Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
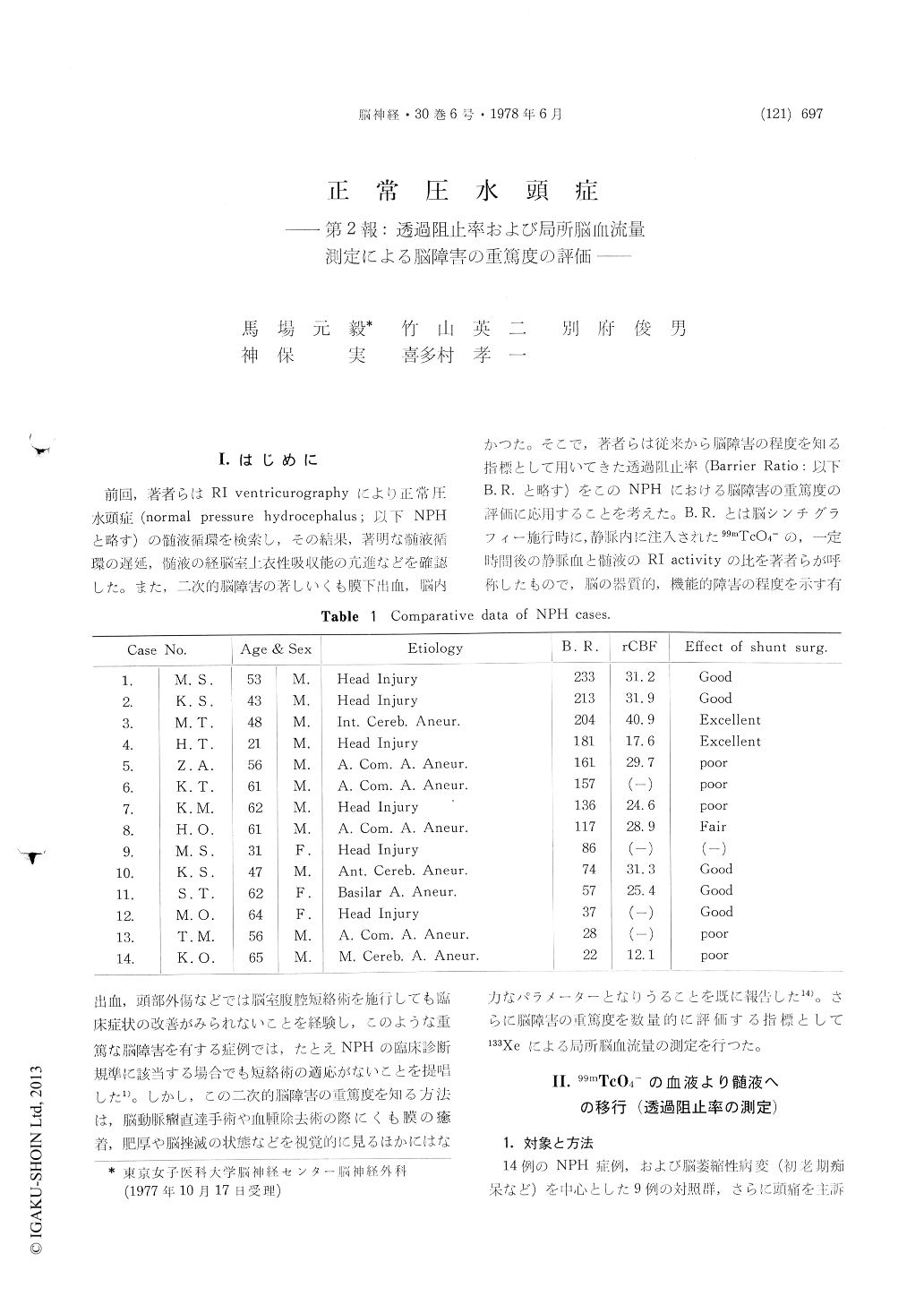
前回,著者らはRI ventricurographyにより正常圧水頭症(normal pressure hydrocephalus;以下NPHと略す)の髄液循環を検索し,その結果,著明な髄液循環の遅延,髄液の経脳室上衣性吸収能の亢進などを確認した。また,二次的脳障害の著しいくも膜下出血,脳内出血,頭部外傷などでは脳室腹腔短絡術を施行しても臨床症状の改善がみられないことを経験し,このような重篤な脳障害を有する症例では,たとえNPHの臨床診断規準に該当する場合でも短絡術の適応がないことを提唱した1)。しかし,この二次的脳障害の重篤度を知る方法は,脳動脈瘤直達手術や血腫除去術の際にくも膜の癒着,肥厚や脳挫滅の状態などを視覚的に見るほかにはなかつた。そこで,著者らは従来から脳障害の程度を知る指標として用いてきた透過阻止率(Barrier Ratio:以下B.R.と略す)をこのNPHにおける脳障害の重篤度の評価に応用することを考えた。B.R.とは脳シンチグラフィー施行時に,静脈内に注入された99mTcO4—の,一定時間後の静脈血と髄液のRI activityの比を著者らが呼称したもので,脳の器質的,機能的障害の程度を示す有力なパラメーターとなりうることを既に報告した14)。さらに脳障害の重篤度を数量的に評価する指標として133Xeによる局所脳血流量の測定を行つた。
In the previous study, quantitative analysis of RI ventriculography was reported in fifty-three cases with chronic communicating hydrocephalus.
In this study, according to the same criteria as that of previous report, fifty-three cases were divided into two groups, namely NPH group (twenty-seven cases) and control group, which were considered as mere chronic communicating hydro-cephalus without and NPH chalacteristics. (twenty-six cases).
Results of "barrier ratio (B. R.)" measurement and regional cerebral blood flow study in these cases are as follows :
1) "Barrier ratio"using of 99mTcO4-: Concerning about B. R. of 99mTcO4- there was no significant difference between NPH and control group. However it tends to be that shunt surgery is not so effective in NPH cases in which B. R. shows abnormally low value.
2) rCBF by 133Xe clearance method: Regional cerebral blood flow was diffusely decreased in NPH patients, especially in its frontal area, suggenting the frontal area would be more severely damaged in NPH cases.
These findings leads us to the conclusion that whether the shunt surgery might be effective or not depends on severity of cerebral dysfunction and the cerebral dysfunction is clearly evaluated by RI technique mentioned above.
Copyright © 1978, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


