Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
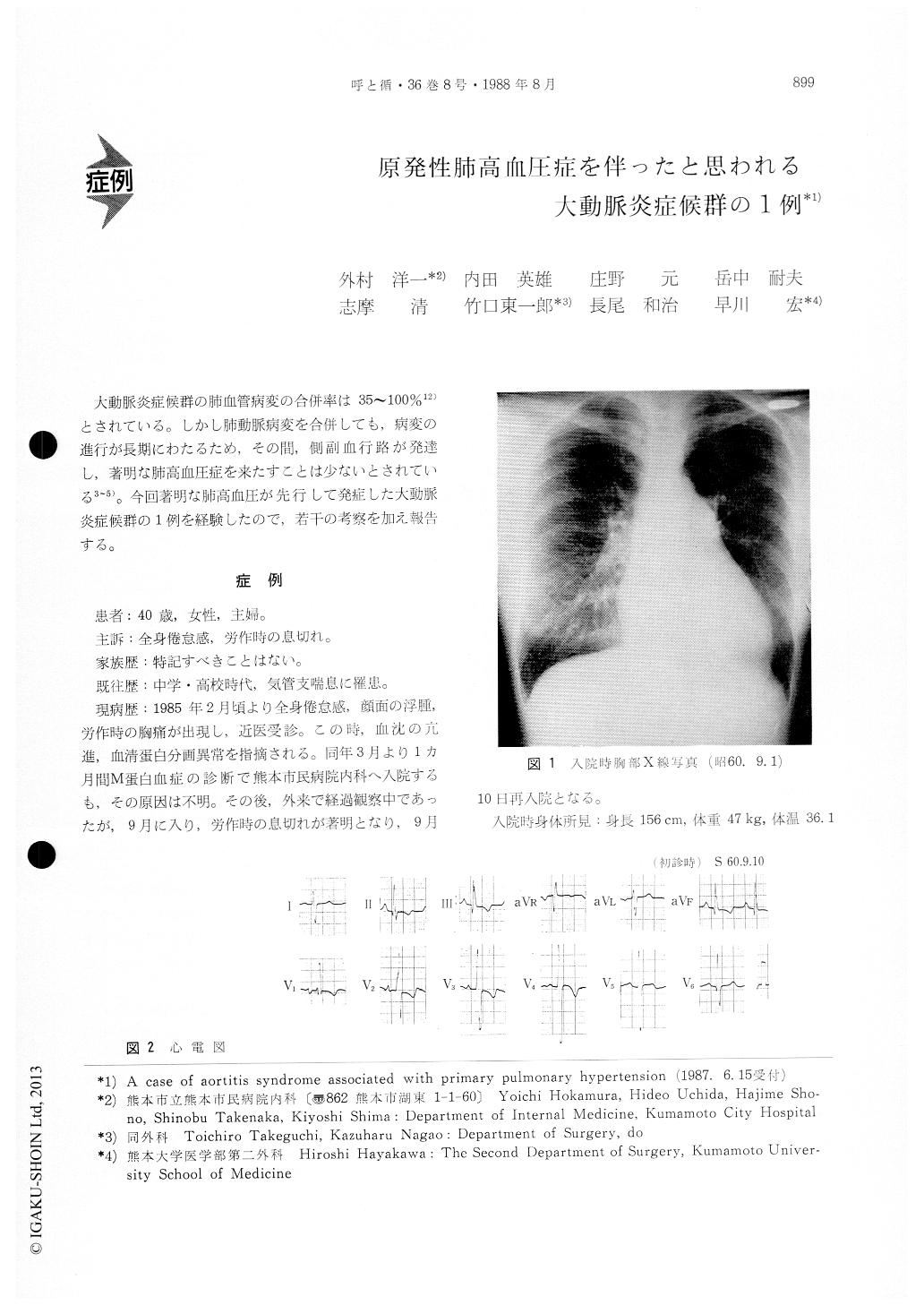
大動脈炎症候群の肺血管病変の合併率は35〜100%12)とされている。しかし肺動脈病変を合併しても、病変の進行が長期にわたるため、その間,側副血行路が発達し,著明な肺高血圧症を来たすことは少ないとされている3〜5)。今回著明な肺高血圧が先行して発症した大動脈炎症候群の1例を経験したので,若干の考察を加え報告する。
The case was a 40 year-old woman admitted to our hospital complaining of exertional dyspnea and palpitation. Initial laboratory studies showed an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 65 mm/hr and increased serum immunoglobulin of IgG (4137 mg/dl). The chest X-ray film showed cardiomegaly (CTR 62%) with marked dilation of the pulmonarytrunk. The ECG showed marked RVH. Cardiac catheterization revealed high PA pressure (mean PA 54 mmHg) and increased total pulmonary vascular resistance. She was shown by aortography to have a thickened, narrowed abdominal aorta and a steno-sed left renal artery. Pulmonary angiography findi-ngs showed marked stenosis, decreased branches of peripheral pulmonary arteries, and disappearance of capillary background. On microscopic examination of the lung biopsy (TBLB), diffuse affecting the small-sized vessel of the pulmonary artery was noted (Fig. 4). Because of the disease of the small-sized vessel, this case may be aortitis syndrome associated with primary pulmonary hypertension.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


