Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
頭部外傷,脳血管障害,その他種々の中枢神経障害に伴って急性肺水腫が発生することは古くからよく知られている2,16,17,19).また,その発生機序についても以前から種々検討がなされてきている4,6,7,11).しかしながら,臨床上遭遇する大部分の症例では,原疾患発症前後の身体的要因や治療過程での諸要素等の複雑な因子が,直接,関接の原因と考えられることが多いようである.したがって,Grafら8)の報告のように古典的ないわゆるneurogenic pulmonary edemaと考えられる症例は実際には極めて少ないと思われる.
最近,われわれは重症頭部外傷後,極めて短時期で急性肺水腫の臨床症状を発現した小児例を経験した.本例は厳重な呼吸循環管理にもかかわらず,受傷後約8時間で死亡したが,その臨床経過や検査所見等から頭部外傷に起因したneurogenic pulmonary edemaと考えられるため,症例を呈示し,その発生機序につき若干の考察を加えて報告する.
A case of severe head inury associated with fulminant pulmonary edema considered as neurogenic which developed within short time after the injury was presented.
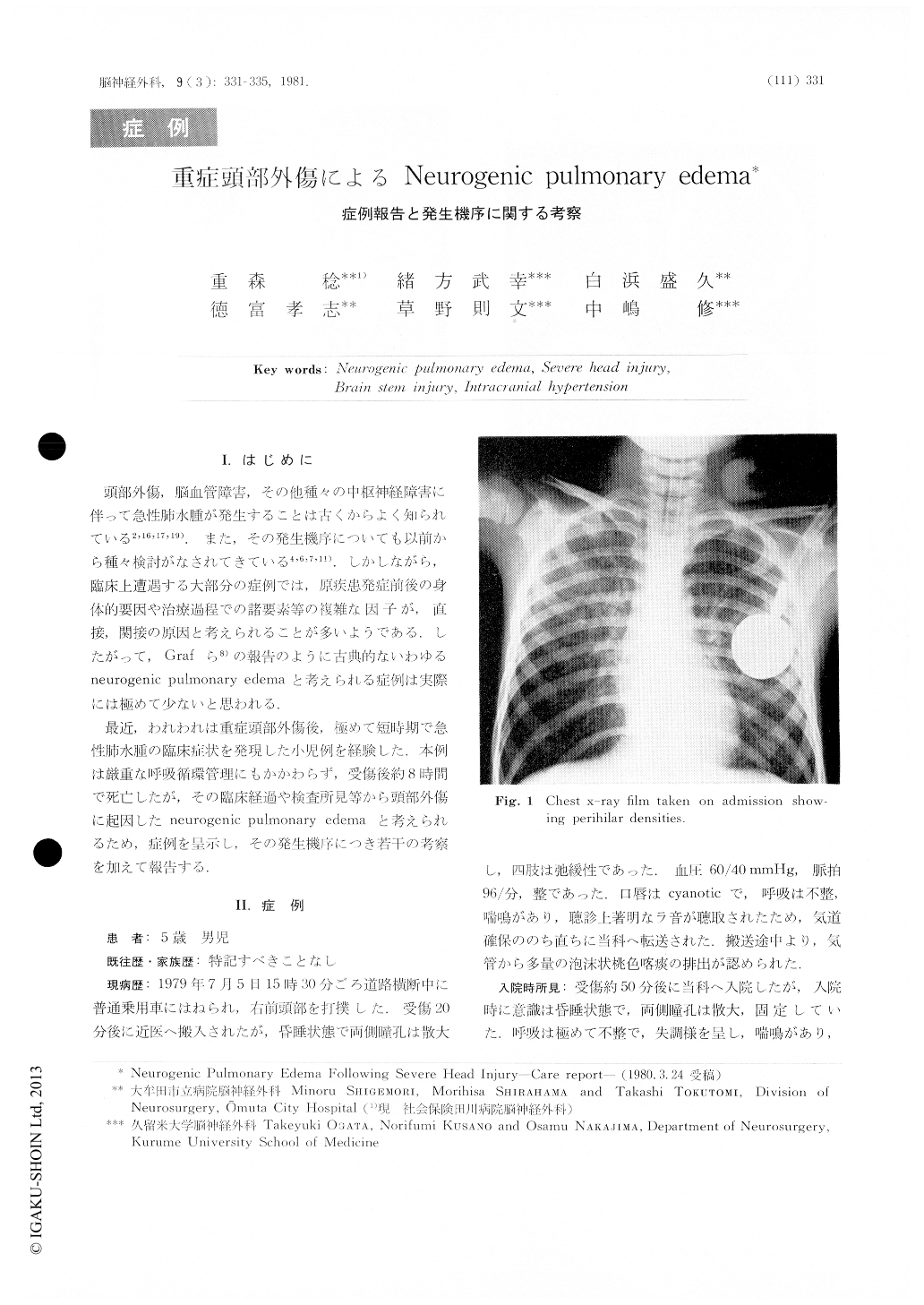
A five-year-old boy who had no previous history of cardiopulmonary disease was struck on his right frontal region by car accident at 15.30PM on July 5 of 1979. Immediately after the impact he lost his consciousness and subsequently transferred to a local hospital where bilateral dilated pupil and flaccid paralysis of the limbs were noted. On transmission of the patient to Omuta City Hospital 30 minutes after the injury, massive foamy fluid was discharged from the tracheal tube.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.