Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
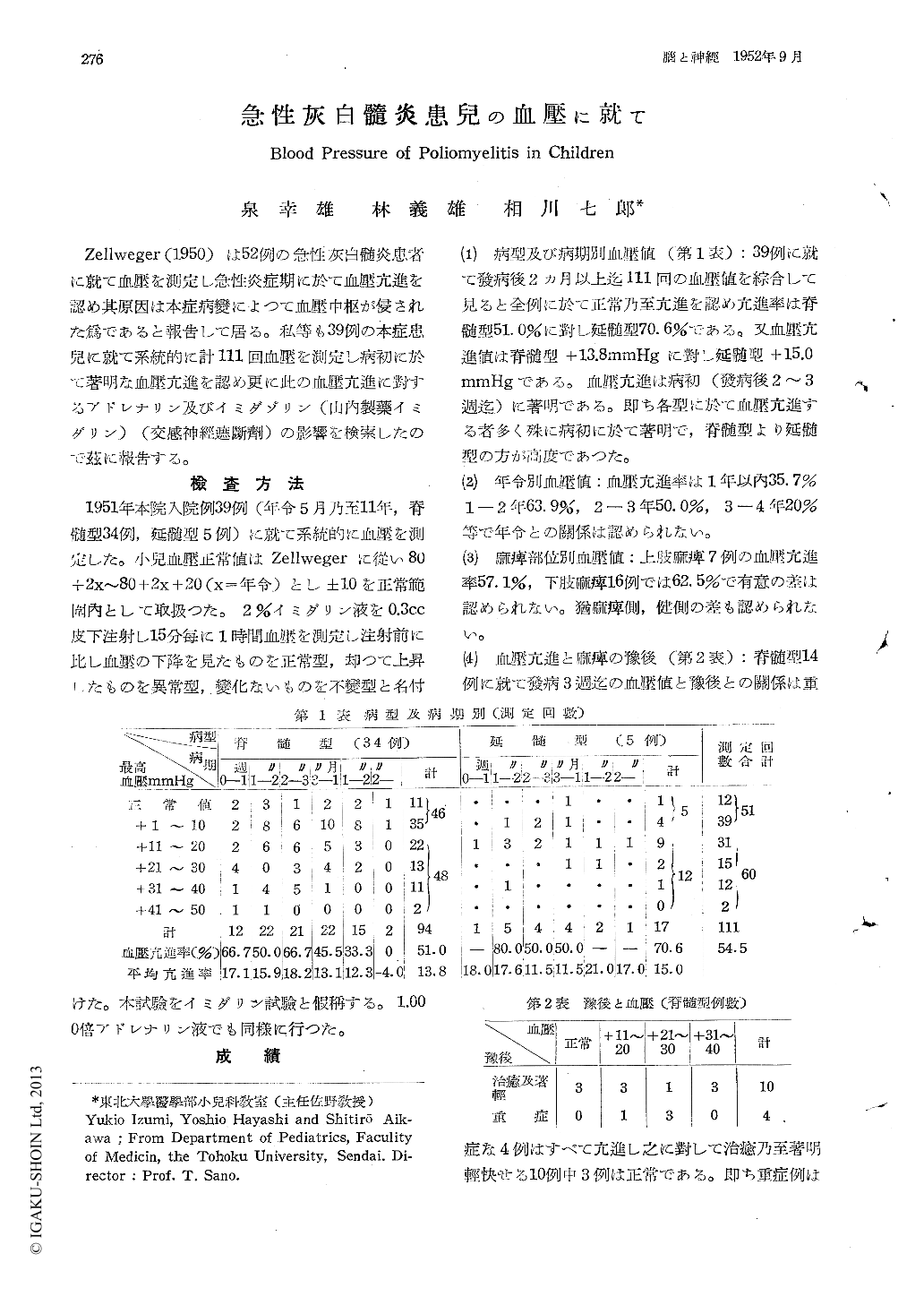
Zellweger (1950)は52例の急性灰白髄炎患者に就て血壓を測定し急性炎症期に於て血壓亢進を認め其原因は本症病變によつて血壓中枢が侵された爲であると報告して居る。私等も39例の本症患兒に就て系統的に計111回血壓を測定し病初に於て著明な血壓亢進を認め更に此の血壓亢進に對するアドレナリン及びイミダゾリン(山内製藥イミダリン)(交感神經遮斷剤)の影響を検索したので茲に報告する。
39 cases of poliomyelitis-34 spinal types and 5 bulbar types-admitted to our Clinic in 1951. The age incidence was from 5 months to 11 years. The blood pressure of these cases were investigated systematically. We considered nor-mal range for the systolic blood pressure bet-ween 80+2x and 80 +2x +20mmHg (x: corres-ponding to the age in years). We observed ranges of ±10mmHg as normal. 51 of 111 times of blood pressure investigation were normal and 60 (54.5%) were high. The rate of hyper-tension was 51.1 % in spinal type, and 70.6% in bulbar type, and they were marked in acute stage (2-3 weeks of illness) in both types. There was no relationship between hypertension and age group or the location of paralysis. The blood pressure in 4 severe cases was all high, and in 3 cases among 10 healed or markedly improved cases was normal. The direct rela-tionship between hypertension and autonomic nervous symptoms, especially about pain might not be recognized. Blood pressure curve after 0.3cc. subcutaneous injection of Imidalin (2% solution of 2-benzyl-4, 5-imidazoline hydrochlo-ride) was observed. The curve of blood pressure in bulbor type increased or did not change, and in spinal type decreased, increased or did not change. Among 17 cases of spinal type within 3 weeks after onset, 6 severe cases gave all decreased curves, while there were 6 improved cases among 10 cases which gave an increased curve.
Copyright © 1952, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.