Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
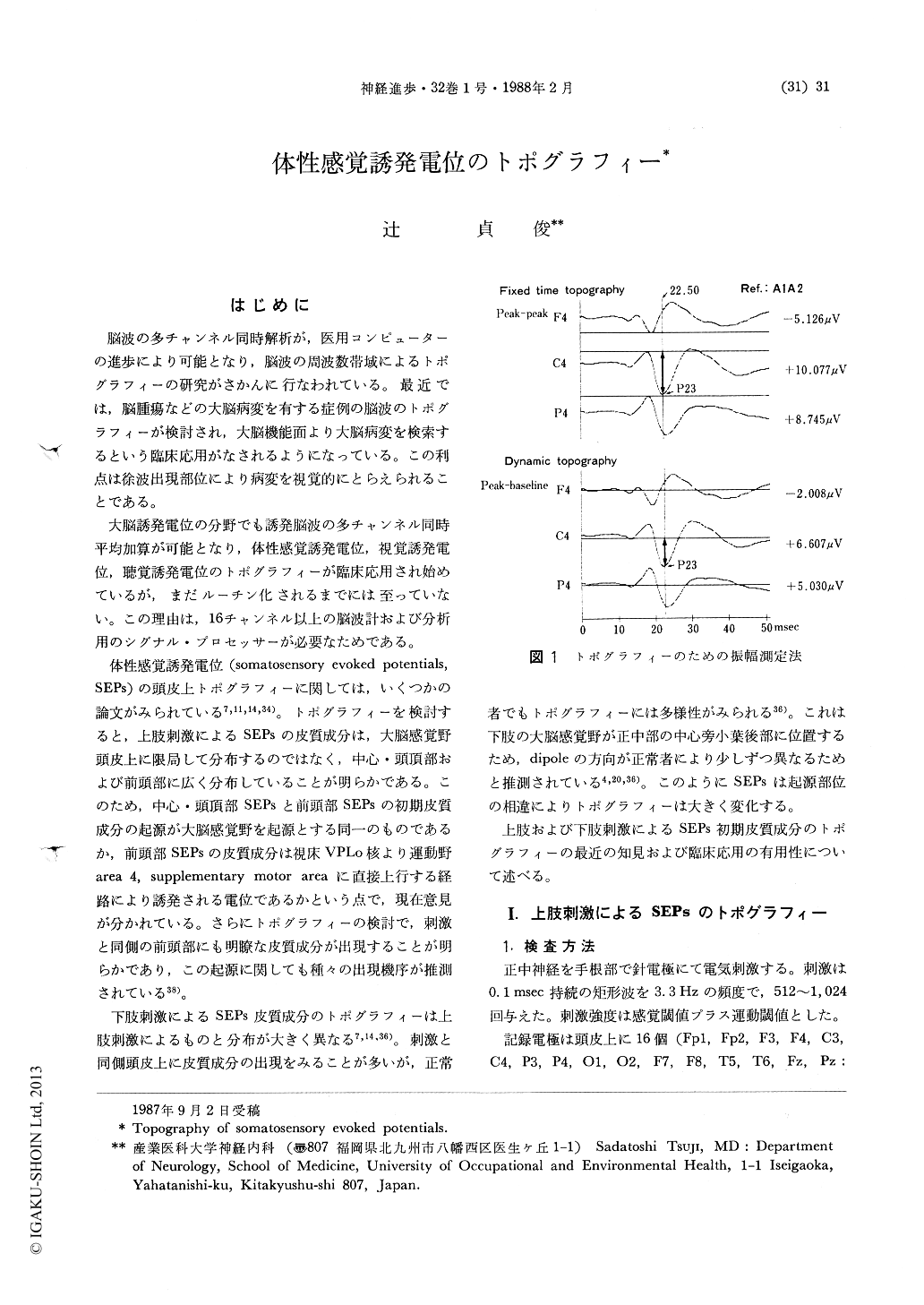
脳波の多チャンネル同時解析が,医用コンピューターの進歩により可能となり,脳波の周波数帯域によるトポグラフィーの研究がさかんに行なわれている。最近では,脳腫瘍などの大脳病変を有する症例の脳波のトポグラフィーが検討され,大脳機能面より大脳病変を検索するという臨床応用がなされるようになっている。この利点は徐波出現部位により病変を視覚的にとらえられることである。
大脳誘発電位の分野でも誘発脳波の多チャンネル同時平均加算が可能となり,体性感覚誘発電位,視覚誘発電位,聴覚誘発電位のトポグラフィーが臨床応用され始めているが,まだルーチン化されるまでには至っていない。この理由は,16チャンネル以上の脳波計および分析用のシグナル・プロセッサーが必要なためである。
Topographies and distributions of SEPs to median and posterior tibial nerve stimulation were studied in normal controls and patients with sensory and motor disturbance. SEPs recorded from the right centro-parieto-temporal electrodes to left median nerve stimulation were composed of 3 early negative (N16, N20, N30) and 3 early positive components (P13, P23, P25), whereas those recorded from both frontal electrodes dis-closed 2 early negativities (N16, N26) and 2 early positivities (P13, P20). N20 and P20 reversed across the rolandic fissure with no significant difference in their peak latencies. N20 and P20 had a dipolar distribution with a N20 at con-tralateral central and posterior areas to the stimulation site and P20 at both frontal areas in topography. On the other hand, P23 was ap-peared at first in the contralateral central area and then P25 at contralateral posterior areas and N26 at both frontal areas respectively in dynamic topography.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


