Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
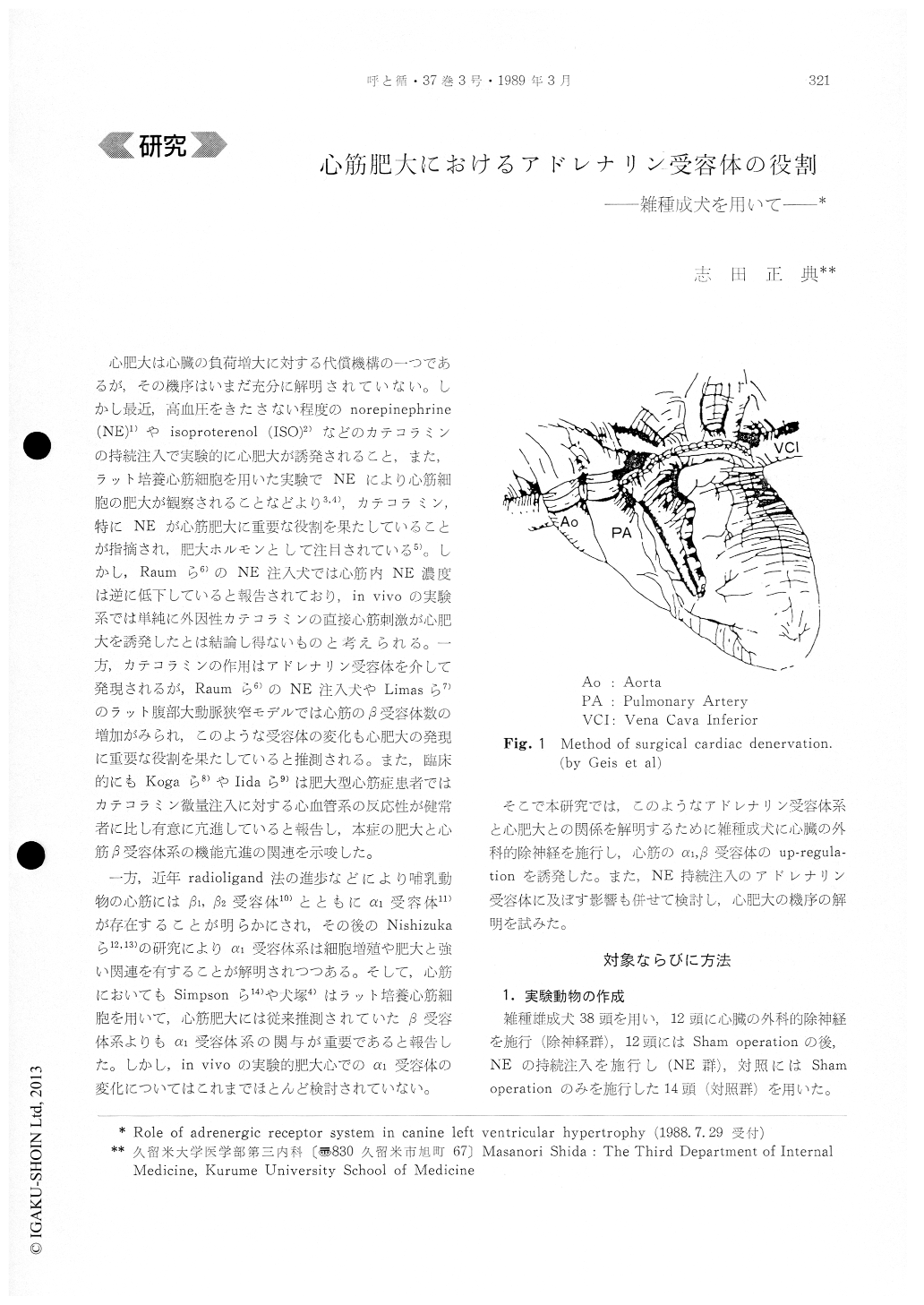
心肥大は心臓の負荷増大に対する代償機構の一つであるが,その機序はいまだ充分に解明されていない。しかし最近,高血圧をきたさない程度のnorepinephrine(NE)1)やisoproterenol(ISO)2)などのカテコラミンの持続注入で実験的に心肥大が誘発されること,また,ラット培養心筋細胞を用いた実験でNEにより心筋細胞の肥大が観察されることなどより3,4),カテコラミン,特にNEが心筋肥大に重要な役割を果たしていることが指摘され,肥大ホルモンとして注目されている5)。しかし,Raumら6)のNE注入犬では心筋内NE濃度は逆に低下していると報告されており,in vivoの実験系では単純に外因性カテコラミンの直接心筋刺激が心肥大を誘発したとは結論し得ないものと考えられる。一方,カテコラミンの作用はアドレナリン受容体を介して発現されるが,Raumら6)のNE注入犬やLimasら7)のラット腹部大動脈狭窄モデルでは心筋のβ受容体数の増加がみられ,このような受容休の変化も心肥大の発現に重要な役割を果たしていると推測される。また,臨床的にもKogaら8)やIidaら9)は肥大型心筋症患者ではカテコラミン微量注入に対する心血管系の反応性が健常者に比し有意に充進していると報告し,本症の肥大と心筋β受容体系の機能冗進の関連を示唆した。
Although sympathetic nervous system and cate-cholamines have been postulated to play an impor-tant role in the development of myocardial hypert-rophy, the precise mechanism is still ill-defined. We then developed two experimental canine models ; 12 dogs with surgical cardiac denervation by the method of Geis et al, inducing up-regulation of myocardial adrenergic receptors, and 12 dogs with chronic infusion of subhypertensive dose of nor-epinephrine (NE) at a rate of 0.04 mg/kg/day.
After two months, both models induced myocar-dial hypertrophy, as indicated by significant incre-ases in left ventricular (LV) wall thickness and cell diameter as compared with 14 sham-operated control dogs.
Cardiac denervation remarkably depleted myocar-dial NE contents, while plasma NE remained un-changed. Both alpha-1 and beta receptors were up-regulated, Bmax increasing by 90% and 50% res-pectively. Decrease in myocardial cyclic-AMP con-tent was relatively small as compared with the marked reduction in myocardial NE, probably by the compensatory augmentation of beta receptor system activity.
Chronic NE infusion also reduced myocardial NE content possibly due to stimulation of presynaptic alpha-2 receptor inhibiting NE synthesis and release. Number of alpha-1 and beta receptors also increased by 90% and 30% respectively, while myocardial cyclic-AMP content remained unchanged.
These observations indicate that neither direct stimulation of NE on the myocardial cell nor in-creased in cyclic-AMP is the mechanism for cardiac hypertrophy in both models. Greater increase in alpha-1 receptor than beta receptor in both models rather imply that disproportional augmentation of alpha-1 receptor system may play an important role in the development of myocardial hypertrophy.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


