Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
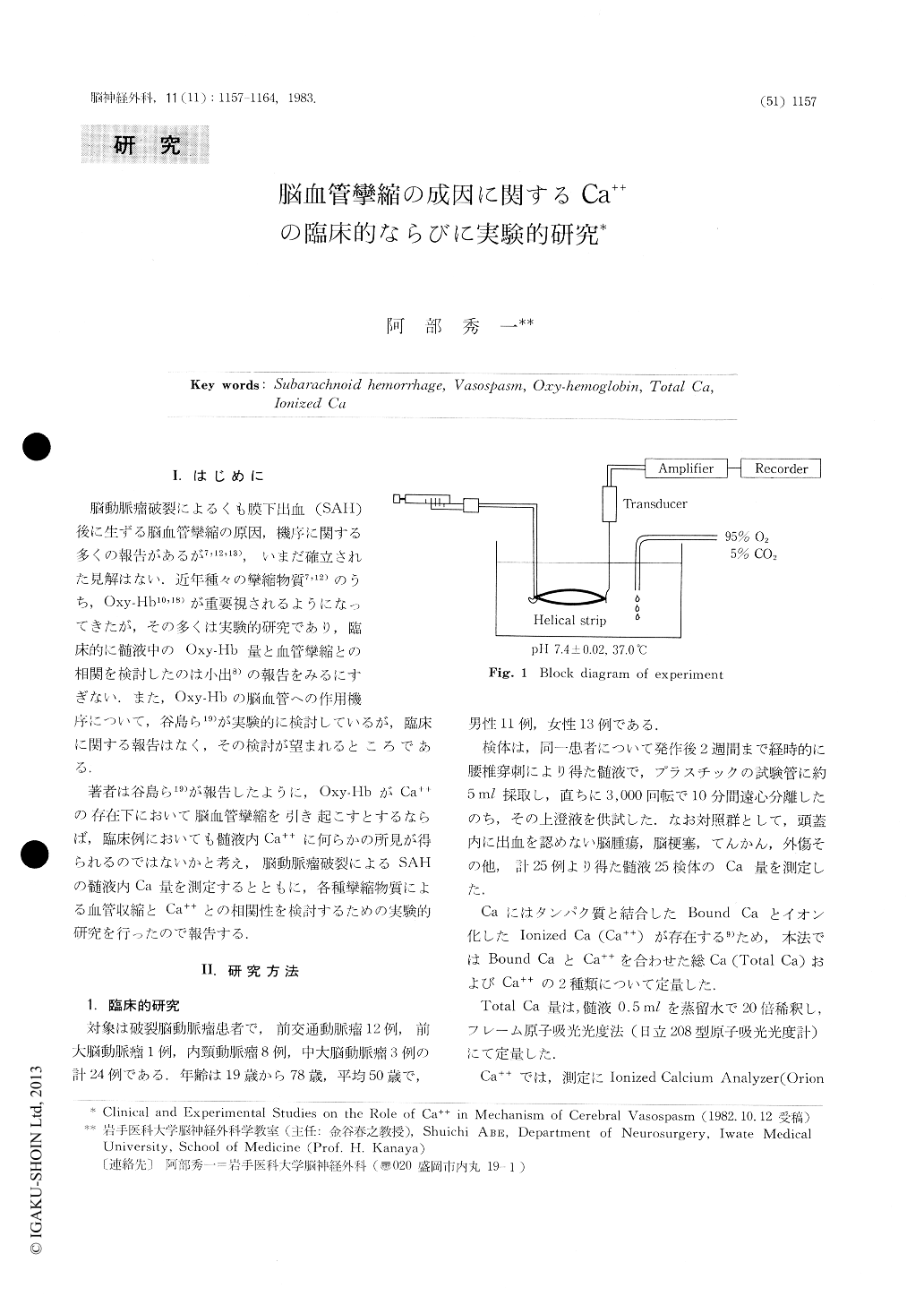
I.はじめに
脳動脈瘤破裂によるくも膜下山血(SAH)後に生ずる脳血管攣縮の原因,機序に関する多くの報告があるが7,12,13),いまだ確立された見解はない.近年種々の攣縮物質7,12)のうち,Oxy-Hb10,18)が重要視されるようになってきたが,その多くは実験的研究であり,臨床的に髄液中のOxy-Hb量と血管攣縮との相関を検討したのは小出8)の報告をみるにすぎない.また,Oxy-Hbの脳血管への作用機序について,谷島ら19)が実験的に検討しているが,臨床に関する報告はなく,その検討が望まれるところである.
著者は谷島ら19)が報告したように,Oxy-HbがCa++の存在下において脳血管攣縮を引き起こすとするならば,臨床例においても髄液内Ca++に何らかの所見が得られるのではないかと考え,脳動脈瘤破裂によるSAHの髄液内Ca量を測定するとともに,各種攣縮物質による血管収縮とCa++との相関性を検討するための実験的研究を行ったので報告する.
Total Ca and Ca++ in cerebrospinal fluid were mea-sured from the patient with subarachnoidal hemorrhagedue to ruptured cerebral aneurysm. Ralationship wasstudied between the values of total Ca and Ca++ andgrades of cerebral vasospasm on cerebral angiograms.Additionally, experimental studies were performedon helical strip of dogs' basilar arteries with constric-table substances such as serotonin (5-HT), prosta-glandin F2α (PGF2α), KC1 and oxy-hemoglobin (Oxy-Hb). Findings were as follows:
Copyright © 1983, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


