Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
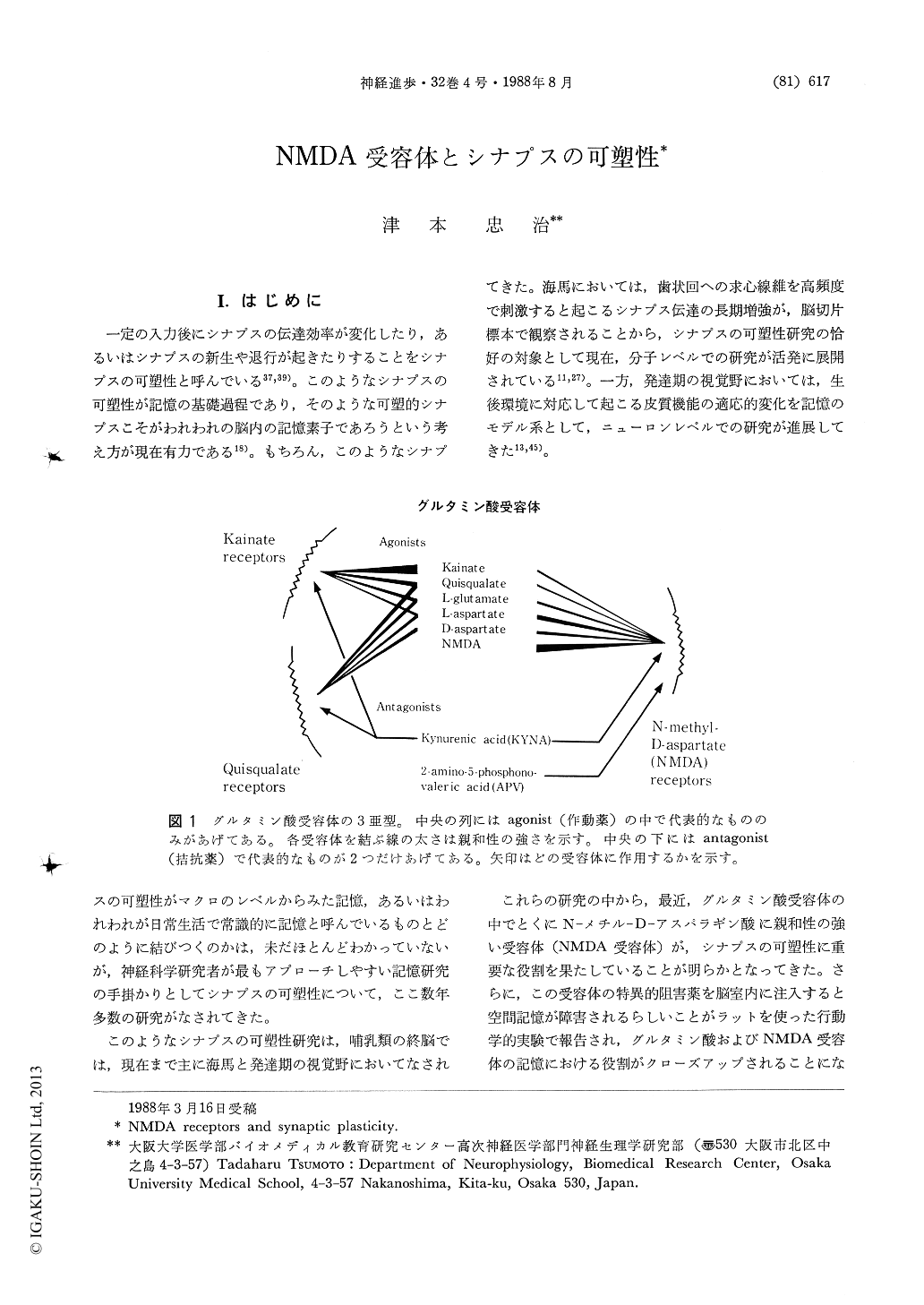
一定の入力後にシナプスの伝達効率が変化したり,あるいはシナプスの新生や退行が起きたりすることをシナプスの可塑性と呼んでいる37,39)。このようなシナプスの可塑性が記憶の基礎過程であり,そのような可塑的シナプスこそがわれわれの脳内の記憶素子であろうという考え方が現在有力である18)。もちろん,このようなシナプスの可塑性がマクロのレベルからみた記憶,あるいはわれわれが日常生活で常識的に記憶と呼んでいるものとどのように結びつくのかは,未だほとんどわかっていないが,神経科学研究者が最もアプローチしやすい記憶研究の手掛かりとしてシナプスの可塑性について,ここ数年多数の研究がなされてきた。
このようなシナプスの可塑性研究は,哺乳類の終脳では,現在まで主に海馬と発達期の視覚野においてなされてきた。海馬においては,歯状回への求心線維を高頻度で刺激すると起こるシナプス伝達の長期増強が,脳切片標本で観察されることから,シナプスの可塑性研究の恰好の対象として現在,分子レベルでの研究が活発に展開されている11,27)。一方,発達期の視覚野においては,生後環境に対応して起こる皮質機能の適応的変化を記憶のモデル系として,ニューロンレベルでの研究が進展してきた13,45)。
In this review I described some evidence indi-cating a role of a type of excitatory amino acid receptors, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) recep-tors, in synaptic plasticity which has been considered as a neuronal basis of memory pro-cesses in the brain. Among the three types of excitatory amino acid receptors, quisqualate and kainate receptors (non-NMDA receptors) are implicated in the mediation of afferent synaptictransmission at low frequencies in the hippo-campus and visual cortex, whereas NMDA recep-tors are suggested to be involved in synaptic plasticity in the developing visual cortex on the basis of the following three findings ; 1) during the "critical period" of postnatal development when synaptic plasticity is at the highest level in the kitten visual cortex, a selective NMDA antagonist, D, L-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV), blocks visual responses of cortical neurons more effectively than it does in the adult, 2) continuous intracortical infusion of APV renders visual cortical cells aplastic so that they become resistant to the effects of monocular visual depri-vation, and 3) the induction of long-term potentia-tion (LTP) of synaptic efficacy, which is a form of synaptic plasticity seen in slice preparations of the visual cortex of rat pups, is blocked by an application of APV through the perfusion medium.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


