Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
外傷性頸動脈海綿静脈洞瘻(以下CCFと略す)は受傷後早期に発症するのが大部分であるが,時に発症が遅れることがある3).また,CCFにクモ膜下出血を伴うことは少ない4).今回われわれは外傷5年後にクモ膜下出血にて発症したCCFを経験したので,発症が遅れた原因,およびクモ膜下出1飢をきたす機序について,若干の考察を加え,報告する.
Abstract
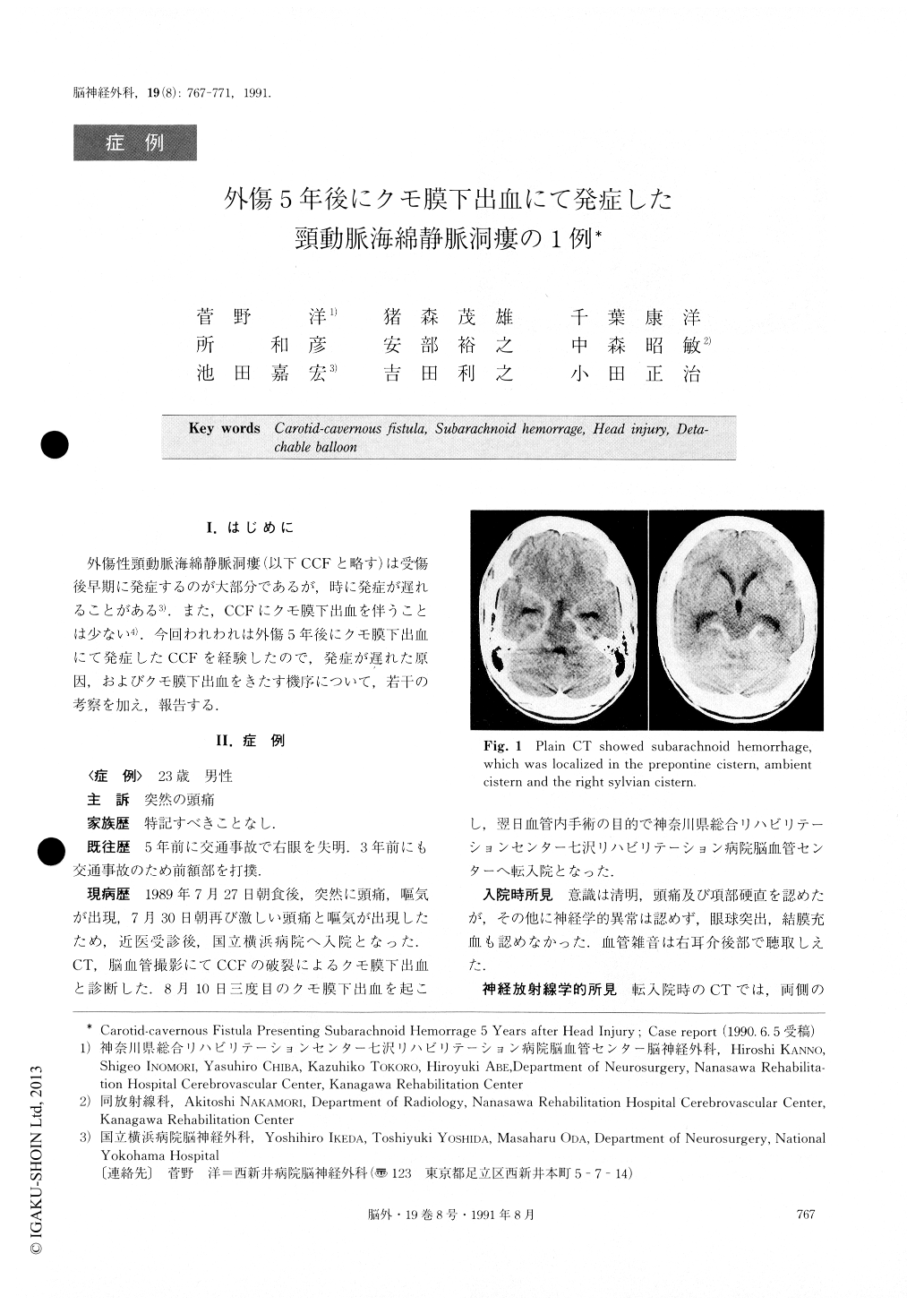
A case of traumatic carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) which presented subarachnoid hemorrhage long after the injury is reported. A 24-year-old male was admitted to the National Yokohama Hospital with complaints of severe headache and nausea. CT scan and cerebral angiography showed subarachnoid hemorrhage due to ruptured CCF. His right visual acuity has disappeared after a traffic accident 5 years before, and he had hit his forehead again 3 years previously. He experienced severe headache twice for 2 weeks after his admission. He was transferred to Kanagawa Rehabilitation Center to be treated with intravascular surgery. Plain CT showed high density areas in the basal cisterns. CT af-ter contrast infusion disclosed a small enlarged high den-sity area in the right cavernous sinus, and showed an enhanced mass lesion in contact with the right ventro-lateral side of the midpons. The right internal carotid angiogram showed high flow CCF, fed only by the in-ternal carotid artery. It drained mainly into the basilar plexus, partially into the basal vein of Rosenthal and the inferior petrosal sinus. The CCF was found at the C4 portion of the right internal carotid artery. CT and the angiogram revealed a part of the CCF developing into a varix in the ventral side of the prepontine cistern.It ruptured and the patient developed subarachnoid hemorrhage 5 years after the head injury. The CCF was intravascularly embolized by a detachable balloon. Early treatment for CCF is necessary to prevent theoccurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhage if a part of the CCF develops into a varix.
It ruptured and the patient developed subarachnoidhemorrhage 5 years after the head injury. The CCFwas intravascularly embohzed by a detachable balloon.Early treatment for CCF is necessary to prevent theoccurrence of subarachlloid hemorrhage if a part of theCCF develops into a varix.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


