Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
脳(中枢)神経細胞は,再生しにくいので,ひとたび傷害されると変性におちいり,その部の脱落症状をきたす。中枢,末梢をとわず,変性疾患に対しては,一般にその原因や発症の機構が十分に解明されていないことが多く,したがって現在なお保存・対症療法や薬物療法が主な治療手段である。神経難病の一つであるパーキンソン病の治療には,減少したドパミン(DA)を補うためにL-dopaの内服が行なわれている。これは一種の補充療法であるが,無動,固縮などの症状を劇的に軽減させることができる。しかしL-dopa療法も長期にわたると,大量に投与することにともなう副作用や,レセプター感度の変化によるジスキネジーなどが現われ,所期の効果が得られなくなることが多い。近年,変性・脱落してしまった神経細胞を移植により補充して,必要な活性物質を補い,必要な神経回路と機能を再構築しようとする,より積極的なアプローチが試みられるようになってきた。
L-dopa administration is the most favored andeffective treatment of Parkinson's disease. It re-duces the symptoms (akinesia, rigidity, tremor…), and allows patients to lead an ordinary life. However, when L-dopa treatment is extended over long periods, such as ten years, unfavorable dyskinesia or severe gastrointestinal side effects often appear. In recent years, brain transplantation of dopamine (DA) secreting cells has become one of the promising methods for repairing disturbances in DA metabolism both in basic neuroscience research as well as in clinical practice.
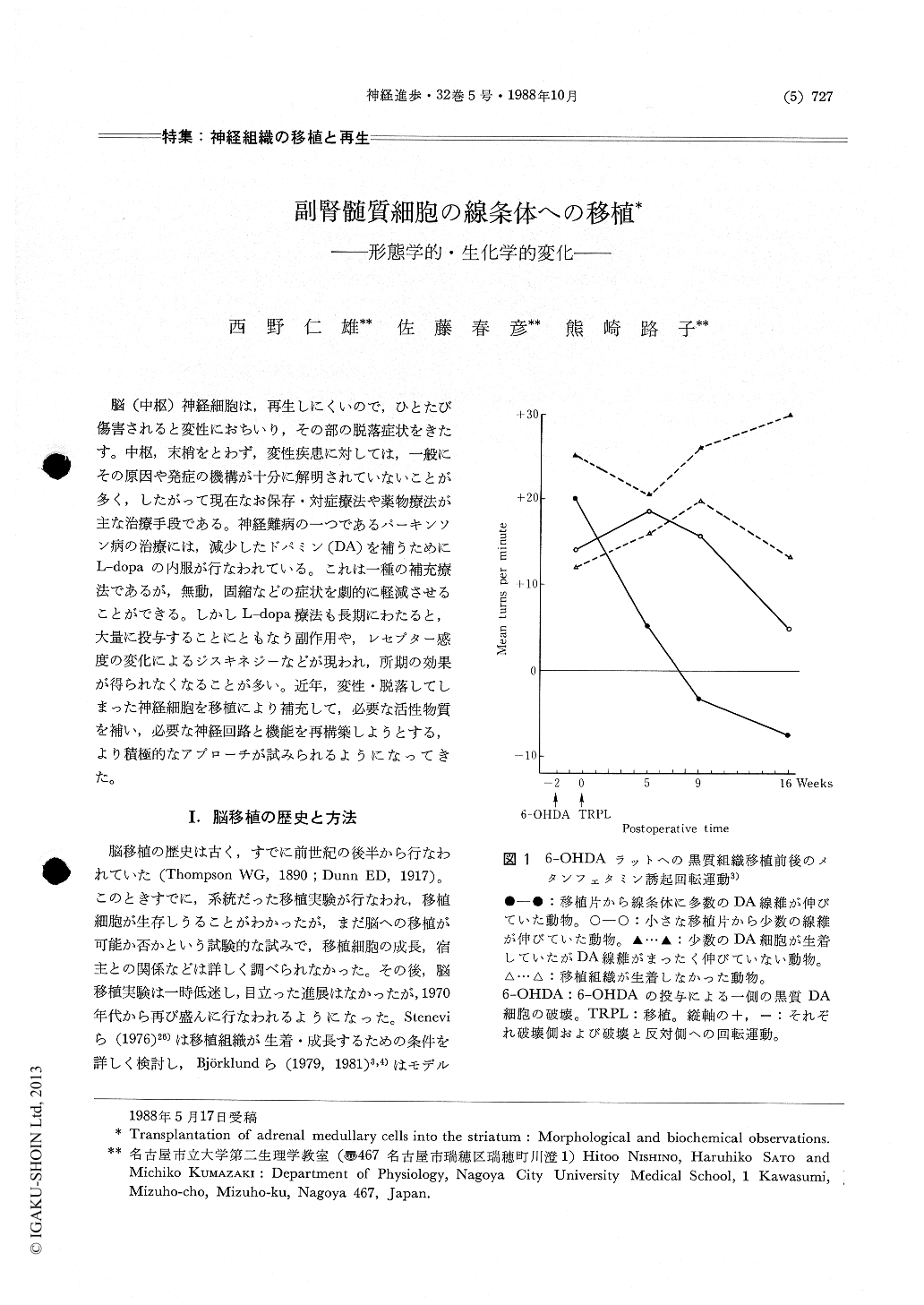
Brain transplantation experiments had already been performed in the late 19 th century, and became very popular in the 1970's. In the treatment of animal models of Parkinson's disease transplantation of nigral DA cells, adrenal medulla, sympathetic ganglia or PC-12 cells is performed. Adrenal medulla, when transplanted into the eye chamber, chromaffin cells extend processes inside of the graft and innervate the cografted CNS tissue such as cerebral cortex. When grafted in the cerebral ventricle, catecholamine-fluorescent cells survive and extend a limited number of short processes into the caudate.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


