Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
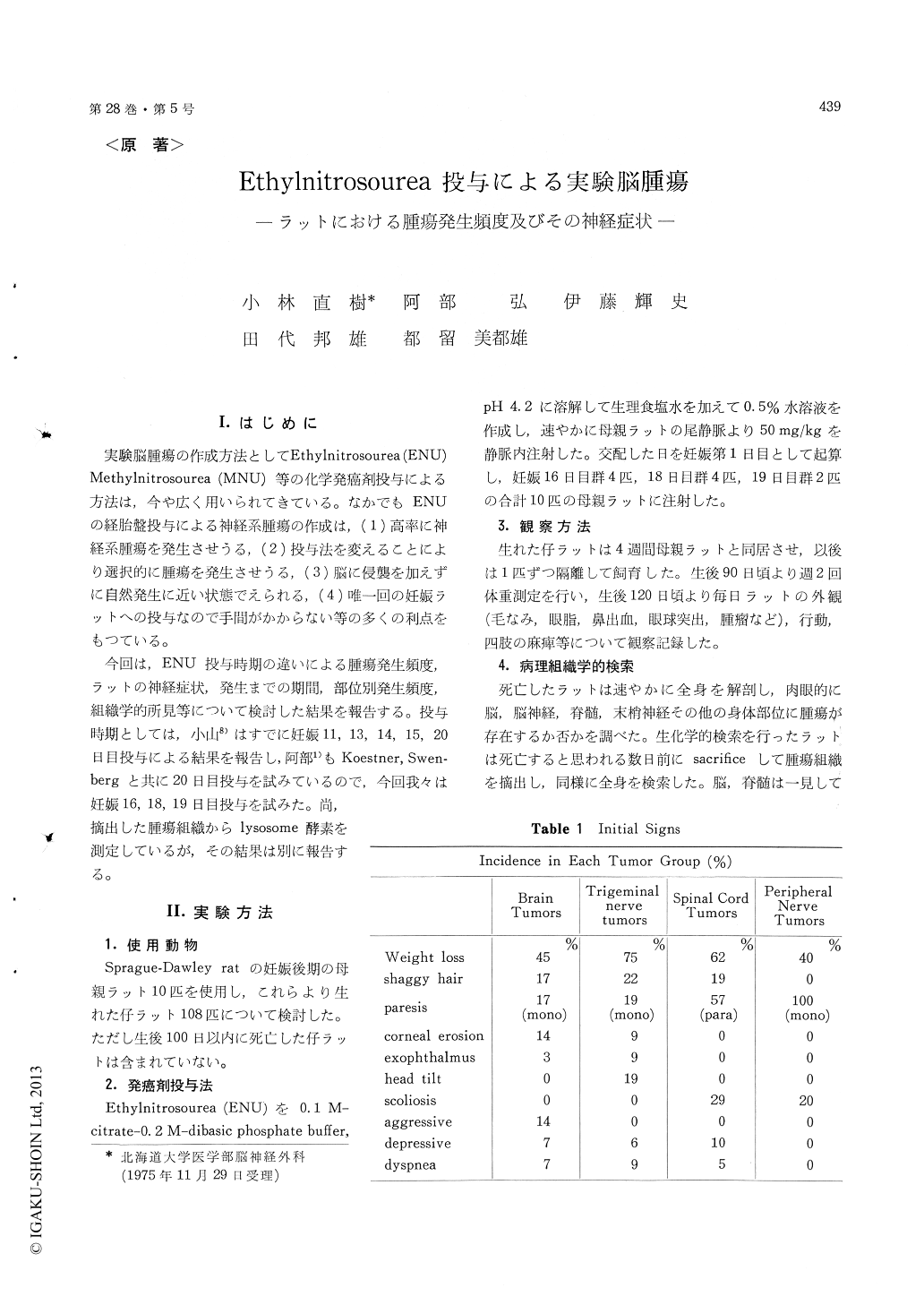
I.はじめに
実験脳腫瘍の作成方法としてEthylnitrosourea (ENU)Methylnitrosourea (MNU)等の化学発癌剤投与による方法は,今や広く用いられてきている。なかでもENUの経胎盤投与による神経系腫瘍の作成は,(1)高率に神経系腫瘍を発生させうる,(2)投与法を変えることにより選択的に腫瘍を発生させうる,(3)脳に侵襲を加えずに自然発生に近い状態でえられる,(4)唯一回の妊娠ラットへの投与なので手間がかからない等の多くの利点をもつている。
今回は,ENU投与時期の違いによる腫瘍発生頻度,ラットの神経症状,発生までの期間,部位別発生頻度,組織学的所見等について検討した結果を報告する。投与時期としては,小山8)はすでに妊娠11,13,14,15,20日目投与による結果を報告し,阿部1)もKoestner,Swen—bergと共に20日目投与を試みているので,今回我々は妊娠16,18,19日目投与を試みた。尚,摘出した腫瘍組織からlysosome酵素を測定しているが,その結果は別に報告する。
Ethylnitrosourea (ENU) was found to be an ef-fective neurogenic carcinogen to rats when adminis-tered transplacentary. We injected 50mg/kg bodywt. of ENU intravenously in 10 pregnant Spraque-Dawley rats on 16th, 18th and 19th day of gestationand induced neurogenic tumors in their offspring.Weight loss was the most important initialsymptoms caused by intracranial or spinal cordtumors. Shaggy hair, mono-paresis and depressivestate also suggested intracranial tumors. The oc-currence of aggressive state rather suggested thebeginning of brain tumor, however, head tilt andexophthalmos were seen in trigeminal nerve tumors.Occasionally sudden death was encountered becauseof bleeding into brain tumor. Spinal cord tumorswere easily diagnosed by paraparesis. and monopar-esis with generally good state suggested peripheralnerve tumors. Trigeminal nerve tumors snd spinalcord tumors had relatively short latent periods. Ahalf of them showed initial symptoms between163rd day and 207th day after birth. Brain tumors,in contrast, presented relatively long latent periods.A half of them showed initial symptoms between230th day and 265th day. The induction rate ofneurogenic tumor to the number of offspring re-vealed as high as 90%. With delayed administration of ENU, number of neurogenic tumors induced inone individual rat increased. The induction rateof brain tumor ranged constantly between 56 and74% regardless of time of administration of ENU.The induction rate of trigeminal nerve tumor,however, showed gradual increase from 18% to 54% with delayed administration of ENU.
We classified brain tumors induced by ENU ac-cording to the classification by Koestner, et al (1971).Oligodendroglioma occured most frequently (25-41%), followed by mixed glioma (17-26%) and ana-plastic glioma (13-32%).
4 meningiomas were also induced. It is veryinteresting that with delayed administration ofENU, incidence of well differentiated tumors likeoligodendroglioma or astrocytoma has increased, onthe other hand incidence of undifferentiated tumorslike anaplastic glioma or anaplastic ependymomahas decreased. Gliomas of our series resembledhuman gliomas histologically. But most of neu-rinomas induced in rats by ENU, unlike those ofhuman cases, were anaplastic. Meningiomas alsodiffered from human meningioma without anywhorl formation. The differentiation of menin-giomas from well differentiated neurinomas wasquite difficult histologically, however the locationof tumor without continuation with trigeminalnerve, as well as benign histological nature madeus conclude the diagnosis of meningioma.
Copyright © 1976, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


