar impression, aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation, atheroscleroses and natural aging. From these hypothesis, MVD may be superior to GI as for permanent cure because the procedure of MVD directs toward the causative lesion. The satisfac-tion rate is significantly higher in patients treated by MVD (85.8%) than GI (64.1%) because the failed and recurred cases are more in patients treated by GI (13 patients out of 27) than MVD (3 patients out of 29) and post-operative sensory disturbance is also more in pa-tients treated by GI (44.4%) than MVD (17.9%). However the rate is not different statistically between the pain-free patients in two groups (GI: 88.6%, MVD: 90.4%). The technique of GI is safe and its complica-tion is acceptable. So the authors may choose GI for all patients even if the patient is the younger, and can ex-pect 50% probability of pain-free state with minimal sensory disturbance at 7 years following GI procedure. If the trigeminal neuralgia recurs, the patient can be treated enough by MVD at that time.
Copyright © 1993, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


