Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
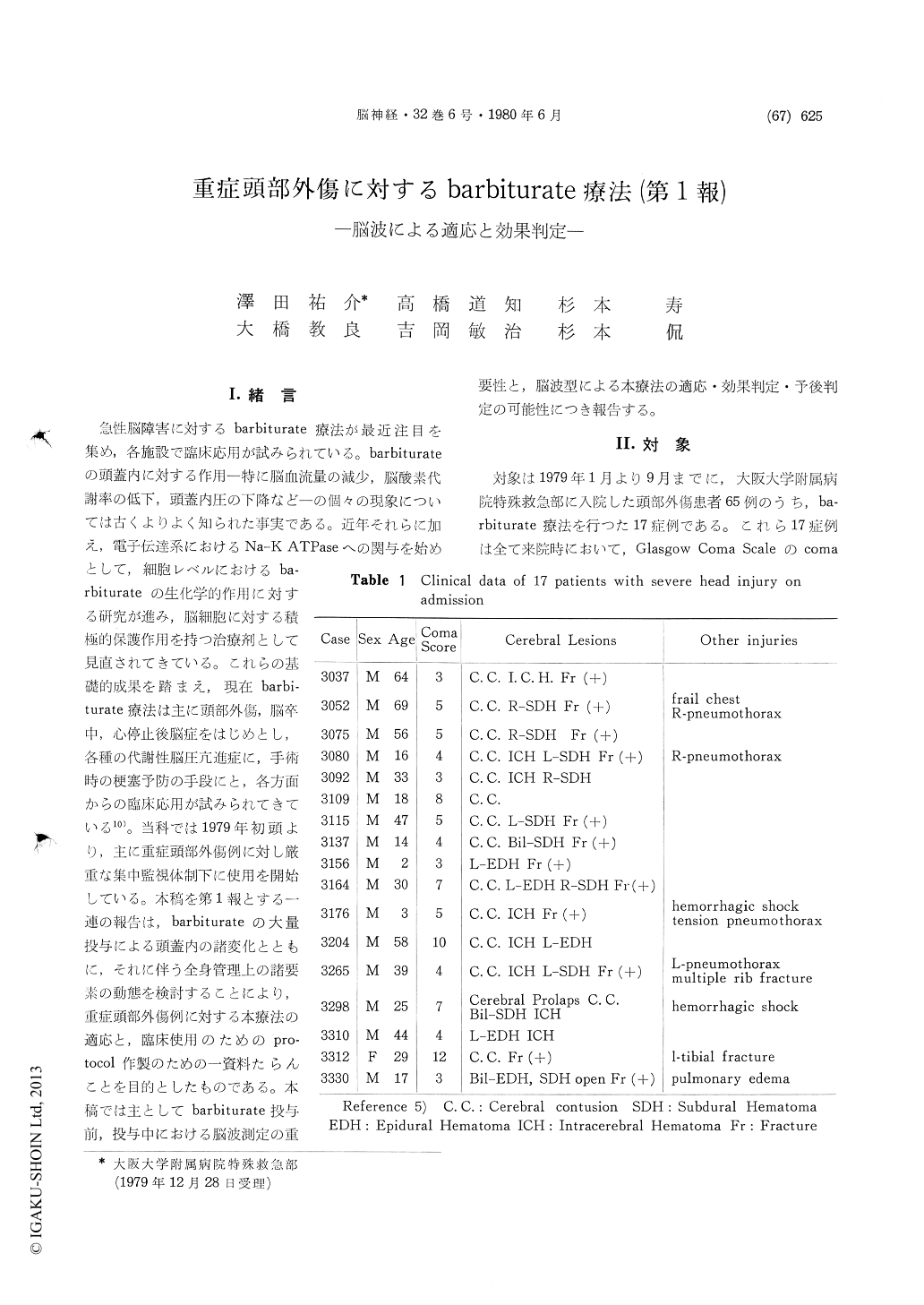
I.緒言
急性脳障害に対するbarbiturate療法が最近注目を集め,各施設で臨床応用が試みられている。barbiturateの頭蓋内に対する作用—特に脳血流量の減少,脳酸素代謝率の低下,頭蓋内圧の下降など—の個々の現象については古くよりよく知られた事実である。近年それらに加え,電子伝達系におけるNa-K ATPaseへの関与を始めとして,細胞レベルにおけるba—rbiturateの生化学的作用に対する研究が進み,脳細胞に対する積極的保護作用を持つ治療剤として見直されてきている。これらの基礎的成果を踏まえ,現在barbi—turate療法は主に頭部外傷,脳卒中,心停止後脳症をはじめとし,各種の代謝性脳圧亢進症に,手術時の梗塞予防の手段にと,各方面からの臨床応用が試みられてきている10)。当科では1979年初頭より,主に重症頭部外傷例に対し厳重な集中監視体制下に使用を開始している。本稿を第1報とする一連の報告は,barbiturateの大量投与による頭蓋内の諸変化とともに,それに伴う全身管理上の諸要素の動態を検討することにより,重症頭部外傷例に対する本療法の適応と,臨床使用のためのpro—tocol作製のための一資料たらんことを目的としたものである。本稿では主としてbarbiturate投与前,投与中における脳波測定の重要性と,脳波型による本療法の適応・効果判定・予後判定の可能性につき報告する。
The effects of barbiturate (thiamylal) on changes of EEG, ICP and long term prognosis were investi-gated in 17 patients with severe head injury be-tween JAN/'79 and SEP/'79.
Changes of ICP could be classified into three distinct types with respect to the dosage of thiamylal (15 mg/kg) administered.
i) Type A ; ICP showed a gradual decrease reaching the lowest level within 15-20 minutes of thiamylal administration and recovering the pre-administration level within 60 minutes. There were 7 patients belonging to this type with Good Recovery (GR) in 4, Moderate Disability (MD) in 1, Vegetative state (Veg.) in 1 and Death (D) in 1. After thiamylal administration, these patients exhibited interesting changes on EEG. When the ICP reached the lowest level, a suppression-burst pattern appeared on EEG. With the persistance of the suppression-burst pattern, the ICP remainedin the lowest level attained. The lowest level of the ICP and suppression-burst pattern was main-tained with thiamylal administration of 4-6 mg/kg/ hr.
ii) Type B; The ICP showed a transient fall recovering the pre-administration level within 5 minutes. 4 patients were in this group with Veg. in 1 and death in the remaining 3 cases. A flat pattern on EEG ensued immediately after thiamylal administration and no suppression-burst pattern was observed. Further additional doses of thiamylal produced an abrupt drop in blood pressure with no change in the ICP.
iii) Type C; The ICP showed a decrease with no recovery to the pre-administration level. The EEG maintained a flat pattern leading to death.
The initial ICP was 23.5±1.0 mmHg in type A, 25.2±1.4 mmHg in type B and 29.4±1.4 mmHgin type C. It was impossible to predict the ICP pattern from the initial ICP, with no statistic significant difference among the three groups. From these results, it can be seen that the thiamylal administration produced three types of ICP alteration patterns relating closely to prognosis with GR and MD. Regarding the types B and C, we feel that there is little indication for barbiturate therapy. Also, the suppression-burst pattern on EEG parallels with the lowest ICP level attained.
We conclude that only cases following into type A group will show good prognosis with thiamylal administration and the suppression-burst EEG pattern determines the type A. Retrospective study shows that the barbiturate dosage can be determined by the monitoring of EEG.
Copyright © 1980, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


