Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
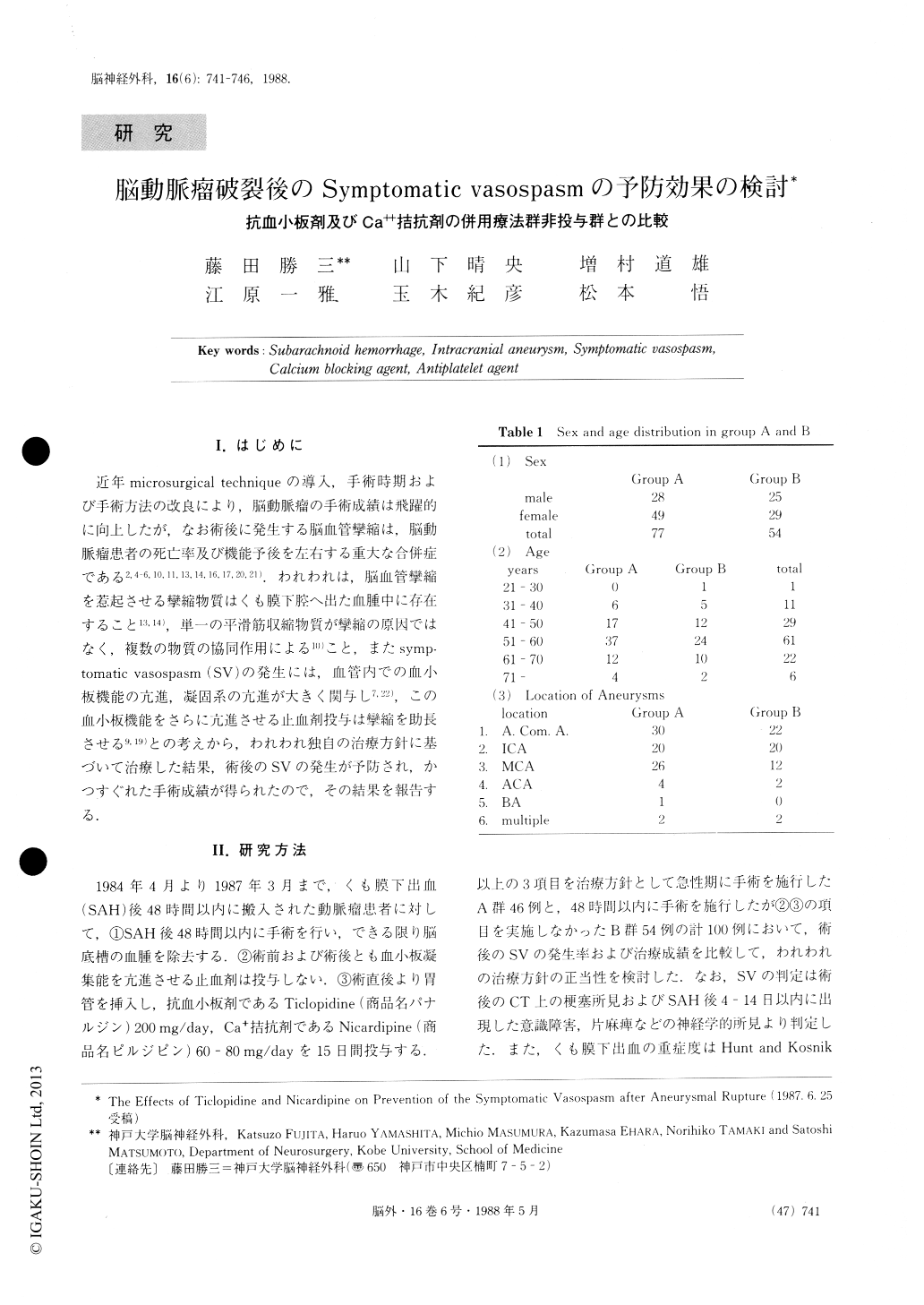
I.はじめに
近年microsurgical techniqueの導入,手術時期および手術方法の改良により,脳動脈瘤の手術成績は飛躍的に向上したが,なお術後に発生する脳血管攣縮は,脳動脈瘤患者の死亡率及び機能予後を左右する重大な合併症である2,4-6,10,11,13,14,16,17,20,21).われわれは,脳血管攣縮を惹起させる攣縮物質はくも膜下腔へ出た血腫中に存在すること13,14),単一の平滑筋収縮物質が攣縮の原因ではなく,複数の物質の協同作用による10)こと,またsymp—tomatic vasospasm(SV)の発生には,血管内での血小板機能の亢進,凝固系の亢進が大きく関与し7,22),この血小板機能をさらに亢進させる止血剤投与は攣縮を助長させる9,19)との考えから,われわれ独自の治療方針に基づいて治療した結果,術後のSVの発生が予防され,かつすぐれた手術成績が得られたので,その結果を報告する.
From the previous reports that the pathogenesis of cerebral vasospasm is most likely multifactorial process and that early removal of the clot may decrease the in-cidence or severity of the ischemic deficits and also that antifibrinolytic therapy increases the incidence and the severity of the symptomatic vasospasm, we attemp-ted at prevention of the symptomatic vasospasm in aneurysmal patients with our own protocol.
One hundred twenty-one consecutive patients with a ruptured aneurysm were operated upon within 98 hoursafter subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


