Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
細胞間の情報を担うホルモン,神経伝達物質,細胞増殖分化因子など(アゴニスト)の多くは,細胞膜上の特異的な結合部位(受容体)に結合して,その情報を細胞内に伝達する。アゴニストが受容体に結合すると,その情報は細胞膜で種々の様式で変換され,細胞内に伝達されるが,受容体と細胞内での新たな情報を生み出す効果器(エフェクター)系との間には,多くの場合情報の増幅・変換因子としてGTPと結合するGタンパク質が介在している。
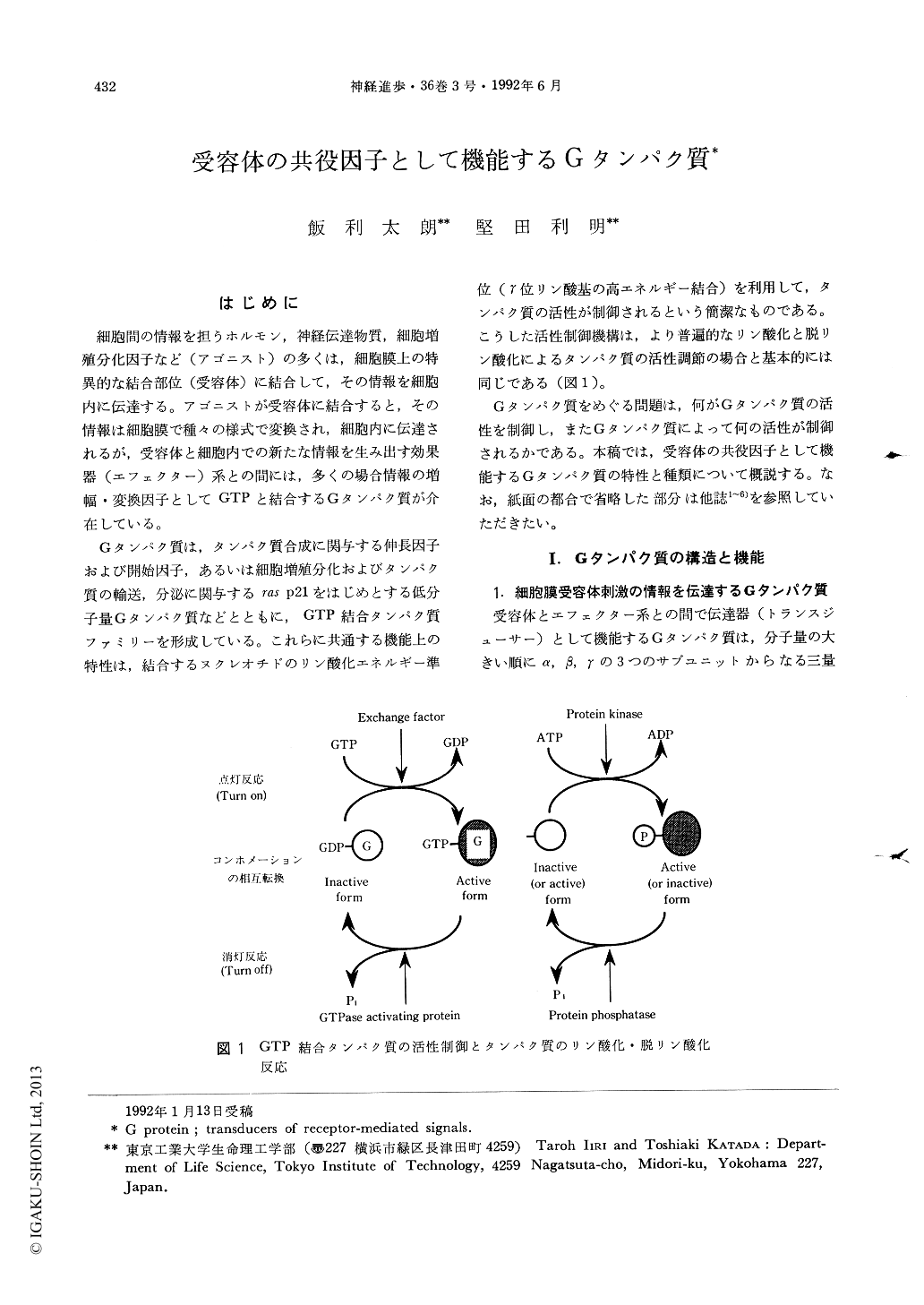
Gタンパク質は,タンパク質合成に関与する伸長因子および開始因子,あるいは細胞増殖分化およびタンパク質の輸送,分泌に関与するras p21をはじめとする低分子量Gタンパク質などとともに,GTP結合タンパク質ファミリーを形成している。これらに共通する機能上の特性は,結合するヌクレオチドのリン酸化エネルギー準位(γ位リン酸基の高エネルギー結合)を利用して,タンパク質の活性が制御されるという簡潔なものである。こうした活性制御機構は,より普遍的なリン酸化と脱リン酸化によるタンパク質の活性調節の場合と基本的には同じである(図1)。
A family of αβγ-trimeric G proteins carries a variety of extracellular signals (neurotransmitters, and growth factors) from membrane-bound receptors to effectors such as enzymes and ion channels. G protein as the signal transducers have the following unique properties.
1. Amplification of signals
Function of G proteins is regulated cyclically by, a) dissociation of bound GDP from α-subunits, b) association of GTP with α-subunits, and c) hydrolysis of GTP to GDP and Pi. The agonist-recep tor complex stimulates formation of GTP-G, which in turn activates the appropriate effectors; the activation persists until G hydrolyzes the bonnd GTP. There is a period longer than the duration of the agonist-receptor complex in the active form of GTP-G due to a low rate of GTPase activity.
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


