Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
脳の各部は解剖学的にも物質の分布も異り生命に対する比重が異る以上各部で生化学的変化が異る態度をとる事は想像にがたくない。先ず私共は最も実験的に入りやすい皮質の部位差について研究した。
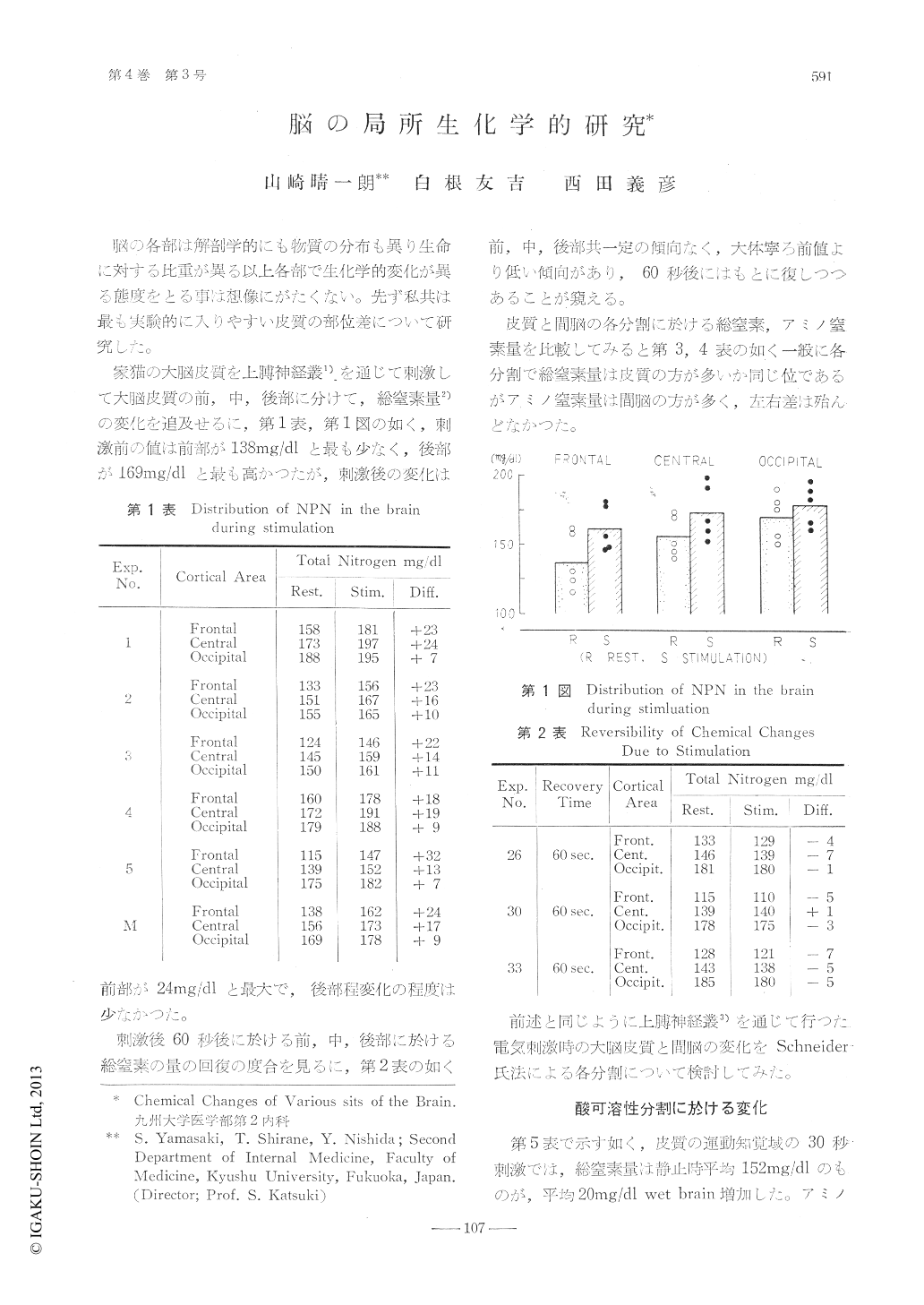
家猫の大脳皮質を上臆神経叢1)を通じて刺激して大脳皮質の前,中,後部に分けて,総窒素量2)の変化を追及せるに,第1表,第1図の如く,刺激前の値は前部が138mg/dlと最も少なく,後部か169mg/dlと最も高かつたが,刺激後の変化は前部が24mg/dl,と最大で,後部程変化の程度は少なかつた。
Chemical changes of frontal, central and occipital regions of the brain cortex were investigatedduring the stimulation of the brachial plexus onthe opposite side with an alternation current of 60cycles for ten sec.
The chemical analysis of the rested brain cortexwere as follows; the total nitrogen of frontalcortex of the acid soluble fraction was the highestin any other cortical regions. However, maximalchanges were observed in the stimulated frontalcortex.
Chemical changes in cat's diencephalon afterelectric stimulation under the same condition werestudied. It was found that the mean level ofamino acid nitrogen in diencephalon was higherthan in the cortex, and chemical changes in diencephalon was less. According to other observations, the variation of total nitrogen in acidsoluble fraction was nearly equal as the sum ofchanged values in lipid fraction and nucleic acidfraction.
Chemical changes in diencephalon by acetyl-choline stimulation were less than in the braincortex.
In the electroencephalogram of cat's brain cortexin which bean sprouts were inplanted for severalclays, the wave of depression was found in theinplanted area.
The chemical changes of the brain cortex wherebean sprouts were found to be quite contrary tothose produced by electric stimulation.
Copyright © 1960, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


