Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
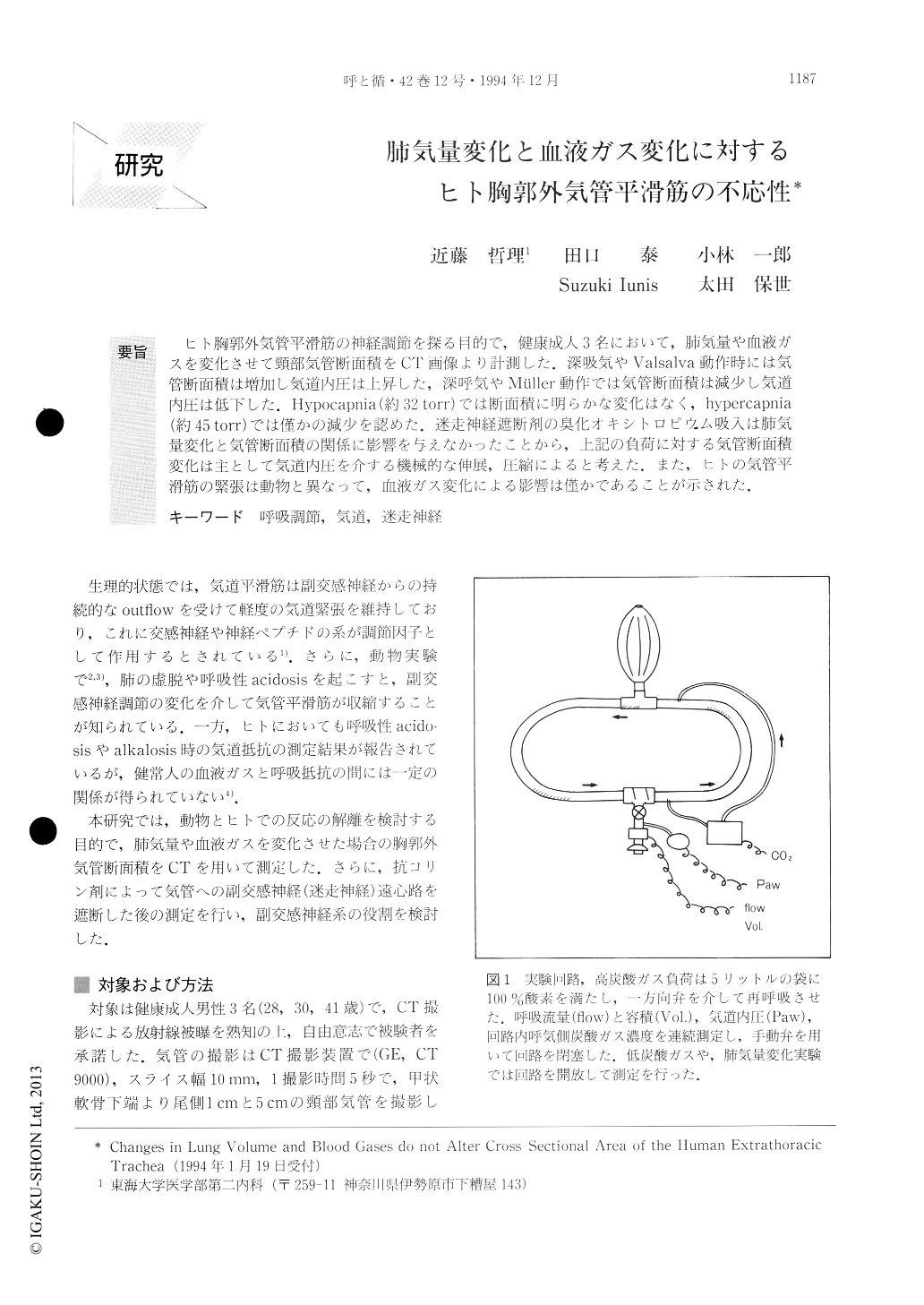
ヒト胸郭外気管平滑筋の神経調節を探る目的で,健康成人3名において,肺気量や血液ガスを変化させて頸部気管断面積をCT画像より計測した.深吸気やValsalva動作時には気管断面積は増加し気道内圧は上昇した,深呼気やMüller動作では気管断面積は減少し気道内圧は低下した.Hypocapnia(約32torr)では断面積に明らかな変化はなく,hypercapnia(約45torr)では僅かの減少を認めた.迷走神経遮断剤の臭化オキシトロピウム吸入は肺気量変化と気管断面積の関係に影響を与えなかったことから,上記の負荷に対する気管断面積変化は主として気道内圧を介する機械的な伸展,圧縮によると考えた.また,ヒトの気管平滑筋の緊張は動物と異なって,血液ガス変化による影響は僅かであることが示された.
Neural control of the human tracheal smooth muscle was indirectly assessed by measuring tracheal cross-sectional area (TXA) using computed tomography. TXA was measured in three healthy humans at differellt lung volume and blood gases. TXA and airway pressure (Paw) increased at maximal inspira-tion and during Valsalva maneuver,while both of them decreased at maximal expiration and during müller maneuver. TXA did not change at hypocapnia (~32torr) and slightly decreased at hypercapnia (~45torr).
Copyright © 1994, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


