Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
MexiletineはVaughan Williams分類のIb群に属する抗不整脈剤で,心室性不整脈に対する有効性が従来より報告されてきた。一方,心房性不整脈に対しては一般にIb群抗不整脈剤は無効であるとされるため,mexiletineのatrial vulnerabilityに対する臨床電気生理学的検討はほとんど行われていない。また,心房性不整脈の有効例が報告されているものの,その作用機序についてはなお不明の点が多い。今回,我々はmexile-tineのatrial vulnerabilityに及ぼす影響を検討したので報告する。
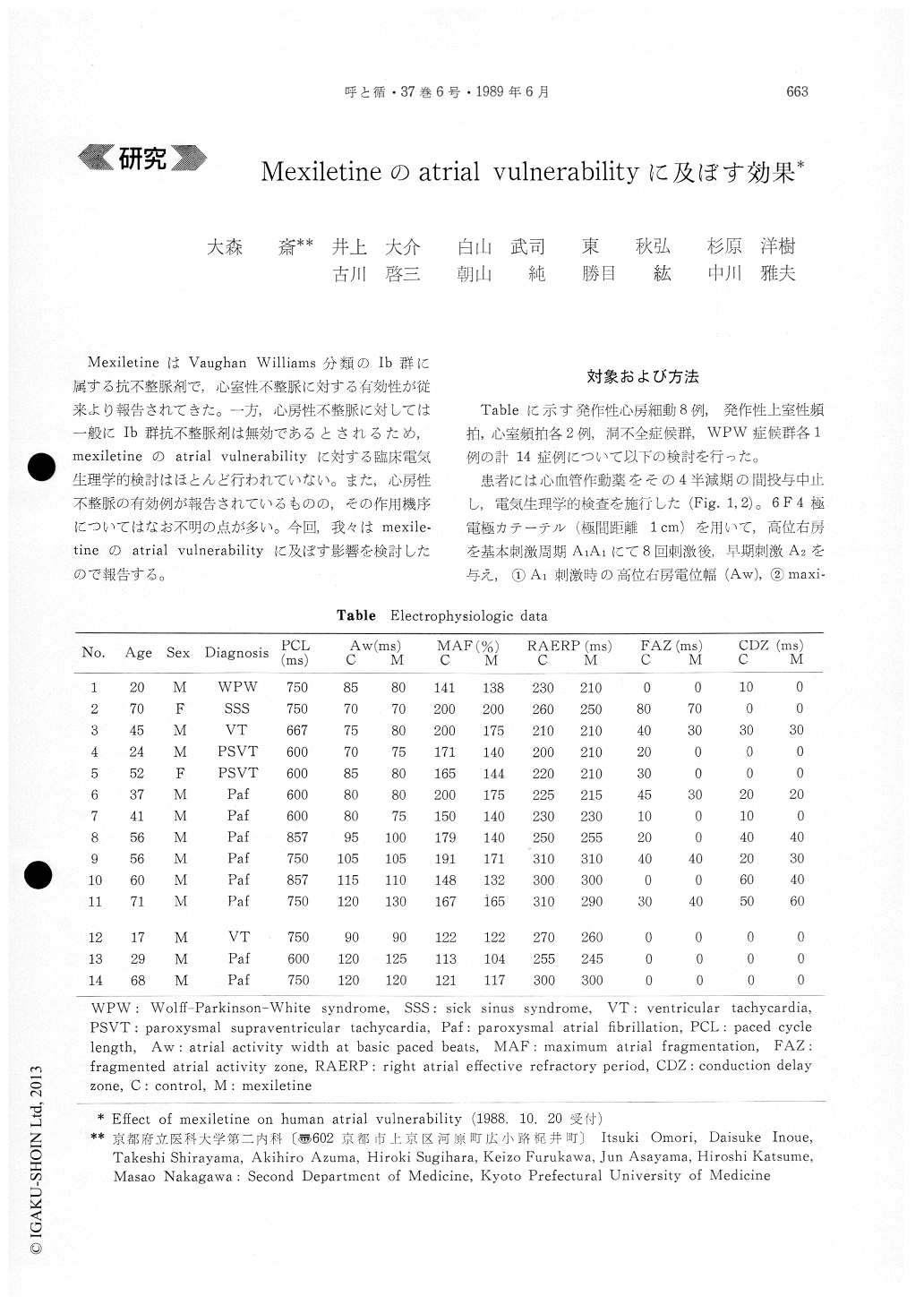
The effect of mexiletine on human atrial vulnera-bility was investigated in 14 subjects (8 with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, 2 with paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, 2 with ventricular tachycardia, 1 with sick sinus syndrome and 1 with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome).
During the electrophysiologic study, after 8 consecutive stimuli (A1) were delivered through theelectorode catheter positioned at high right atrium, premature stimulus (A2) was introduced, and follo-wing measurements were made ; 1) Aw : atrial activity width of A1, 2) maximum atrial fragmenta-tion (MAF) : the longest atrial activity width of A1, which was expressed by the relative value against Aw, 3) fragmented atrial activity zone (FAZ) : the zone of the coupling interval (A1A2) with the prolongation of the atrial activity width at A2 more than 150% against Aw, 4) conduction delay zone (CDZ) : the zone of A1A2 with the prolongation more than 20 msec of the intraatrial conduction time at A2 from high right atrium to coronary sinus or low right atrium against the intraatrial conduction time at A1, and 5) right atrial effective refractory period (RAERP). These measurements were repeated after the intravenous administration of mexiletine (2 mg/kg/10 min).
3 cases (case 12, 13 and 14), whose FAZ and CDZ were 0 msec, were excluded from the following evaluation. Mexiletine showed little effect on Aw and RAERP, but singnificantly shortened MAF and FAZ (p<0. 001 and p<0.05, respectively). CDZ were also reduced in 3 cases and remained unchan-ged in 6 cases, though no statistical difference of CDZ was recognized between before and after the administration of mexiletine.
We conclude that mexiletine could reduce human atrial vulnerability, and that the mechanism of this reduction might be owing to the improved intraatrial conduction delay by mexiletine.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


