Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
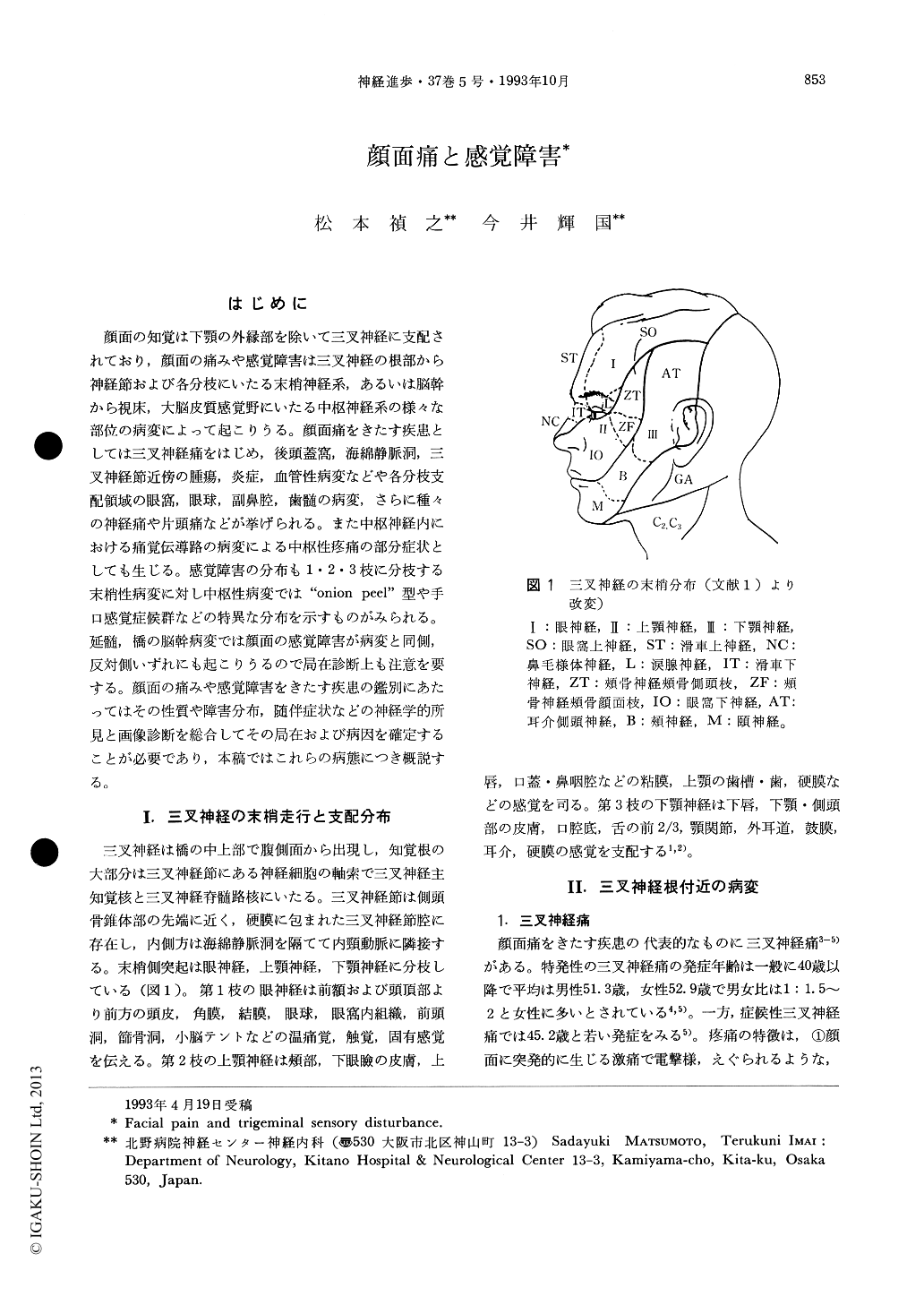
顔面の知覚は下顎の外縁部を除いて三叉神経に支配されており,顔面の痛みや感覚障害は三叉神経の根部から神経節および各分枝にいたる末梢神経系,あるいは脳幹から視床,大脳皮質感覚野にいたる中枢神経系の様々な部位の病変によって起こりうる。顔面痛をきたす疾患としては三叉神経痛をはじめ,後頭蓋窩,海綿静脈洞,三叉神経節近傍の腫瘍,炎症,血管性病変などや各分枝支配領域の眼窩,眼球,副鼻腔,歯髄の病変,さらに種々の神経痛や片頭痛などが挙げられる。また中枢神経内における痛覚伝導路の病変による中枢性疼痛の部分症状としても生じる。感覚障害の分布も1・2・3枝に分枝する末梢性病変に対し中枢性病変では“onion peel”型や手口感覚症候群などの特異な分布を示すものがみられる。延髄,橋の脳幹病変では顔面の感覚障害が病変と同側,反対側いずれにも起こりうるので局在診断上も注意を要する。顔面の痛みや感覚障害をきたす疾患の鑑別にあたってはその性質や障害分布,随伴症状などの神経学的所見と画像診断を総合してその局在および病因を確定することが必要であり,本稿ではこれらの病態につき概説する。
Facial pain and sensory disturbance are caused by various lesions situated along the peripheral and central pathway of the trigeminal sensory system. Trigeminal neuralgia is a well known disease, showing paroxysmal pain, frequently triggered by sensory stimulus and lasts only seconds. The cause of trigeminal neuralgia is probably multifactorial. Compression of the trigeminal root usually by tortuous arteries, rarely by veins or tumors, are frequently found. Microvascular decompression showed excellent pain relief in many patients. Lesions of the skull base such as metastatic tumor and carcino-matous leptomeningeal lesions, leukemic or lymphomatous infiltration and meningitis can cause trige-minal sensory defect. Lesions of the middle cranial fossa between trigeminal ganglion and the internal carotid artery may show Raeder's syndrome composed of trigeminal dysfunction and incomplete Hor-ner's syndrome. Damage to the trigeminal nerve and abducens nerver (Gradenigo syndrome) is due to a lesion of the apex of the temporal bone. Trigeminal sensory dysfunction and ophthalmoplegia are caused by lesions of the superior orbital fissure, cavernous sinus or orbital apex. Tumors, aneurysm and infections are responsible for these syndromes. Tolosa-Hunt syndrome, which responds well to steroid therapy, is a granulomatous inflammation showing cavernous sinus syndrome. Peripheral bran-ches of the trigeminal nerve are involved in herpes zoster and lesions of the orbit, nasal sinus, teeth and temporomandibular joint. Isolated mental neuropathy (numb chin syndrome) and isolated infraorbital nerve (numb cheek syndrome) are usually due to malignant neoplastic lesions. Isolated trigeminal sensory neuropathy is occasionally associated with mixed connective tissue disease and various other connective tissue diseases.
Copyright © 1993, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


