Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
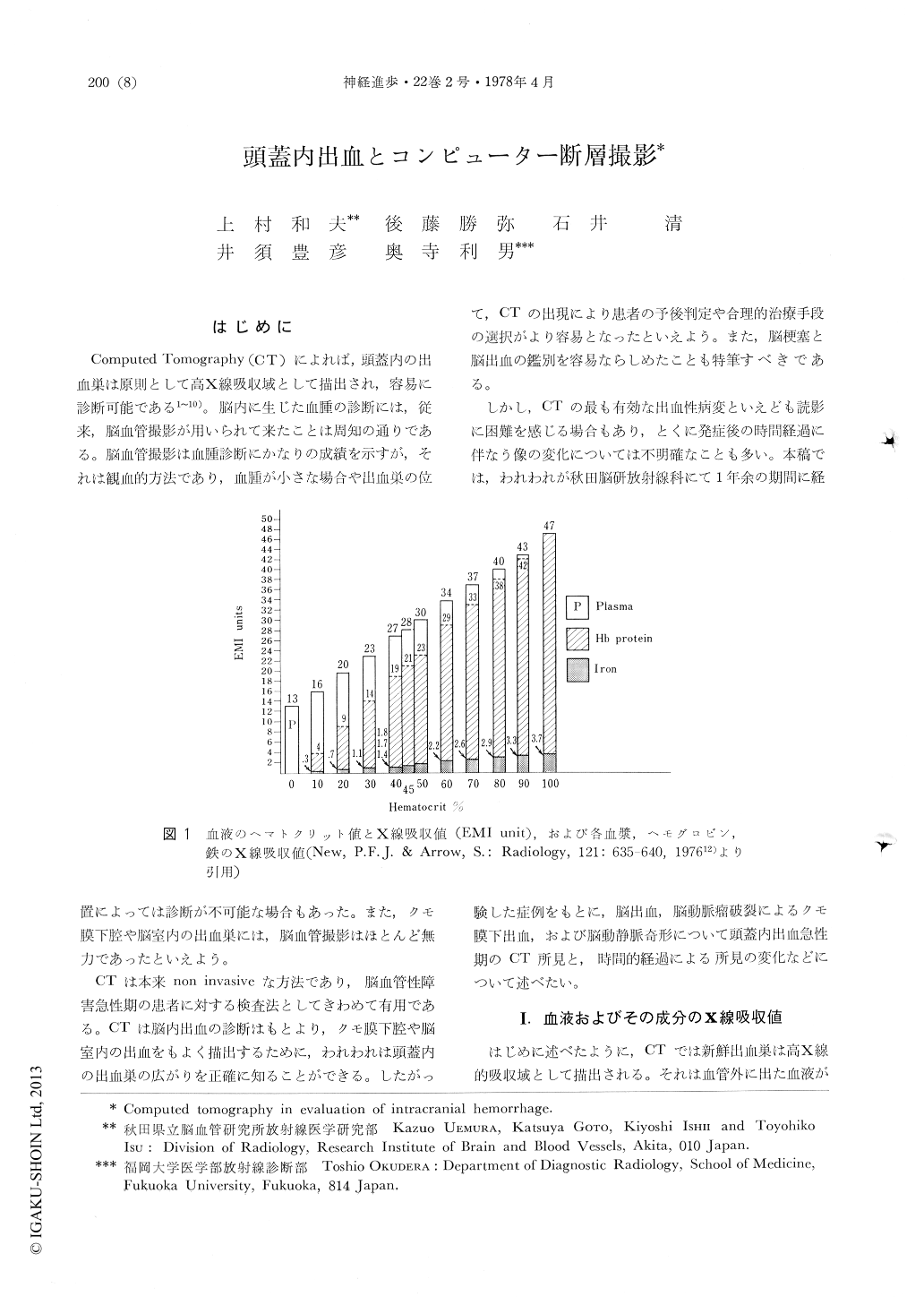
はじめに
Computed Tomography(CT)によれば,頭蓋内の出血巣は原則として高X線吸収域として描出され,容易に診断可能である1〜10)。脳内に生じた血腫の診断には,従来,脳血管撮影が用いられて来たことは周知の通りである。脳血管撮影は血腫診断にかなりの成績を示すが,それは観血的方法であり,血腫が小さな場合や出血巣の位置によっては診断が不可能な場合もあった。また,クモ膜下腔や脳室内の出血巣には,脳血管撮影はほとんど無力であったといえよう。
CTは本来non invasiveな力法であり,脳血管性障害急性期の患者に対する検査法としてぎわめて有用である。CTは脳内出血の診断はもとより,クモ膜下腔や脳室内の出血をもよく描出するために,われわれは頭蓋内の出血巣の広がりを正確に知ることができる。したがって,CTの出現により患者の予後判定や合理的治療手段の選択がより容易となったといえよう。また,脳梗塞と脳出血の鑑別を容易ならしめたことも特筆すべきである。
Abstract
Computerized axial tomography is overwhelmingly superior to any other neuroradiological examinations in the diagnosis of intracranial hemorrhage and in the evaluation of its precise spatial distribution. Especially, CT was found to be extremely informative in demonstration of intraventricular, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and brainstem and cerebellar hemorrhages too.
During past fourteen months, at Research Institute of Brain and Blood Vessels, Akita, CT studies were performed on 138 cases of intracerebral hemorrhages, 69 cases of subarachnoid hemorrhages and cases of arterio-venous malformations.
Copyright © 1978, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


