Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
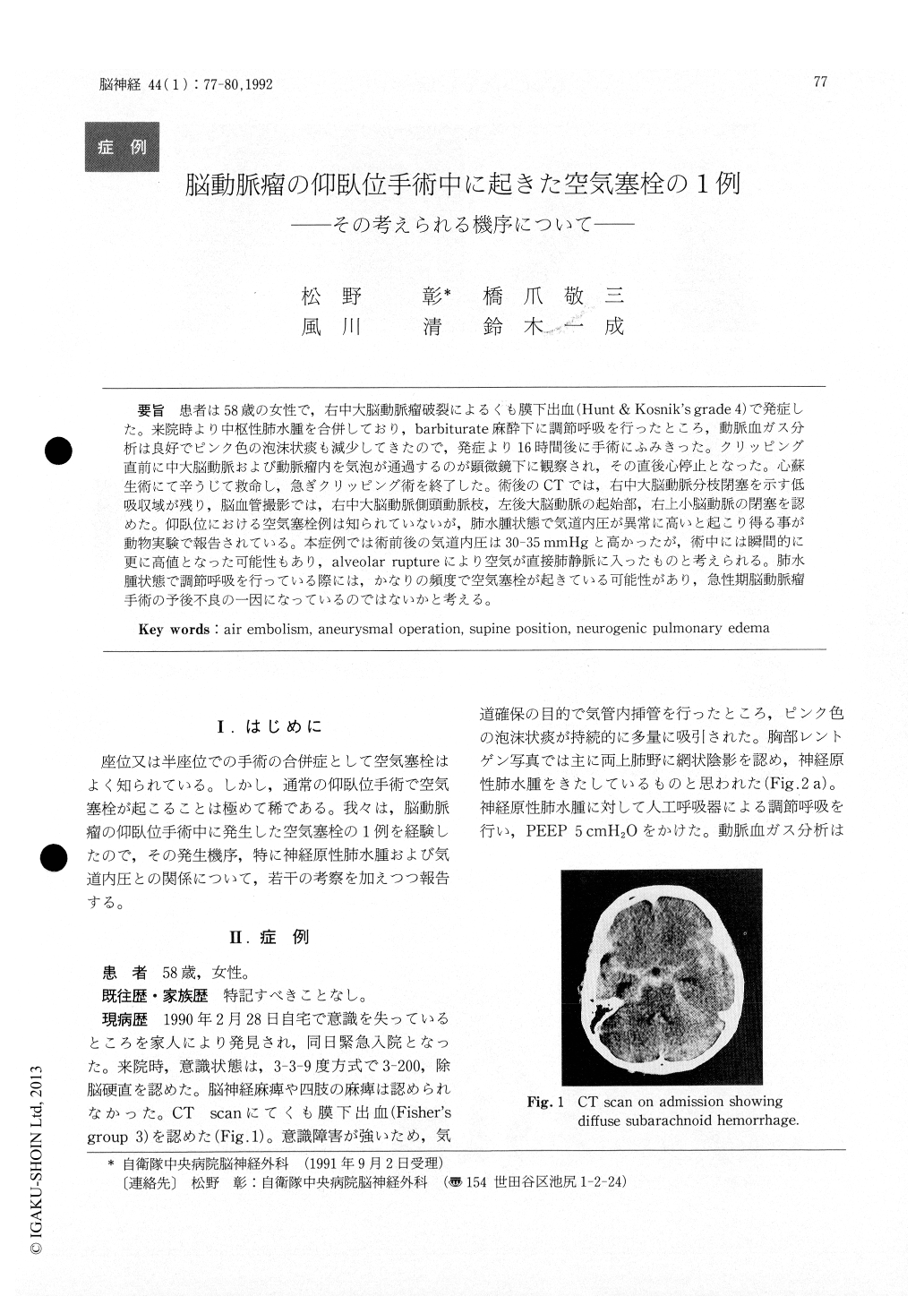
患者は58歳の女性で,右中大脳動脈瘤破裂によるくも膜下出血(Hunt&Kosnik's grade4)で発症した。来院時より中枢性肺水腫を合併しており,barbiturate麻酔下に調節呼吸を行ったところ,動脈血ガス分析は良好でピンク色の泡沫状痰も減少してきたので,発症より16時間後に手術にふみきった。クリッピング直前に中大脳動脈および動脈瘤内を気泡が通過するのが顕微鏡下に観察され,その直後心停止となった。心蘇生術にて辛うじて救命し,急ぎクリッピング術を終了した。術後のCTでは,右中大脳動脈分枝閉塞を示す低吸収域が残り,脳血管撮影では,右中大脳動脈側頭動脈枝,左後大脳動脈の起始部,右上小脳動脈の閉塞を認めた。仰臥位における空気塞栓例は知られていないが,肺水腫状態で気道内圧が異常に高いと起こり得る事が動物実験で報告されている。本症例では術前後の気道内圧は30-35mmHgと高かったが,術中には瞬間的に更に高値となった可能性もあり,alveolar ruptureにより空気が直接肺静脈に入ったものと考えられる。肺水腫状態で調節呼吸を行っている際には,かなりの頻度で空気塞栓が起きている可能性があり,急性期脳動脈瘤手術の予後不良の一因になっているのではないかと考える。
The occurrence of air embolism in supine position operation is extremely rare. We reported a case of air embolism during the operation of a ruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysm in supine position.
A 58-year-old woman was admitted to our hospi-tal in semicomatous state. A CT scan revealed diffuse subrachnoid hemorrhage. Cerebral angio-gram showed a middle cerebral artery aneurysm. Massive pinkish foamy sputum and butterfly shadow on chest x-ray strongly suggested an associ-ation of neurogenic pulmonary edema (NPE) . Babiturate therapy and controlled ventilation with positive end-expiratory pressure (5cmH2O) were started. Her airway pressure was about 35cmH2O. Decrease of pinkish foamy sputum and an improve-ment of chest x-ray findings on the next day encour-aged us to perform a clipping operation. Just before a clip application, air bubbles were observed to pass through the middle cerebral artery under the micro-scope. Subsequently cardiac standstill was brought out. Fortunately, she was ressucitated, and a clip application was finished. A postoperative CT scan revealed an infarction in the middle cerebral artery area. A postoperative cerebral angiogram showed occlusion of a temporal branch of the right middle cerebral artery, P1 portion of the left posterior cerebral artery, and the right superior cerebellar artery.
We speculated that high endotracheal pressure brought out pulmonary alveolar rupture, and in spite of supine position operation massive air, which flowed into systemic circulation from ruptured alveoli, caused cerebral infarction and cardiac arrest.
We consider that unrecognized air embolism might be the one of the factors influencing the prognosis of severe subarachnoid hemorrhage, espe-cially in the cases associated with neurogenic pul-monary edema.
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


