Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
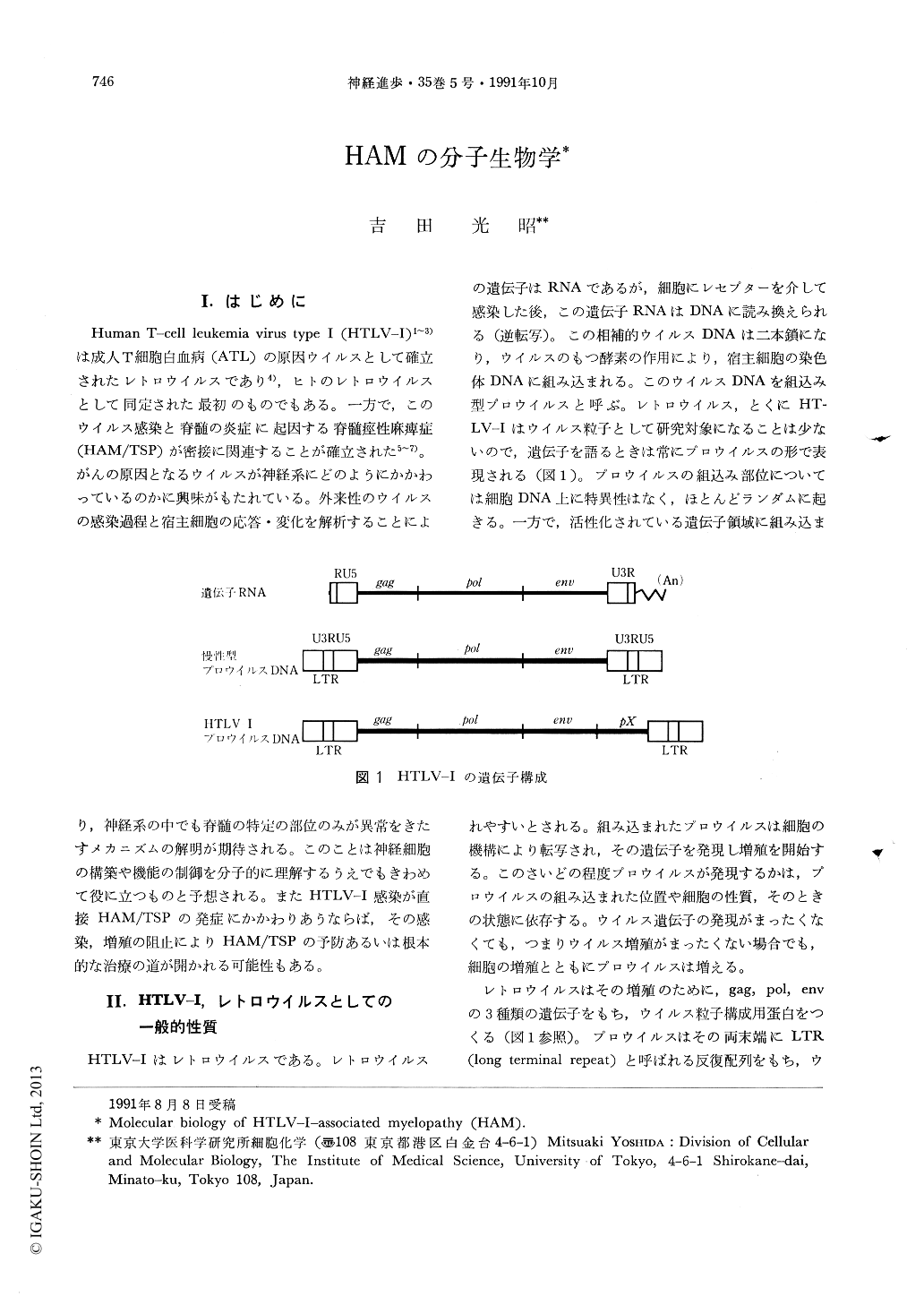
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I(HTLV-I)1~3)は成人T細胞白血病(ATL)の原因ウイルスとして確立されたレトロウイルスであり4),ヒトのレトロウイルスとして同定された最初のものでもある。一方で,このウイルス感染と脊髄の炎症に起因する脊髄痙性麻痺症(HAM/TSP)が密接に関連することが確立された5~7)。がんの原因となるウイルスが神経系にどのようにかかわっているのかに興味がもたれている。外来性のウイルスの感染過程と宿主細胞の応答・変化を解析することにより,神経系の中でも脊髄の特定の部位のみが異常をきたすメカニズムの解明が期待される。このことは神経細胞の構築や機能の制御を分子的に理解するうえでもきわめて役に立つものと予想される。またHTLV-I感染が直接HAM/TSPの発症にかかわりあうならば,その感染,増殖の阻止によりHAM/TSPの予防あるいは根本的な治療の道が開かれる可能性もある。
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) is associated with a slowly progressive myelopathy, HAM/TSP. The viral strains isolated from lymphocytes in peripheral blood or cerebrospinal fluid of HAM/TSP patients were shown to be the same strain as those isolated from adult T-cell leukemia patients. Infection of HTLV-I integrates its proviruses at random sites on host chromosomal DNA, thus random integration was reported in asymptomatic HTLV-I carriers, but the monoclonalintegration was found in patients with adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) including smoldering, chronic and acute states. In patients with HAM/TSP, the random integration was observed indicating that the HAM/TSP patients are in the carrier state in HTLV-I infection. However, much more efficient replication of HTLV-I was detected in 85% of HAM/TSP patients and also among carriers in family of the patients: In most patients and their family, HTLV-I proviral DNA was detected by the standard Southern blotting, whereas was not in most of asymptomatic HTLV-I carriers. Thus it was concluded that certain host factor(s) is associated with both the efficient replication of HTLV-I and development of HAM/TSP. On the other hand, about 2% HAM/TSP patients were found to concurrent ATL, suggesting that the host factor(s) associated with HAM/TSP does not restrict ATL development. Possibility of either mechanism of indirect immunological response and direct infection to spinal cord was discussed.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


