Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
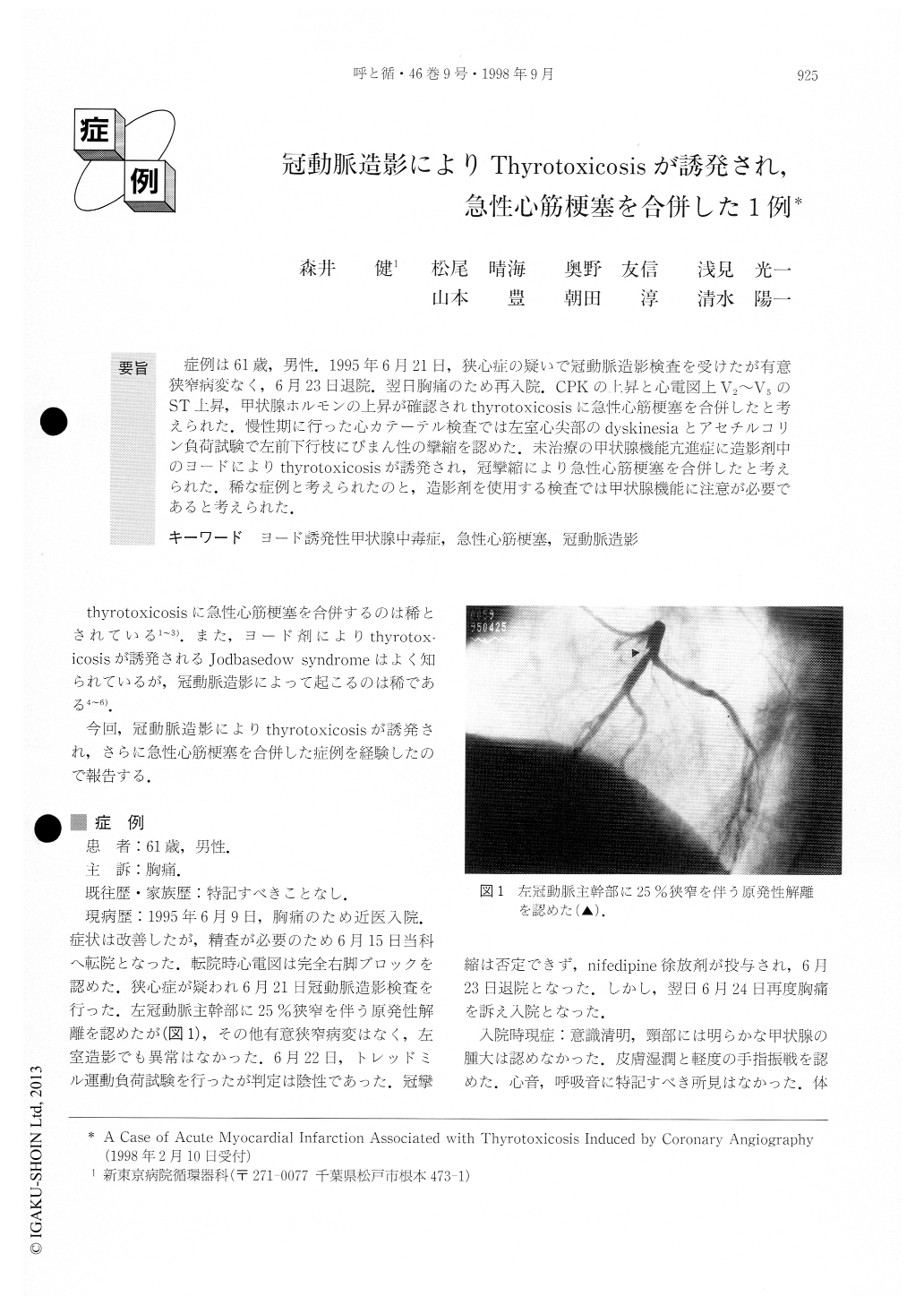
症例は61歳,男性.1995年6月21日,狭心症の疑いで冠動脈造影検査を受けたが有意狭窄病変なく,6月23日退院.翌日胸痛のため再入院.CPKの上昇と心電図上V2〜V5のST上昇,甲状腺ホルモンの上昇が確認されthyrotoxicosisに急性心筋梗塞を合併したと考えられた.慢性期に行った心カテーテル検査では左室心尖部のdyskinesiaとアセチルコリン負荷試験で左前下行枝にびまん性の攣縮を認めた.未治療の甲状腺機能亢進症に造影剤中のヨードによりthyrotoxicosisが誘発され,冠攣縮により急性心筋梗塞を合併したと考えられた.稀な症例と考えられたのと,造影剤を使用する検査では甲状腺機能に注意が必要であると考えられた.
The case presented here was one in which occult hyperthyroidism was aggravated by contrast iodide, resulting in thyrotoxicosis and subsequently in acute mvocardial infarction. The case was a 61-year-old man undergoing coronary angiogram for angina pectoris without any significant lesion. Three days after the procedure he manifested symptoms of thyrotoxicosis, and subsequently developed acute myocardial infarct tion, which was indicated by CPK elevation and ST elevation through V2 to V5. The patient survived, and, later, re-coronary angiogram was performed. It documented the spasm of LAD by acetylcholine provoc-ative test. The case strongly suggested that the thyrotoxicosis was induced by coronary angiography and subsequently, acute myocardial infarction devel-oped due to coronary vasospasm.
Copyright © 1998, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


