Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
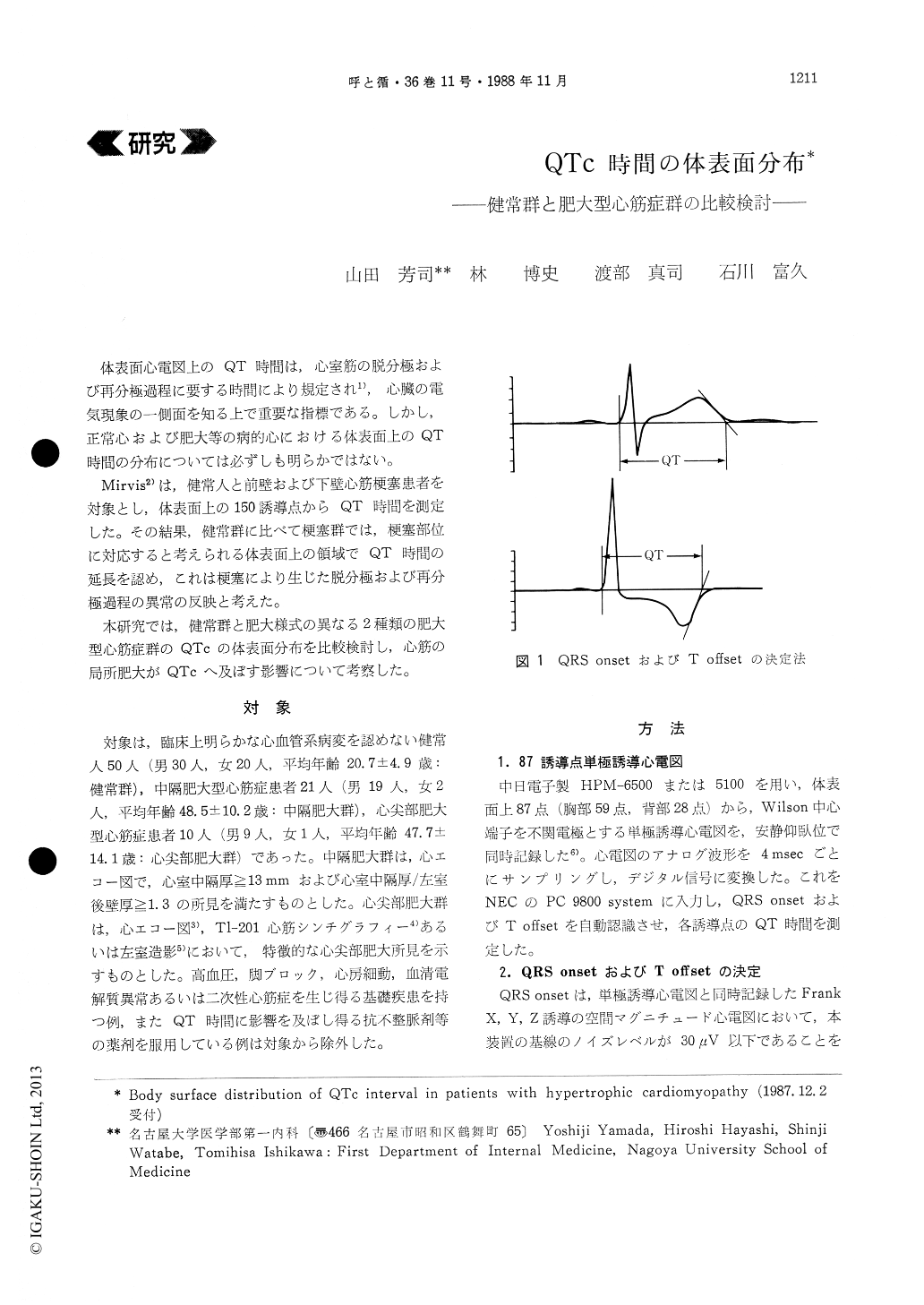
体表面心電図上のQT時間は,心室筋の脱分極および再分極過程に要する時間により規定され1),心臓の電気現象の一側面を知る上で重要な指標である。しかし,正常心および肥大等の病的心における体表面上のQT時間の分布については必ずしも明らかではない。
Mirvis2)は,健常人と前壁および下壁心筋梗塞患者を対象とし,体表面上の150誘導点からQT時間を測定した。その結果,健常群に比べて梗塞群では,梗塞部位に対応すると考えられる体表面上の領域でQT時間の延長を認め,これは梗塞により生じた脱分極および再分極過程の異常の反映と考えた。
The purpose of the study was to examine body surface distribution of QTc interval in normal sub-jects and patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and to study the effect of regional ventricular hyper-trophy on spatial distribution of QTc interval.
Eighty-seven-lead unipolar electrocardiograms were recorded simultaneously from 50 normal sub-jects (group N), 21 patients with septal hypertrophy (group SH) and 10 patients with apical hypertrophy (group AH). QT interval was measured in each lead and QTc isointerval map was constructed.
Mean of all QTc values of groups SH and AH (398±9 and 402±12 msec, respectively) were signifi-cantly longer (p<0.005) than that of group N (364 ±10 msec). In group N, the relatively longer QTc intervals were observed in the left precordium to left lower back and in the right shoulder. In groups SH and AH, the relatively longer QTc intervals were observed in the left precordium to left lateral chest and in the right upper chest to right shoulder. The difference between these two groups was that two areas with relatively longer QTc interval in group SH merged at the midsternal portion. These results may suggest that body surface distribution of QTc interval is influenced by regional ventricular hypertrophy, that is, abnormal ventricular excitation sequences due to hypertrophy of myocardium are reflected as the prolongation of QTc interval at the body surface.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


