Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
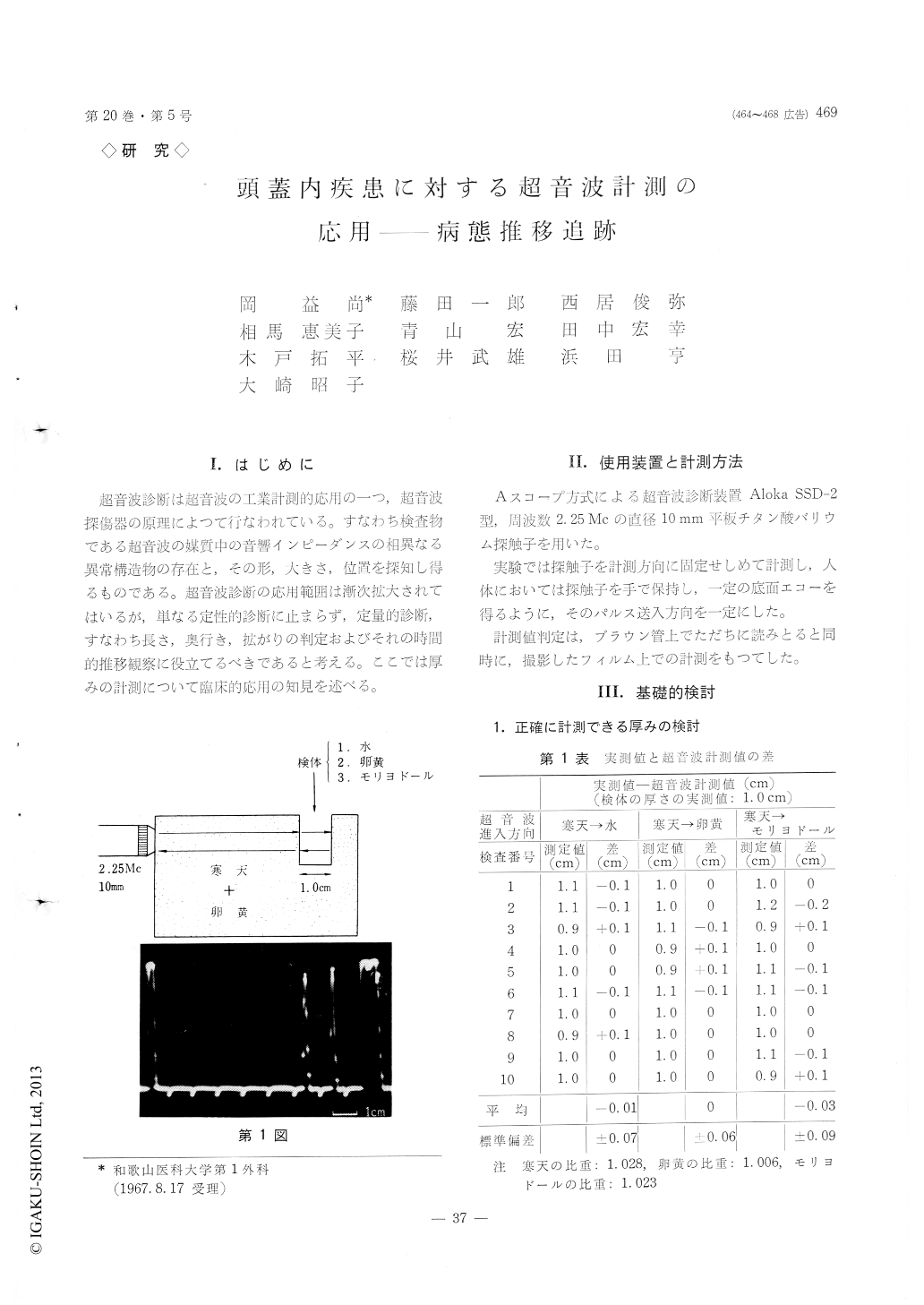
超音波診断は超音波の工業計測的応用の一つ,超音波探傷器の原理によつて行なわれている。すなわち検査物である超音波の媒質中の音響インピーダンスの相異なる異常構造物の存在と,その形,大きさ,位置を探知し得るものである。超音波診断の応用範囲は漸次拡大されてはいるが,単なる定性的診断に止まらず,定量的診断,すなわち長さ,奥行き,拡がりの判定およびそれの時間的推移観察に役立てるべきであると考える。ここでは厚みの計測について臨床的応用の知見を述べる。
The ultrasonic diagnosis is widely used as a quali-tative method in the field of neurosurgery and medi-cine because of its potentiality to detect intracranial masses in their shape, size and location following differences of their sonic impedance. In respect to this potentiality it should be used as a quantitative diagnostic method which indicates the thickness of masses in living bodies.
The accuracy of the measured thickness of masses is examined by measuring the width of gaps in agar and lateral ventricles in fixed brains. The difference between values ultrasonically measured and those directly measured is within ±0.1~±0.2cm.
Continual clinical observations are performed on chronic subdural hematomata, congenital hydrocepha-lus and brain tumors before and after operations. For chronic subdural hematomata their thickness are measured by ultrasonic echoes of silver clips fixed on the bottom of hematomata as well as on the dura.The relapses after the subdural evacuation are easily detectable when the enlarging thickness of hem-atomata is observed.
Congenital hydrocephalus is observed with the continued ultrasonic measurement of the width of enlarged lateral ventricles, as the method is more exact, safer and simpler than the pneumoventricu-lography which is prohibited after the ventriculo-auriculostomy.
Brain tumors are subjected to the ultrasonic mea-surement in changes of their sizes if they are su-pratentorial, i. e., hypophyseal tumor, pinealoma and meningioma and others, whereas infratentorial tumors can be observed easily on the gradually enlarged third ventricles by their development and on the controverse phenomena after the tumor extirpation.
Ultrasonic measurement by A-scope method here described is a proper diagnostic tool of neurosurgery as well as a good inspecting method of gradual changes of intracranial disorders.
Copyright © 1968, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


