Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
日本外傷データバンクによると胸部外傷の症例数は下肢の損傷・頭部損傷に次いで3番目に多く,全体の26%を占める(2019~2021年)1).また,中等症以上が76%を占め,もっとも重症度の高い身体部位である.国内では頻度的には交通事故・転倒・墜落が多いため80%以上が鈍的外傷であるが,刺創や銃創による心肺損傷はただちに生命の危険が及ぶ重篤な状態が多い.
A man in his 50s was stabbed deeply in the back with a knife and brought to the emergency room. He was found to have a significant left hemopneumothorax. He was planned to undergo hemostatic surgery under general anesthesia. However, shortly after the change in a right lateral decubitus position, he experienced ventricular fibrillation. Hemostasis of the intercostal artery injury, the source of bleeding, and suture of the injured visceral pleura were performed under extracorporeal membrance oxgenation (ECMO). Although sinus rhythm was resumed, when positive pressure ventilation was applied to the left lung for an air leak test, ST elevation on the electrocardiogram and loss of arterial pressure occurred. A transesophageal echo revealed air accumulation in the left ventricle. It was determined that air had entered the damaged pulmonary vein from the injured bronchi due to the stab wound, leading to left ventricular puncture decompression and lower left lower lobectomy. Subsequently, his circulatory status stabilized, and ECMO was weaned off. He recovered without postoperative neurological deficits postoperatively. The mortality rate for chest trauma with systemic air embolism is very high. In cases of deep lung stab wounds, there is a possibility of systemic air embolism, so treatment should consider control of airway and vascular disruption during surgery.
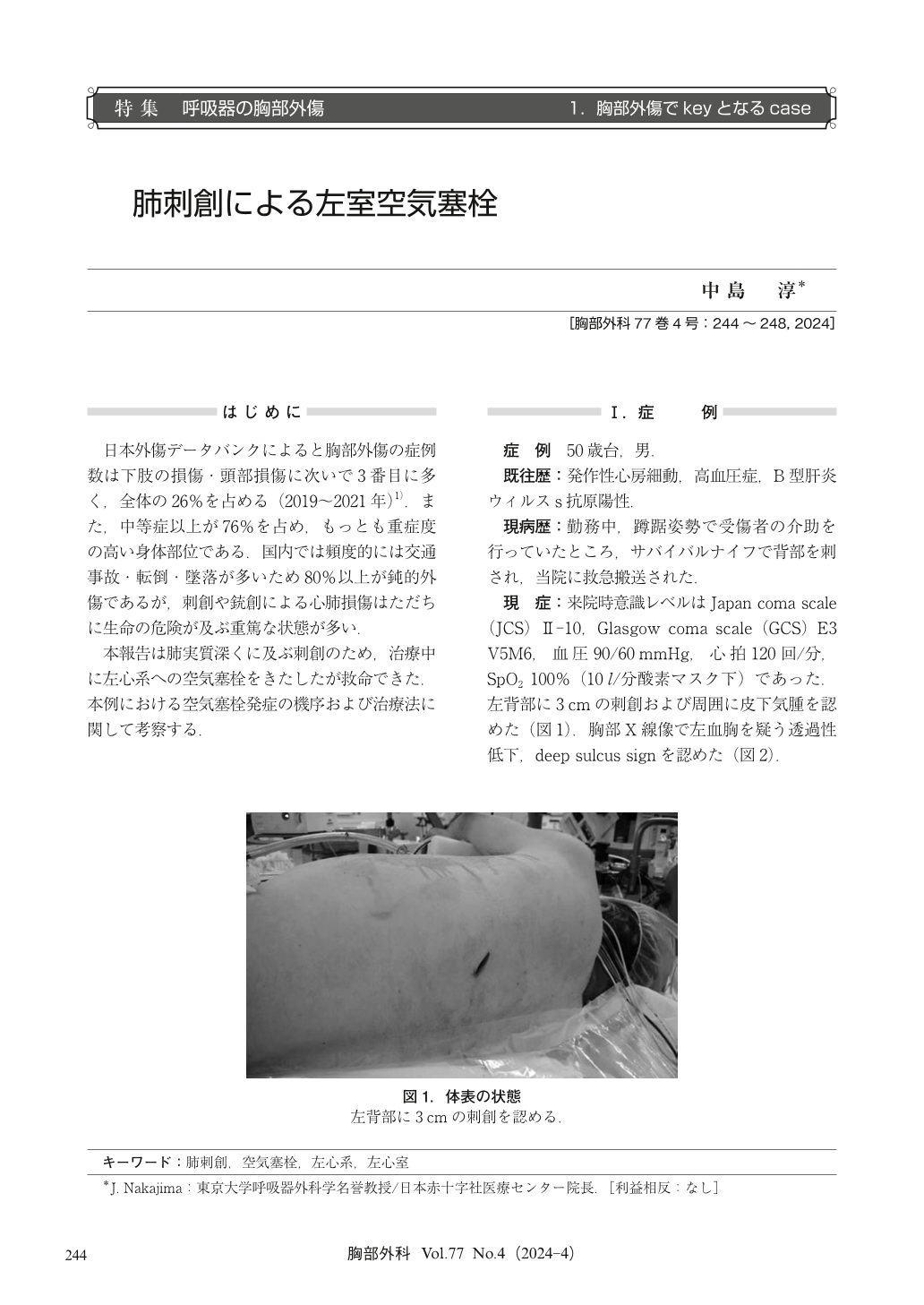
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2024


