Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
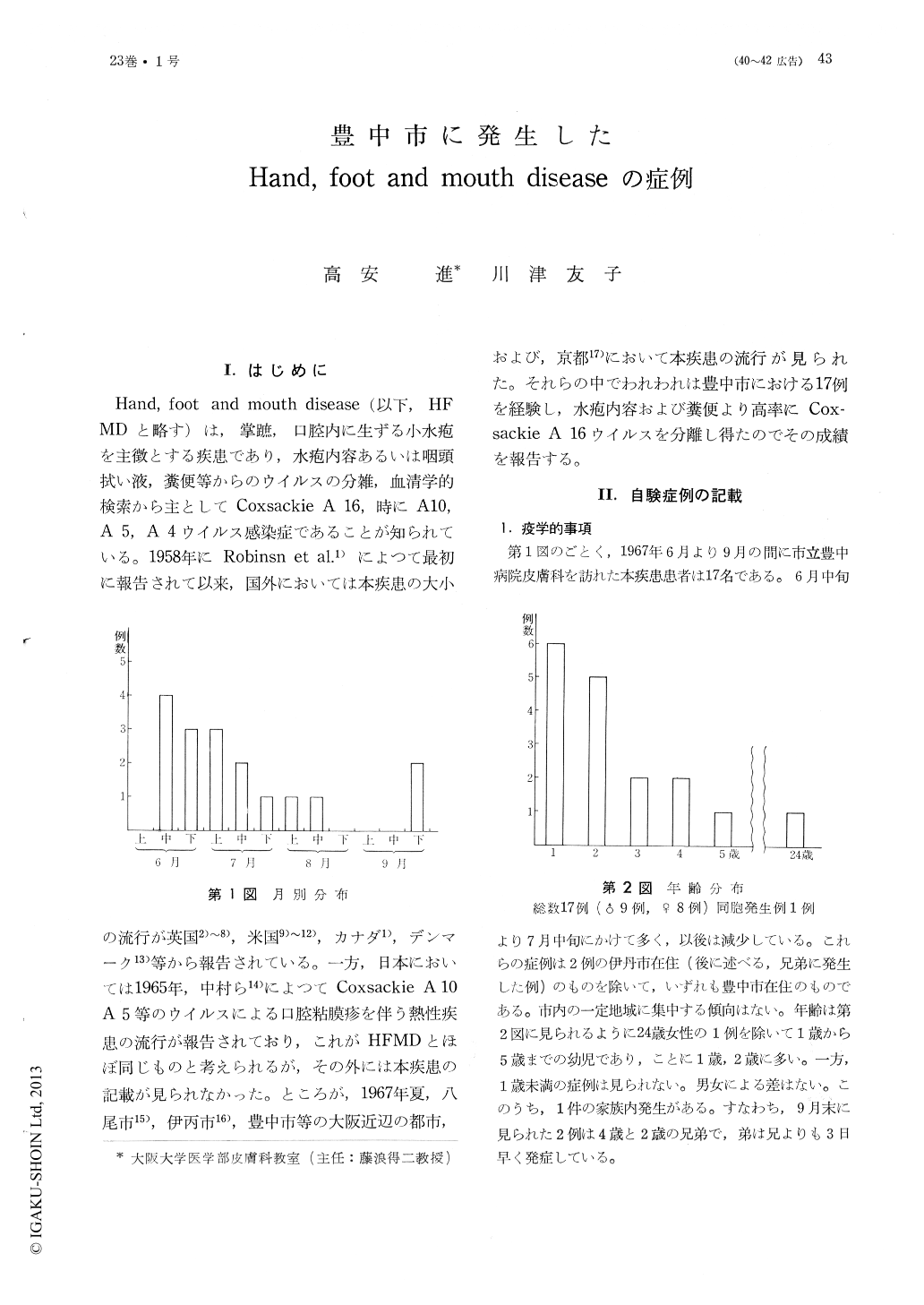
I.はじめに
Hand, foot and mouth disease (以下,HFMDと略す)は,掌蹠,口腔内に生ずる小水疱を主徴とする疾患であり,水疱内容あるいは咽頭拭い液,糞便等からのウイルスの分雑,血清学的検索から主としてCoxsackie A 16,時にA 10,A 5, A 4ウイルス感染症であることが知られている。1958年にRobinsn et al.1)によつて最初に報告されて以来,国外においては本疾患の大小の流行が英国2)〜8),米国9)〜12),カナダ1),デンマーク13)等から報告されている。一方,日本においては1965年,中村ら14)によつてCoxsackie A 10A 5等のウイルスによる口腔粘膜疹を伴う熱性疾患の流行が報告されており,これがHFMDとほぼ同じものと考えられるが,その外には本疾患の記載が見られなかった。ところが,1967年夏,八尾市15),伊丙市16),豊中市等の大阪近辺の都市,および,京都17)において本疾患の流行が見られた。それらの中でわれわれは豊中市における17例を経験し,水疱内容および糞便より高率にCox—sackie A 16ウイルスを分離し得たのでその成績を報告する。
During the summer in 1967, seventeen patients of hand, foot, and mouth disease were odservedin Toyonaka City. Except for one adult woman, the patients were children between one and five year-old. They had several ulcers in the mouth and characterestic vesicles which were oval and ran parallel to the skin lines of palms and soles. In adition, some patients had small papules or vesicles on the buttocks, knies and limbs. The illness was mild and self-limiting.
Histologically, the exanthem on the palms was an intraepidermal vesicle like other viral vesi-cular disease.
Eight virus strains were isolated, using suckling mice, from the vesicle fluid in six and faeces in two cases. Seven strains were identified as Coxsackie A 16 by neutralizing test and one is under examination. No cytopathogenic effect was detected in the tissue cultures of FL cells.
Copyright © 1969, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


